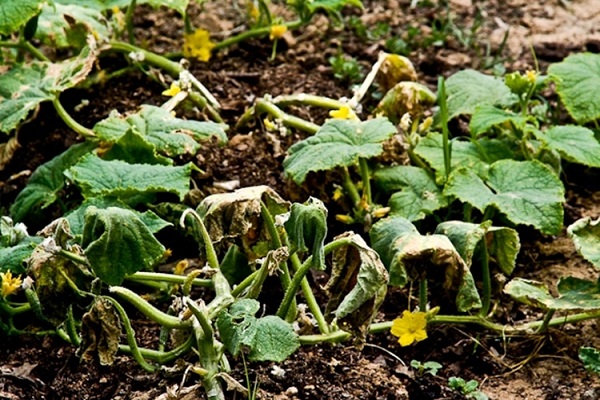
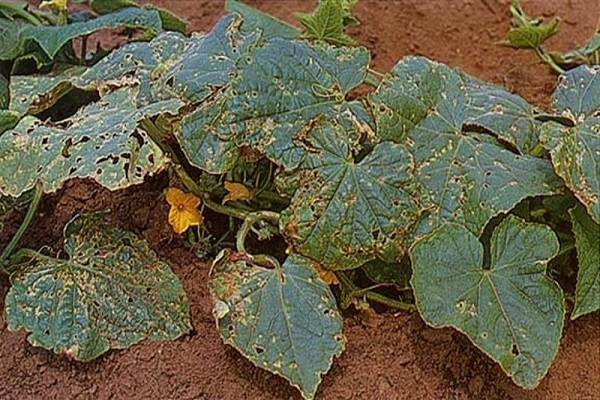
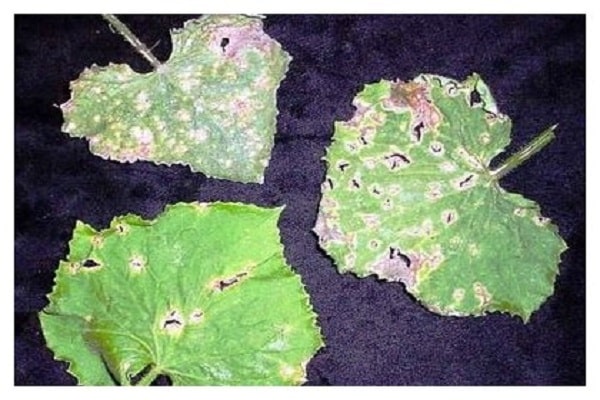
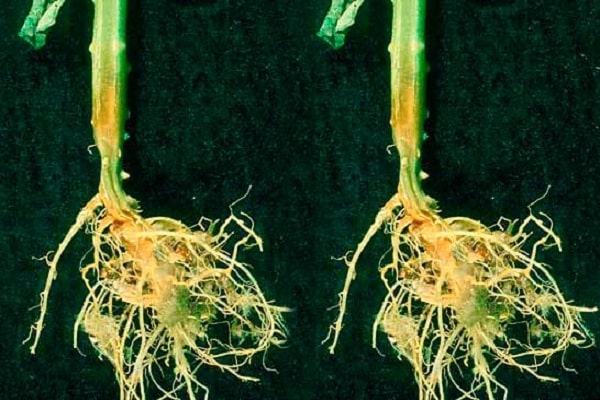
Sometimes you can notice fusarium wilt of cucumbers grown in greenhouse conditions and in open beds. This problem can be caused by various reasons, but most often it occurs due to fungal infection of the vascular system of plants (Verticillium or Fusarium).
Causes
In some cases, cucumbers begin to wither due to underdeveloped root systems. This can happen when planting cucumbers in a greenhouse in soil that is too dense. In this case, the root system cannot provide the grown plant with nutrients and moisture. If you examine such a plant, then it will not reveal signs of damage by microorganisms, but only the underdevelopment of their roots will be established.
Note! If cucumber seeds are planted in affected soil filled with hot water without disinfection, the plants will be affected by thermophilic fungi and pathogens that can cause temporary toxicosis.
Studies of wilted plants show that small roots die as they grow into the soil. The period from the beginning of germination to the withering of the entire plant is sometimes more than a month. When cucumbers wither, they lose their ability to resist diseases caused by various bacteria and infections.
If the soil is enriched with a culture of living bacteria and fungi, the process of its detoxification is accelerated. For this purpose, the following drugs are used: Baktofit, Trichodermin, Fitosporin-M, Integral, Pseudobacterin-2. Compost added to the soil can have the same effect. It helps restore soil fungistaticity.
If the pre-sowing preparatory work of the soil with low moisture capacity is insufficient, cucumbers may be affected by the fungal infection Verticillium albo-atrum. This occurs when they penetrate the vascular system.
