People have been breeding honey bees for a long time to produce tasty and healthy honey. These insects also serve as a source of wax, poison, propolis, and bee bread. They are considered social insects that live in groups. Each bee family includes a queen, drones, and workers. They differ in structure and functions. However, all individuals are interconnected and cannot exist separately.
- Description and structure
- Life cycle
- Queen bee
- Worker bees
- Drones
- Nest
- Behavior in the apiary and in the wild
- Swarming
- Common Breeds
- Maintenance and care
- Terrain
- Arrangement of the house
- Care in spring
- In summer time
- In autumn time
- In winter
- Reproduction
- Benefits of Honey Bees
- Honey herbs for bees
- Diseases and prevention from them
- Difference from wild ones
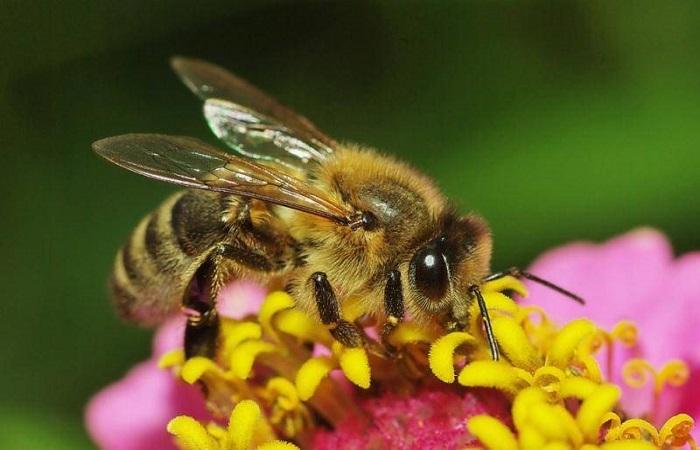
Description and structure
The body of a honey bee includes several components:
- head;
- abdomen;
- breast.
Bees are characterized by the presence of 2 compound eyes and 3 simple eyes. The first are located on the sides of the head, and the second - on the crown. The head contains the tentorium, or internal skeleton. The muscles that are responsible for turning the head, jaw, and proboscis are attached to it.
The role of support is played by the exoskeleton, which is called the cuticle. Inside there are hairs that provide protection against dirt and perform tactile functions. All elements of the body are held together by elastic membranes.
Life cycle
Features of the life cycle of bees depend on the caste. So, the queen lives up to 7 years, worker bees - 8 weeks, and drones - no more than 5.
Queen bee
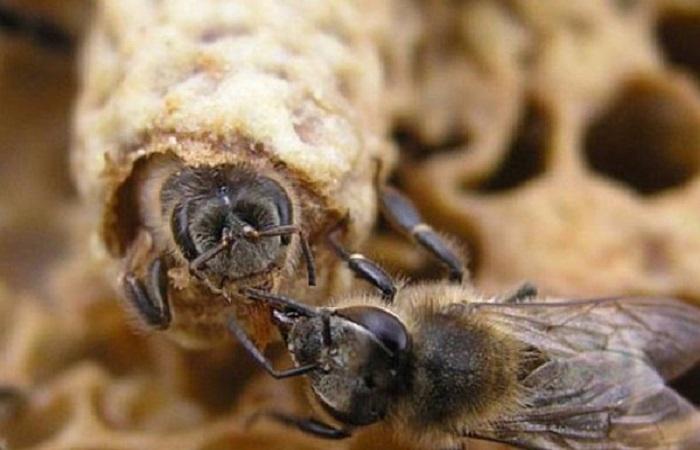
With the arrival of spring, the queen begins to lay eggs. After 3 weeks, the larvae hatch from them. Worker bees feed them for 1 week. After which the larva is sealed with wax and becomes a pupa, and then an adult. After 12 days, the imago appears. This term refers to insects that differ from adults in their soft coverings. Such individuals feed the brood and clean the hive.
The main function of the queen is to replenish the hives with brood and increase the size of the family. She can leave the house only during swarming.
Worker bees
These individuals clean the house of dirt and provide feeding for the brood and drones. On days 16-20 of life, individual individuals process nectar into honey. After 20 days from the moment of birth, the bees fly around and remember their hive. Each time they increase this distance.
