The structure of a bee is characterized by a number of features. Each individual is ideally adapted for the life and development of a family. The body of a working individual has everything necessary to perform a wide range of tasks. They consist of building and maintaining hives, collecting and processing food, caring for offspring and protecting them. Beekeeping is considered a very difficult task. To do it successfully, it is important to have a lot of knowledge. The anatomy of insects is of great importance.
Description of the bee
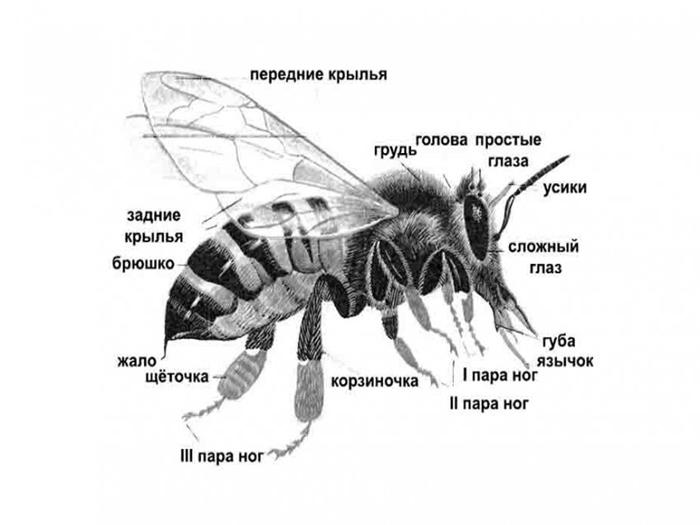
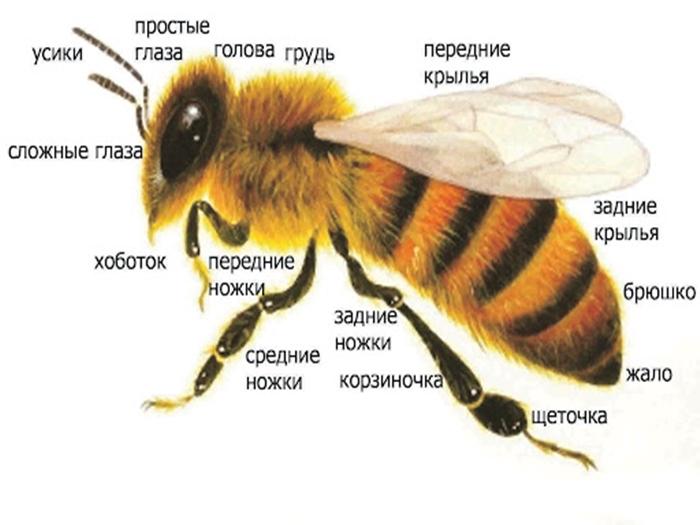
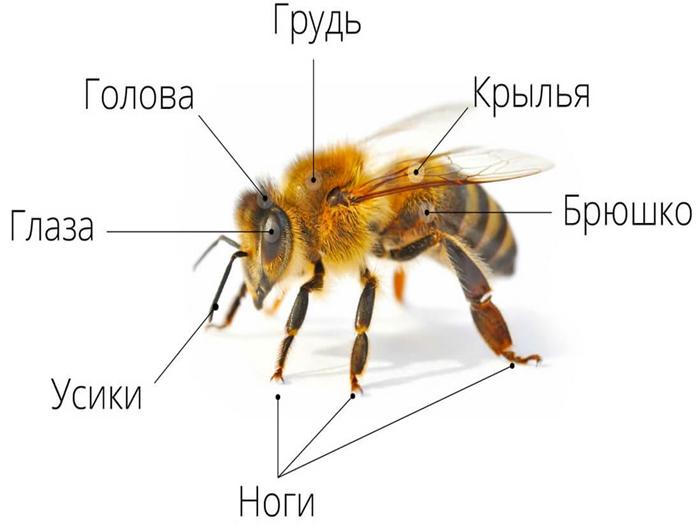
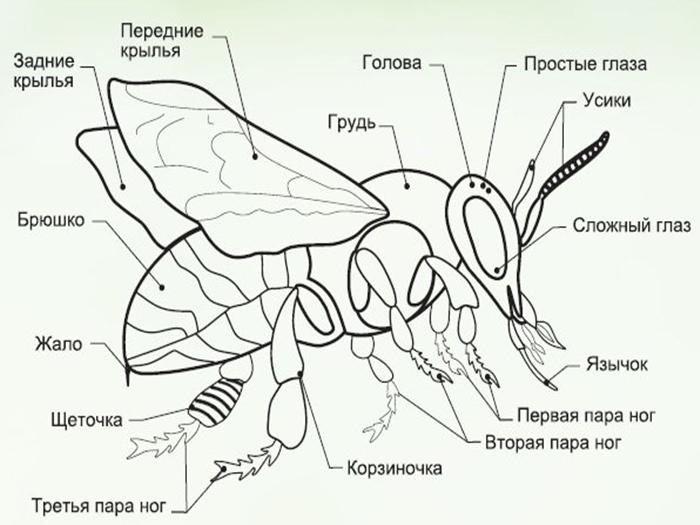
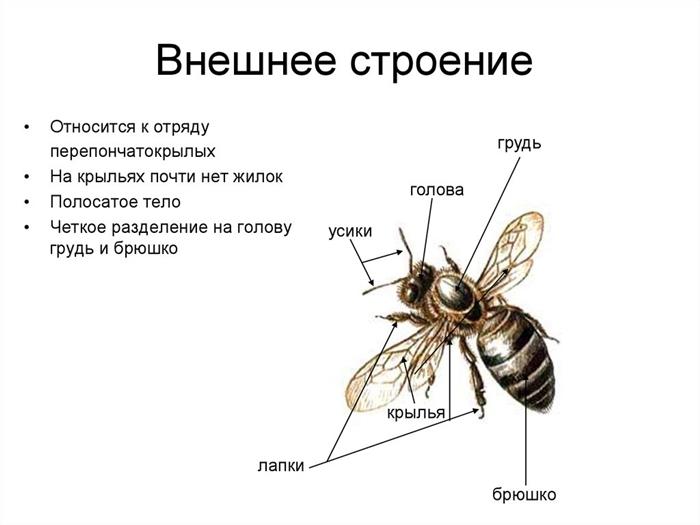
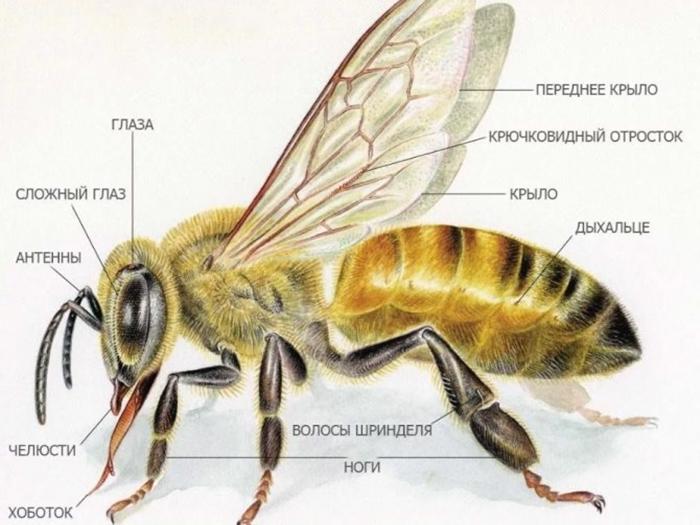
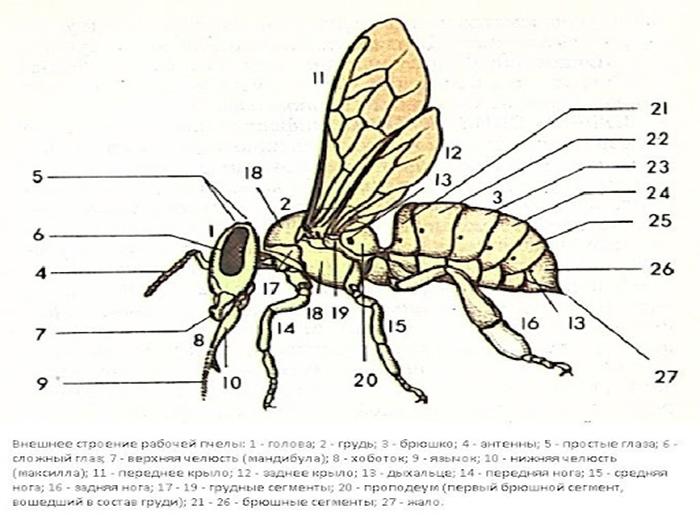
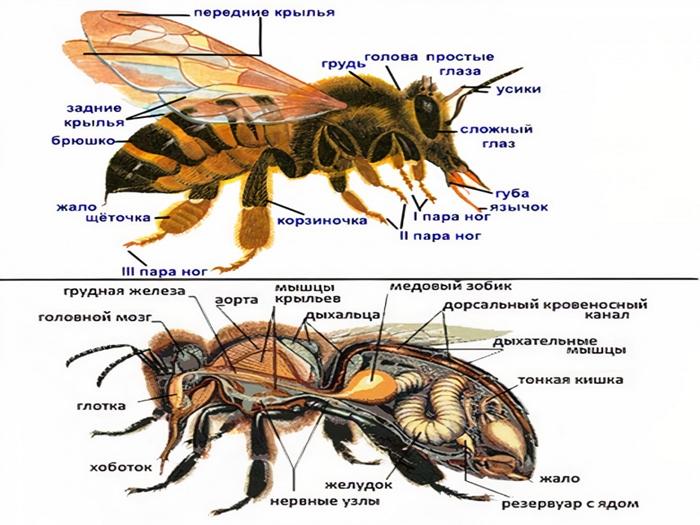
Bees have a segmented body.It contains the following fragments: head, thoracic region, abdomen. The body of bees is covered with hairs, which are organs of touch. In addition, they provide reliable protection of the body from pollution.