You should not create narrow and high beds. When watering them, the water does not have time to penetrate deep, and the plants do not receive the required amount of moisture. If the soil temperature is above 28 degrees, then cucumber root system weakens, and the fungus in the ground begins to infect the plant.
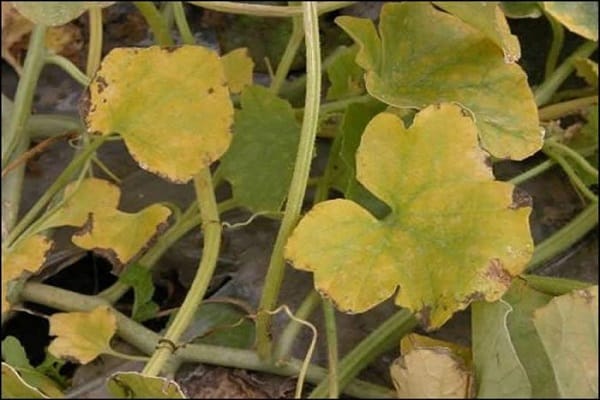
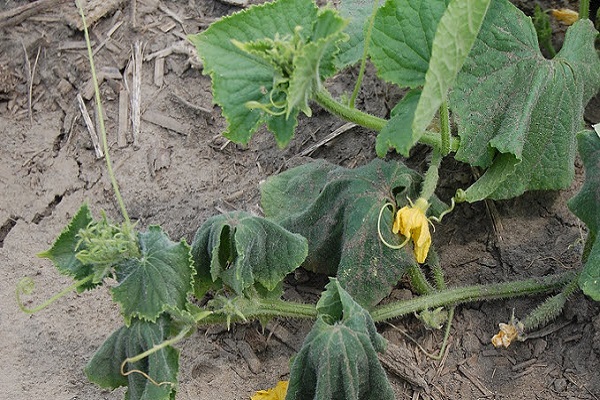
If the leaves of the lower tier are affected, marginal spotting may occur. The leaf blade located between such veins begins to die. The foliage of the upper tier loses its turgor and becomes chlorotic. If you make a section of such a leaf, then under a microscope you can examine the mycelium along with it.
Fusarium (tracheomycosis and verticillium) of cucumber
The danger of this cucumber diseases is to cause great damage to crop yields. The disease can quickly spread over large areas. When the above-ground parts of plants are infected, up to 50% of all grown vegetables can be affected.
Characteristic symptoms of the disease
When affected by this type of disease, not only the foliage dies, but also the stem and root system. Its occurrence is favored by relatively high air temperatures. Fusarium blight on cucumbers is afraid of a drop in temperature.
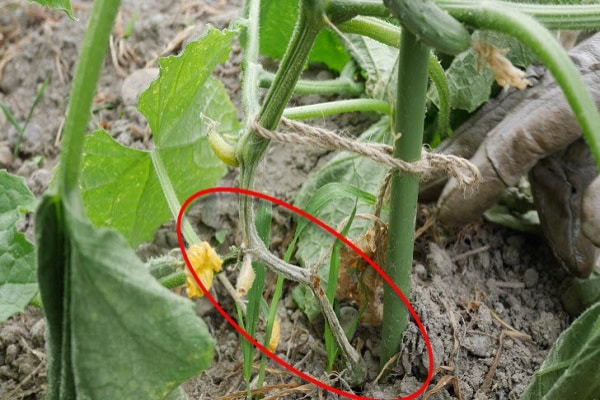
Symptoms of fusarium begin to appear with damage to the root system (root rot). This problem occurs more often in greenhouses and greenhouses. The infection accumulates in the soil and spreads to new areas.
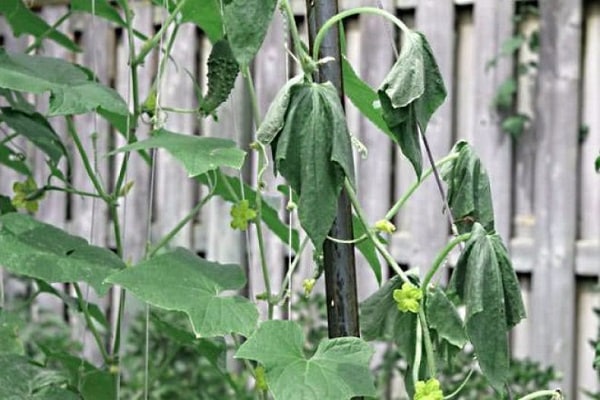
The first signs after the onset of infection appear within a few weeks. Clogging of blood vessels by tracheomycosis, shortly before fruit formation, leads to foliage wilting during the hottest time of day, which ultimately leads to the death of the plant.
