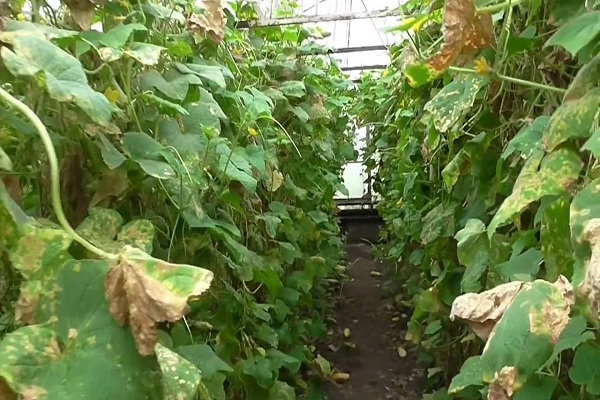
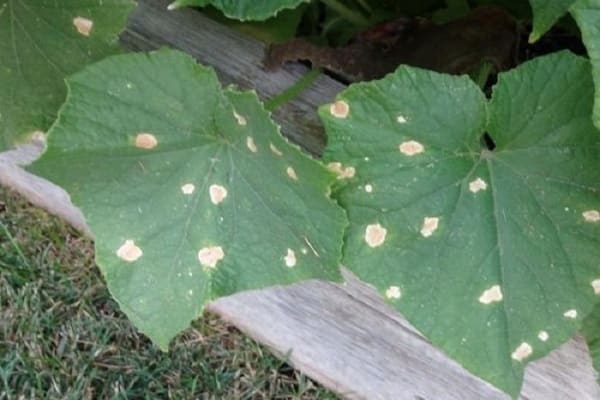
Often, gardeners' seedlings and mature leaves of cucumbers turn yellow, dry out and die. This disease affecting plant leaves is called cucumber leaf chlorosis. Let's look at how to identify and fight it below.
What causes chlorosis and what does it look like?
There are many reasons for the appearance of this disease, and they are very diverse in nature:
- Lack or excess of microelements.
- Insufficient or excessive watering of plants.
- The appearance of viral or infectious diseases.
- Cold or hot weather.
- Lack of lighting.
- Pest infestation.
- Constant drafts.
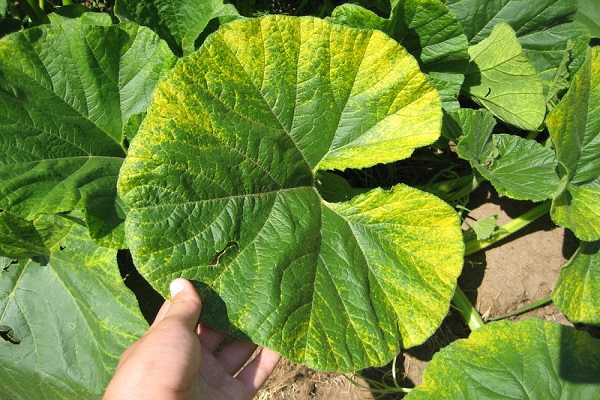
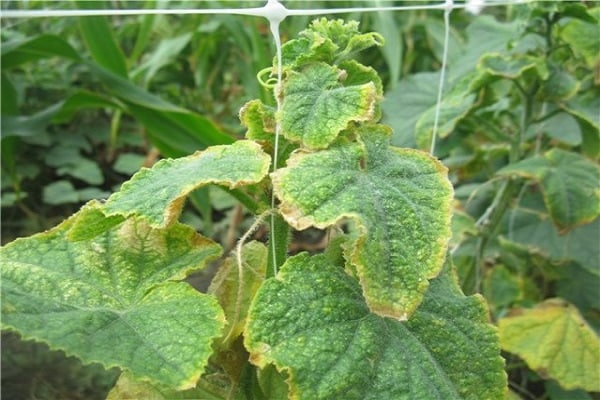
This disease looks like this on cucumber bushes: first, yellow areas appear on the edges of the leaves. Then the areas between the veins become yellow, while the veins themselves remain dark green. Gradually, the greens of the cucumbers completely turn yellow and die. This happens due to a lack of chlorophyll, which is produced to color plants green. But chlorophyll cannot be produced for a number of reasons.