Head
The external structure of the head includes the following elements:
- 2 compound eyes and 3 simple eyes;
- antennas that provide olfactory and tactile functions;
- glands that produce pheromones;
- proboscis, which is pulled up and curled;
- a powerful jaw that kneads and shapes the wax.
Insects have gnawing mouthparts. This structure is considered unique and is found exclusively in bees.
Thoracic region
The thoracic region of the honey bee includes the following elements:
- 2 pairs of wings of different sizes;
- 6 legs.
The wing veins include chitin. This substance ensures the strength and lightness of the aircraft.
Abdomen
The structure of the abdomen includes 6 rings. Each of them includes a tergite and a sternite. The first term is used to refer to the dorsal semi-rings, and the second - to the abdominal ones. These elements are held together by soft membranes. This ensures freedom of movement of each fragment. Due to this, the abdomen grows in length and width. The main internal organs are hidden behind it.
Limbs
Bee feet are characterized by their versatility. They support the torso. Thanks to this, the bees move and clean the body. In addition, in workers, the legs are responsible for collecting pollen and forming wax balls.
Each bee has 3 pairs of legs, which consist of 5 segments.
They are distinguished by a movable connection. The front legs are characterized by the presence of brushes that help insects clean their eyes, mouth, and antennae. These elements scrape pollen from the body. The middle legs are also involved in its removal.They are covered with many hairs, which makes it easier to sweep away pollen.
The hind limbs are also highly mobile. There is a basket on the outside of the paws. In it, insects form pollen, which will be moved to the hive. Such a complex structure of the legs is characteristic only of working individuals. Other bees have a simpler limb structure.
Internal anatomy
Each of the elements has characteristic features.