Drones
These males are characterized by the absence of a stinger and large size. Their main task is considered to be fertilization of the uterus. As soon as this happens, the male falls and dies. Therefore, the life cycle of drones is different. Significantly more individuals emerge from the brood than required. Therefore, bees expel weakened or extra males.
Nest
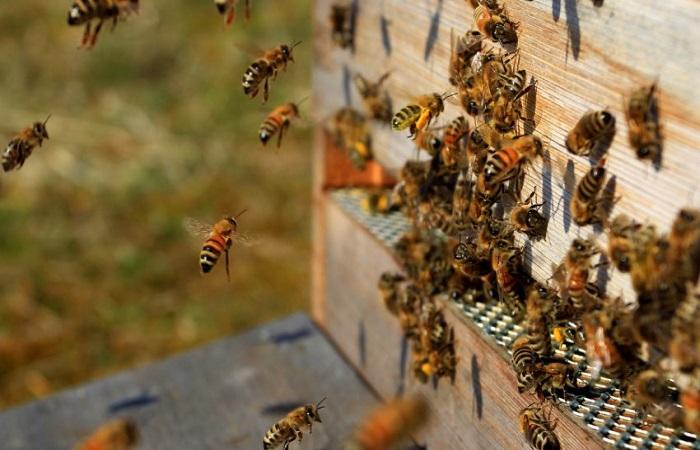
A bee family can include 10-15 thousand individuals. However, sometimes this figure can be significantly higher. Worker bees form nests in their houses. This is where honey, pollen, nectar, and brood are stored.
In the central part of the nest there is brood. There, the optimal temperature regime, which is required for the full development of eggs, is constantly maintained. The stronger the bee colony, the larger the volume of the nest. In this case, the temperature values at the edges and in the center are more different.
Behavior in the apiary and in the wild
In spring, the rapid process of reproduction begins. Bees fly out of the hives and collect nectar from primroses. The bee colony is preparing to swarm. A number of insects will leave the hive with a new queen.
When a new swarm breaks away, an experienced beekeeper catches it and places it in a new hive. In this way, it is possible to increase the number of honey-bearing families storing nectar for the winter.
Summer is considered a period of active honey collection. It begins in May or mid-June and lasts until the end of autumn as long as there are flowers. In autumn, bees begin to actively store honey, insulate their houses and prepare for winter. The beekeeper must ensure that the bees are healthy. It is also important to clear the hives of debris.
Swarming
Bee colonies begin to swarm in April or May - with the arrival of warmth. This is how they reproduce. Families swarm in a small room much more often than in a spacious one. As long as the brood develops normally and the workers feed the larvae, there is no swarming. It begins when a large number of bees accumulate. If insects have sufficient nutrients, swarming will not occur.
To avoid starting this process, it is recommended to do the following:
- move insects to a cool place;
- force bees to feed brood;
- transfer insects to intensive summer work;
- pour in a lot of sugar syrup for processing.
Thanks to timely measures, it will be possible to delay the swarming process or avoid it altogether. At the same time, an excess of nutrients is also undesirable - it will provoke this process.
Common Breeds
Honey bees are part of the order Hymenoptera. The most popular breeds include:
- Gray mountain Caucasian - distinguished by a gray-silver color, a slight tendency to swarm and lack of aggression. These bees are considered to be very hard working. They collect a lot of honey even from poor honey plants. However, representatives of this breed cannot boast of strong immunity to disease or frost.
- Ukrainian steppe - such bees winter well, are hard-working and have productive queens. Individuals have a tendency to swarm, are moderately aggressive and have difficulty accepting foreign queens. Representatives of this breed have a gray color. However, there are also individuals with yellow stripes.
- Carpathian - has a friendly character and high productivity.Additional advantages include resistance to frost and disease. In addition, these bees do not have a tendency to swarm. Such individuals collect a lot of honey even in unfavorable conditions. They are able to easily switch to other plants.
Maintenance and care
For bee breeding to be successful, it is important to provide them with proper care. There are many factors to consider.
Terrain
To choose the right location for the apiary, you should adhere to the following rules:
- The place should be quiet and protected from gusts of wind and direct sunlight.