Types of chlorosis
The most common cause of chlorosis in cucumbers is a lack of microelements. Let's find out what to do if there is a shortage or excess of elements:
- Magnesium deficiency: In this deficiency, the underside of the greens discolors first. In this case, the veins remain green for the first time, then the entire surface turns yellow. The next stage is that they acquire a purple tint around the edges and turn yellow on the bottom and top. To eliminate symptoms, feed with appropriate fertilizer.
- Nitrogen deficiency: leaves begin to turn pale from below, gradually covering all bushes. At first they become pale, then turn yellow, and at the final stage they turn brown. At the same time, the veins also lose pigment. During treatment, the bushes are fed with nitrogen-containing fertilizers.
- Iron deficiency: the shoots at the top turn pale, and the color gradually changes to brown.
- Zinc deficiency: individual areas between the veins turn pale, then the greenery is completely covered with brown spots. The leaves take on a gray tint and then bronze. To eliminate the disease, you need to feed the plants with microelements containing zinc.
- Manganese deficiency: areas between the veins turn pale, while the veins remain dark green. Then the edges take on a rusty tint.
- Potassium deficiency: the lower leaves at the edges begin to turn pale, then the shade suddenly changes to brown. In this case, no yellowing is observed.
Chlorosis also appears due to changes in weather conditions or infection of plants by insect pests.
When there is an excess of moisture, they wither, turn pale, and sag. Serous spots with rot appear on the plate. Eventually all the leaves fall off. If the cause is not eliminated, mold appears on the shoots and the roots become watery. The soil is excessively wet to the touch. To stop, you must stop watering immediately.
When frostbite occurs, the leaves also lose color, becoming completely discolored or in certain areas of the leaf blade. To stop the process, you need to remove the damaged areas.
With a lack of light, the entire plant turns pale, the leaves grow small, and the stems become elongated and thin.
The spider mite destroys seedlings from the bottom of the leaf blade. You can see small cobwebs there. At the same time, the green mass of cucumber seedlings turns pale, turns yellow, and then falls off.
How to deal with the disease?
If there is a lack of microelements, you need to feed it. Depending on the type of deficiency, cucumbers can be treated with the right element.
Iron extract can be prepared at home. To do this, add 4 grams of citric acid and 6 grams of ferrous sulfate to 1 liter of boiled water. The mixture is thoroughly mixed. The solution should be light orange. The mixture is watered over the plants and the leaves are sprayed.
Another effective method of replenishing iron in the soil is to bury a rusty nail in the ground, nothing complicated, but the result is excellent.
For insect pests that cause chlorosis, use ready-made solutions or powders sold in stores.
A popular method for exterminating pests is to finely grate an onion and infuse it in water for several days. This solution is used to spray greens affected by spider mites or thrips.
Disease Prevention
To prevent chlorosis from appearing, it is not necessary to fertilize and treat plants every day. Cucumbers will grow even in sand if you dig in a large amount of last year's crops. humus from grass and other biological waste. After adding humus to the ground, the bed is dug up several times and the seeds are planted. During the growth process, humus decomposes into microelements and is absorbed by cucumbers. Preventive actions:
- To prevent a lack of lighting, you need to thin out the planting beds and plant the beds in areas not shaded by trees or buildings.
- Water as needed to avoid excess moisture in the soil.
- Do not plant seedlings if frost is expected. In case of frost or temperature changes, the plants are covered with film.
- You cannot plant cucumbers on ridges where there is a constant draft; they will become weathered and turn yellow.
If you follow these simple rules, you don’t have to worry about chlorosis. The plantings will not die and will produce a wonderful harvest.