Growing a crop is not just about watering and weeding. You should carefully monitor the appearance of the plants. The appearance of various spots on cucumbers speaks volumes. Understanding the reasons is not so easy.
How to treat brown spots on cucumber leaves?
It is impossible to answer this question unequivocally. Because there is more than one reason for their appearance. It is necessary to carefully look at the appearance of the spots and determine their features. Only then decide what methods to eliminate the problem.
Cladosporiosis
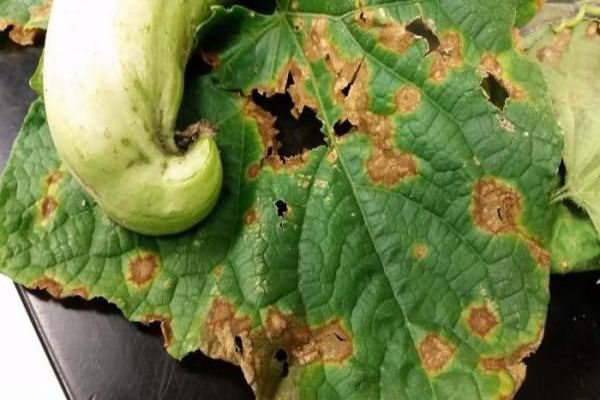
A fungal disease, another name for cucumber olive spot. Round, angular spots form throughout the leaf.When it dries, the structure of the leaf inside the stain is destroyed. The whole plant is covered with ulcers, they have an olive tint. The spot noticeably expands already on the 3rd day. The infection affects young fruits, they become crooked and covered with spots.
A favorable environment for the spread of the disease is:
- Rain.
- Cloudy cool weather.
- Sudden temperature changes.
- Late in the growing season, when the nights get colder, a lot of dew falls.
Peddlers:
- Wind.
- Water.
- Rain.
The peculiarity of the disease is that the infection persists for a long time in the soil and plant debris.
The spread of the disease can be limited by just following a few simple steps:
- Cucumbers should not grow in one place more than once every 4 years.
- Water only with warm water, at the root.
- Feed cucumbers in a timely manner.
- Remove all plants and vegetables from the beds without leaving them in the bed.
- When growing in a greenhouse, constantly ventilate.
If cucumbers have cladosporiosis, then the bushes should be treated immediately. But first, stop watering for 4-5 days. It is advisable that the temperature be +20 ⁰C; if it is lower, then you can cover the beds with material and close the greenhouse well at night.
The methods of struggle are varied:
- Spraying bushes with Bordeaux mixture. A solution at a concentration of 1%.
- 03–04% copper oxychloride solution. Treat 3-4 times per season, break 10-12 days.
- Fumigation with sulfur dioxide for 2 days (in a greenhouse).
- Spraying bushes with iodine chloride.
- Treatment with serum and water solution 1*10.
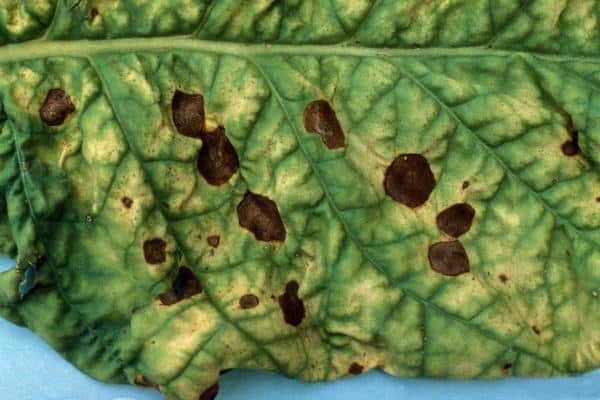
Ascochyta blight
Large brown spots form on the leaves of the plant, and gray-white spots on the stems. It affects young ovaries and large cucumbers, causing them to rot. The disease arises and develops under unfavorable weather conditions.
Prevention measures.
- Spraying bushes with infusions of tobacco, tomato and potato tops, onions, garlic.
- Dusting with wood ash.
- For 10 liters of water, 30 drops of iodine, 1 liter of milk and 30 g of soap. Once every 10 days.
If affected by the disease, you should:
- Treat with a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture and a suspension of copper oxychloride 0.3%.
- Prepare a weak solution of copper sulfate. Take 5 g of the substance and dilute 10 liters of water. 10 g of urea is also added there.
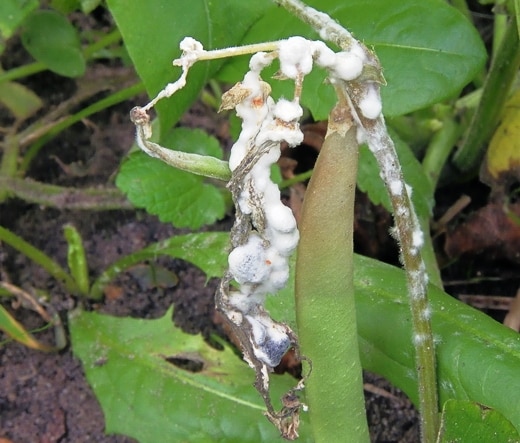
Gray rot
The defeat of this disease is characterized by the appearance on the leaves of brownish spots covered with a gray coating. The shoots begin to rot, the leaves dry out, and necrotic spots appear.
Distribution environment:
- Damp cloudy weather.
- High humidity.
- Low temperature.
Bacteria can be spread by:
- Wind.
- Contaminated soil.
Prevention consists of:
- Maintaining crop rotation.
- Processing of planting material.
- Removing all plant debris from the beds.