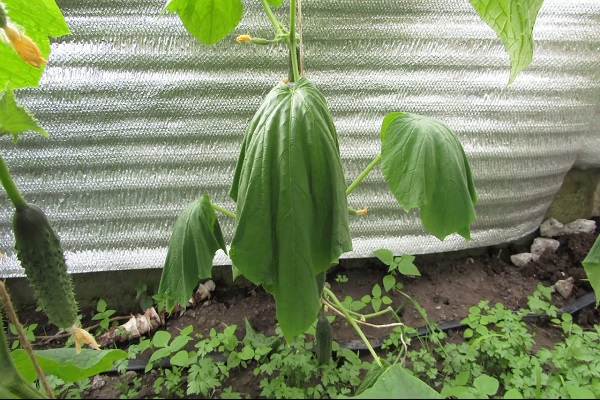
During the formation of greens, the symptoms of fusarium on hot days may change. Plant vessels blocked by tracheomycosis do not affect the development of the root system. The disease progresses sluggishly, but the plants stop growing ahead of schedule.A microscopic examination of the stems reveals fungal mycelium, as well as new formations in the vessels in the form of a granular brown substance.
At the same time, silvery-white mycelium appears at the base of adult plants. The mycelium that appears on the stems leads to the rapid death of the plant.
Biological features of fusarium and verticillium
For the causative agent of verticillium, high soil temperatures (more than +26 degrees), as well as the absence of moisture, are favorable. At the same time, fusarium is favored by low temperatures and waterlogged soil.
Both of these diseases prefer soil that is highly acidic. Plants affected by this disease exhibit the following types of disorders: vascular blockage, toxicosis, wilting, tissue necrosis.
Fungi can penetrate plants both immediately after sowing and after the seeds germinate. When the root system is injured, a kind of gate is formed for infection to penetrate through it.
Fungi form colonies in the vascular system, and then gradually reach the parenchyma. If the soil containing even a small colony of conidia is not disinfected, it will be practically unsuitable for growing cucumbers.
But the presence of a pathogen does not always lead to drying out and death of the plant. With properly organized care, the number of infected bushes is reduced by about 3 times. Conversely, incorrectly carried out agrotechnical measures significantly increase this indicator.
Sources of pathogenic infections
The main source of spread of pathogenic infection is the seeds used for planting. If production technologies are not followed, the source of infection can be soil and plant residues.
Measures to protect against fusarium and wilt
Pathogenic microorganisms are very resistant and measures to protect against them are not always successful. The best preventive measures are sowing healthy seeds. If, after removing a dead plant, another plant is planted, then disinfection of the soil in the hole should be provided, otherwise the newly planted plant will also die.
How to deal with the problem of fusarium
When growing cucumbers, vegetable growers use special agrotechnical techniques to cope with fusarium blight on cucumbers and prevent the spread of the disease:
- The use of preventive measures to disinfect the soil in the beds using chemicals or heat treatment.
- Purchasing or preparing substrates for planting seeds, taking into account their terms of use.
- To ensure the length of the growing season of cucumbers, at the time of their active fruiting, additional soil is poured out to ensure the formation of an additional root system. Compost is used for this purpose, and is sometimes rolled for optimal aeration.
- Irrigation using the drip method requires drainage so that moisture does not form stagnation.
The formation of plants and regular harvesting reduces the load on the plants, as a result of which the aging process of the plant’s root system slows down.
Biological agents used
Treatment of fusarium wilt of cucumbers is carried out using certain strains of Trichoderma. Such drugs are created in laboratories. You can treat the finished product by adding it to moist soil 2-3 days before planting vegetables. Subsequently, such a suspension is sprayed on the stems, foliage and soil in the beds.
Chemicals
Often, fungicides do not have a significant effect in controlling cucumber wilt. This result is a consequence of increased pathogen resistance.
Studies of means to eliminate seminal infections have found that Fundazol is the most effective. Other similar drugs had weaker activity.
Good results in destroying Fusarium infection of seeds are obtained by gradually warming the seeds before planting (the first day - 35 degrees, three days - 55 degrees, fourth day -72 degrees).
Preventive measures to combat the manifestation of fusarium and wilting of cucumbers consist of disinfecting the soil in greenhouses, as well as the composts and other substrates used for planting seedlings using steam, with the further introduction of biological preparations.
The prepared fungicide solution is poured under the root of infected plants. If the infection has spread throughout the beds in the form of a focus, then their treatment should be carried out on the entire affected part. To cope with the spread of the disease, it is necessary to carry out 1-2 treatments.
In this case, drugs from the benzimidazoles group have a positive effect.
In some cases, fusarium, while in plants, develops slowly, without causing significant harm. This occurs due to the treatment of seeds with fungicides (as seed enterprises do).
Also, if you follow the rules of agricultural technologies for growing cucumbers, the plants develop sufficient immunity that prevents the development of the stem form of the disease throughout the entire growing season.The drug Fungicide can protect the plant for only 2-3 weeks, and the main problem with the development of fusarium is considered to be drafts, changes in soil and air temperature levels, and insufficient agrotechnological care of plants.