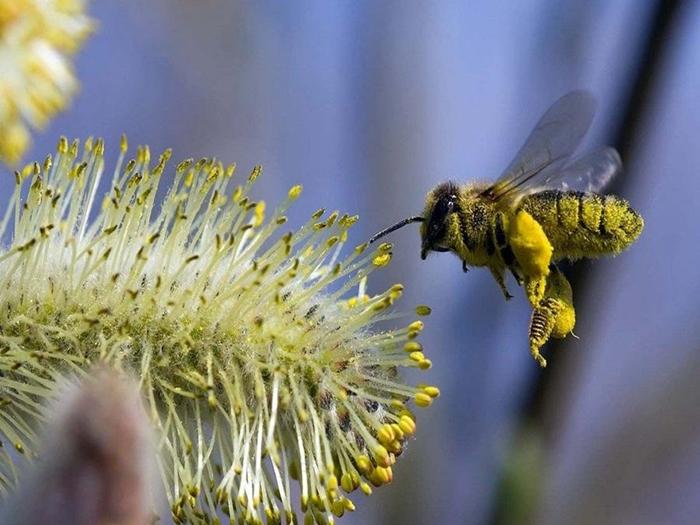
During the flowering of honey plants, bees fly out of the hive every day for nectar and pollen, which are necessary for the full functioning of a large family. The amount of nectar produced directly depends on the distance covered by working insects. How far insects fly, and how long bees can stay away from the hive, we will look into the details further.
What is the average and maximum speed of a bee in km/h
Working individuals that collect delicacy are born in mid-spring, and after 2-3 weeks they are able to go for a bribe. Minke whales obtain nectar and pollen, from which honey and beebread are prepared to feed the family during the cold season.
When choosing a location for an apiary, beekeepers calculate the flight range of insects and how fast they move in different conditions.
Movement speed may vary depending on many reasons:
- weather and climatic factors in the form of rain, gusty wind, high air temperature;
- the terrain where insects fly over;
- bees are overloaded with nectar and pollen.
The average speed of a working individual without prey is from 30 to 35 km/h. If insects move without a bribe against a gusty wind, the indicator drops to 18-20 km/h. With nectar and pollen, the speed of movement in strong winds is reduced to 12-13 km/h.
Under normal conditions, minke whales loaded with prey reach speeds of up to 20-22 km/h. The maximum speed recorded by beekeepers on a flat expanse of meadows and fields is 60 km/h.
Important! In the presence of a large concentration of trees and shrubs, minke whales cannot fly quickly, so in forests the speed of movement of bees is reduced to 250-300 m/h.
Height and radius
During daylight hours, each working individual makes approximately 10 flights from the nest, during which it manages to collect up to 2 g of pollen. In the process of moving, workers expend a lot of strength and energy, and they need constant nutrition, which they receive from the collected nectar. Over 1 km of distance covered, the minke whale eats up to 0.5 mg of the sweet product collected from flowers.
When placing hives, beekeepers calculate the flight radius of insects, which ranges from 1 to 2 km.
In this case, hardworking flyers easily reach flowering plants and return to the hive with prey without significant losses.
In clear, windless weather, the height of movement of insects flying out of the hive for a bribe is from 8 to 10 m above ground level. After collecting the necessary products, the bees become heavier, so the height when flying to the nest does not exceed the 5-meter mark. In case of strong and gusty winds, the flight altitude of insects is reduced to 1 m from the ground surface.
Interesting! To ensure maximum collection of beekeeping products, experienced beekeepers purchase mobile hives, which are transported close to the place where honey plants are flowering.
How far do bees fly from the hive?
The flight range of working individuals directly depends on the distance of the apiary from flowering plants. On average, beekeepers expect that insects will have to travel no more than 1-2 km to the bribe site. But if the bees have discovered that there are plants with a high content of pollen and sugar in the nectar in the access zone, they can easily cover a distance of up to 4.5 km from the location of the hives.
Flying out of the nest, insects fill the crop with up to 2 g of food necessary for flight. In the process of collecting nectar, bees from strong families can obtain up to 50 mg of nectar in one flight. The average rate of delicacy production by one individual from an ordinary nest varies from 7.5 to 20 mg.
In well-developed families, working individuals are characterized by excellent endurance and, if necessary, fly up to a distance of 10-12 km from the apiary.Typically, such flights are provoked by flowering in remote areas of clover, forest raspberries, linden, sweet clover, apple and pear trees.
Important! The flight distance of bees from the apiary is affected by weather conditions and the presence of flowering honey plants.
How many times does a bee fly in a day?
During the period of active nectar collection, the working day of hardworking minke whales begins at sunrise and continues until sunset. Bees are also able to work in extreme conditions under the full moon or on white nights, but they do this only if there are suitable honey plants.
Depending on the location of the apiary, the flight for valuable products takes one bee from 30 minutes to 2 hours. Next, the workers bring the prey to the hive, hand over the collected prey to their brothers and fly back to the fields for the next portion of nectar and pollen.
During a working day, one individual makes about 8-12 flights, each of which ranges from 3 to 8 km. Based on such data, it can be calculated that during daylight hours an insect travels from 40 to 90 km.
When collecting nectar from flowering shrubs, workers fly around one plant with many honey-bearing flowers, which significantly reduces the total distance covered by insects per day.