- A selection of disease-resistant varieties.
Processing is carried out in several ways. The decision remains with the summer resident, either to use chemicals, or to use folk methods.
Control measures:
- Fungicide treatment.
- Trichodermin, a biochemical control agent.
- 10 liters of water + 300 g of wood ash + 300 g of chalk + 1 teaspoon of copper sulfate. Treat 2 plants with this volume.
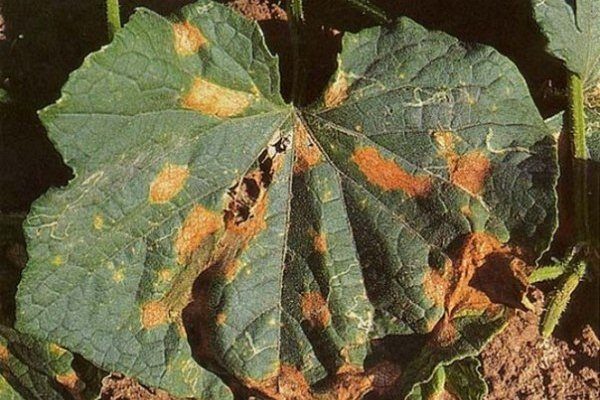
Anthracnose
The second name is copperhead. Depressed spots appear on the stems. This prevents nutrients from moving through. As a result, the plant dries out and dies, infecting all nearby bushes. The speck that appears on the leaf is yellow with a brown tint.
Favorable conditions for the development of the disease:
- High humidity.
- Heat.
- Lack of potassium and phosphorus.
- Increased soil acidity.
Preventative work:
- Feeding with complex preparations.
- Soil moisture control.
- Treatment against pests.
- Treatment with weak solutions of fungicides.
- A selection of varieties that are immune to the disease.
- Treating the seed.
How to deal with a developing disease:
- A 1% solution of colloidal sulfur suspension is used.
- Also a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture.
- 0.5% solution of copper sulfate. After treatment, be sure to dust the plants with chalk, charcoal, and lime.
- Preparations "Zineb", "Tsiram".
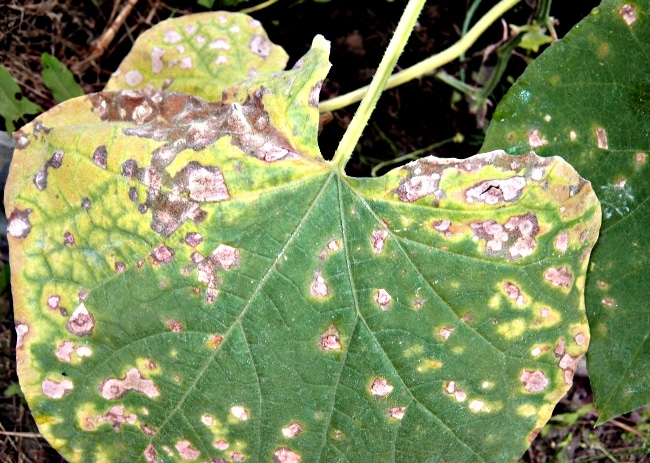
Bacteriosis
Holes form on the leaves, and sores appear on the fruits. The disease is bacterial, transmitted by insects or through water. Dark brown spots form on the outside of the leaf. The fruits are deformed. It spreads during periods of high humidity and temperature changes.
What to do to avoid infection:
- Do not plant a crop more than once every 4 years in one place. If absolutely necessary, it is necessary to remove the top layer of soil.
- Treat the seeds.
- Remove infected fruits and leaves from plants.
Treatment is carried out using chemicals. They are also treated with Bordeaux mixture or copper oxychloride.
General measures to prevent the development of the disease
Nothing helps in this difficult matter more than the advice of experienced summer residents who have encountered diseases. General measures to prevent all of these and other diseases consist of following simple recommendations.
It is easier to prevent the development of viruses and infections than to treat plants.
Prevention measures:
- First of all, adjust the method of watering; it is best to use drip irrigation, or watering directly under the root.
- More attention is paid to soil moisture.Its shortage, as well as its excess, leads to the development of various diseases.
- Watering time in open ground in the evening after sunset, in a greenhouse in the morning.
- Compliance with the ventilation regime when growing in protected soil.
- A crop that grows in one place year after year is much more susceptible to disease.
- It is better to use complex fertilizing, this will increase the overall tone of the bushes and increase resistance.
- When grown in a greenhouse, constant treatment and disinfection of the room is required.
- Tools used in work must be disinfected.
- Temperature for healthy development of the crop is +20⁰С. When it decreases, covering material should be used.
Fertilizers
The presence of any external abnormalities in a plant does not always indicate the development of a disease. Often the reason is a lack of minerals in the soil.
It is necessary to feed the plant regularly; in addition to introducing organic fertilizers, solutions containing potassium and magnesium are used.
Excess copper causes the plant to develop brown spots on the leaves and they begin to fall off.
Variety selection
The main advantage of the modern gardener is the abundance of choice of crop varieties. You can choose the characteristics of the species that satisfy the requirements of the family.
In order not to suffer from constant struggle and preventive treatments of bushes, you can purchase special varieties. They are most often hybrid and resistant to major diseases. But you should remember that collecting seeds yourself will lead nowhere. Since such varieties do not retain the hereditary genes of their parents.
Fruiting of many species does not depend on climatic conditions. They set fruit even in unfavorable weather.
The appearance of spots on the leaves of a cucumber indicates that the plant needs something. Before starting treatment for all diseases or starting to mindlessly feed the bushes, they understand the reasons for their appearance.