- The hives should be located with a slope to the south. This will provide enough light.
- The apiary is located far from highways, large bodies of water, industrial facilities and farms.
- There should be many plants around the apiary that provide nectar. However, they should differ in flowering time.
- The apiary and 2-3 kilometers around it should not include persistent foci of disease.
Arrangement of the house
You can buy hives or make your own using soft wood. It is important to open the structures with a special varnish paint, which will provide protection from moisture and help you find your home faster. Optimal colors include yellow, green, and blue.
Care in spring
When the temperature reaches +8 degrees, it is recommended to move the hives outside and transplant bee colonies with intact frames into a new home. In this case, you need to print a honey frame. There should be at least 8 kilograms of honey in the hive.
In summer time
During this period, it is necessary to monitor the swarming process and take only the first swarm from the hive. It is recommended to collect it using a ladle and a scoop. If individuals do not want to move to the swarm, they can be driven there using smoke. If necessary, it is necessary to remove extra queens from the swarm or, on the contrary, to replant them. Filled magazines must be cleaned and put back so that insects can drain the frames. By the end of summer they are removed.
In autumn time
Before wintering, it is important to check the quality and quantity of honey for the presence of honeydew. To do this, it is recommended to take samples and send them for laboratory testing or do it yourself. If honeydew is detected from the honeycombs, it is necessary to remove the honey and store it for use as spring feeding.
In winter
At this time, it is important to maintain the temperature at a level of at least 0…+4 degrees. At higher parameters, increased ventilation of the space is required. Optimal humidity levels are 80%. In this case, the room itself should be dark.
Wintering bees require complete rest and the absence of rodents. Wire can be used to clean the tapholes. This procedure is carried out at intervals of 30 days. Sometimes it is recommended to inspect the dead for the presence of pathologies and parasites.
Reproduction
To reproduce, the queen mates with a drone in the air. After this, the males are immediately expelled from the hive, which entails their death.Once every 30 days, the queen bee lays approximately 1,500 eggs. Some queens live up to 6-7 years. In this case, they can lay up to 3 million eggs during their lifetime.
Benefits of Honey Bees
These insects bring honey, which people eat and also use in medicine and cosmetology. In addition, when breeding bees, you can get royal jelly, wax, propolis, bee bread and bee venom. The listed bee products are considered natural antibiotics that can be used for medical purposes.
In addition, the benefits of bees are associated with the pollination of entomophilous plants. This helps to increase productivity and obtain seed material.
Honey herbs for bees
Not all plants are suitable for collecting pollen and nectars. The most common honey crops include:
- Grain and feed – buckwheat, clover, sweet clover. Bees also collect honey from sainfoin and seradella.
- Medicinal - these include sage, mint, thyme. In addition, bees use coriander and oregano to collect honey.
- Oilseeds - effective honey plants include sunflower, tobacco, chicory, rapeseed, and mustard.
Diseases and prevention from them
The most common pathologies of honey bees include:
- American Foulbrood – This disease often affects larvae.
- Ascopherosis is a fungal pathology that provokes the death of larvae.
- European foulbrood also attacks larvae.
- Sacbrood is a quarantine infection that mainly affects the brood.
- Acarapidosis is a disease caused by a tick that infects the spiracles.
To prevent the development of pathologies, experienced beekeepers advise adhering to the following rules:
- insulate the hives well and provide them with adequate ventilation;
- periodically inspect and replace nesting combs;
- disinfect honeycombs and tools in the apiary;
- after the bribe, increase young bees to improve families;
- provide the bees with high-quality food;
- perform centralized pumping of honey;
- choose strong bee colonies and exclude closely related relationships.
Difference from wild ones
Wild bees differ from domestic ones in properties and appearance. They are considered more hardworking and resistant to temperature fluctuations. However, wild individuals are much more aggressive. At the same time, they produce higher quality and healthier honey, since it has time to fully ripen in the hollow. The number of wild individuals decreases every year. This is due to the influence of anthropogenic factors that cause their death.
Honey bees are beneficial insects. They provide honey and other products that have pronounced healing properties. In order for bee breeding to be successful, it is recommended to follow a number of rules and nuances.