Nervous system
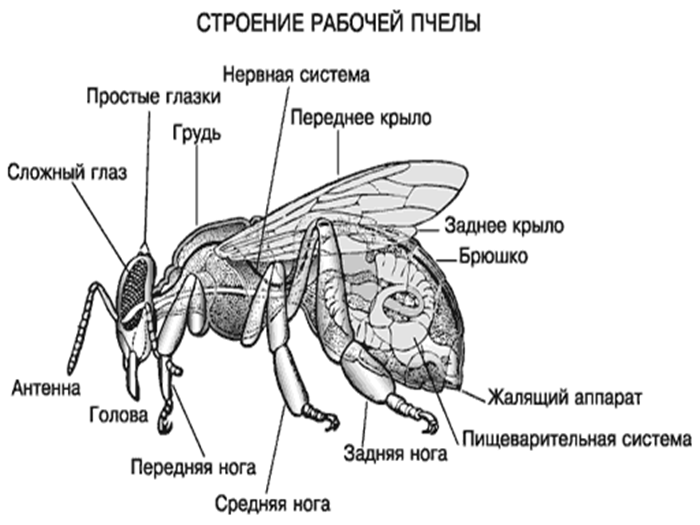
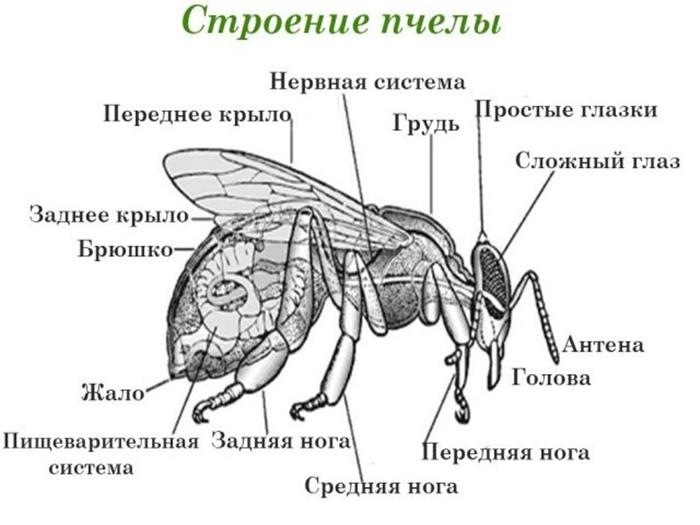
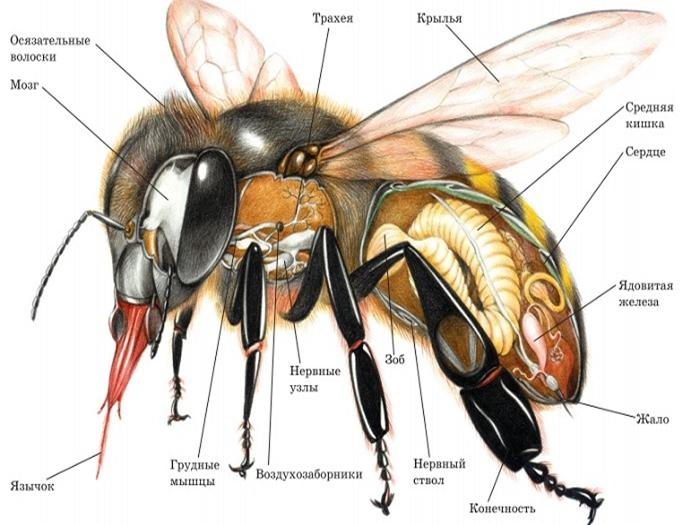
The structure of the nervous system includes 3 sections - central, sympathetic, peripheral. The central section includes the brain. It also contains the ventral chain of nerves that replace the spinal cord. The frontal node represents the beginning of the sympathetic department, which is responsible for the functioning of the digestive, circulatory and respiratory organs.
Since the brain is considered the main hub of the nervous system, it contains most of the neurons. The maximum number of such components is present in the mushroom body and in the optic lobe.
The size of the brain is influenced by the functions of the bee. In drones it is considered the largest. In this case, the maximum number of developed sections is observed in working individuals.
Nerve cells, or neurons, are considered the main structural units of the nervous system. They have a single long process that transmits nerve impulses. The structure also includes a branched process. It is capable of receiving and transmitting signals from other neurons.
Circulatory system
Bees are characterized by an open circulatory system. In this case, the blood always moves in a specific direction.This effect can be achieved due to the coordinated functioning of the aorta, heart, dorsal and abdominal diaphragm.
The heart resembles a long tube and is located along the back. The aorta is located in the chest, which supplies blood to the head. The structure of the tube includes 5 drops, which are connected through partition valves. They pass blood in a certain direction - from the abdomen to the head. In a calm state, the heart pulsation is 60-70 beats per minute. During the flight, this figure increases to 150.
The dorsal and abdominal diaphragms are also part of the circulatory system. They are responsible for the flow of blood in the torso. Blood moves to the paws, antennae and wings due to bubbles that are located at the base of these parts of the body.
Reproductive system
Female bees have 2 varieties. These include queens and workers. However, only the first species can produce high-quality offspring. There is usually one queen in a bee colony. Working individuals are characterized by reproduced reproductive organs.
There are no developed tubes in the ovaries and oviducts. They begin their development only in specific conditions - for example, the queen died, and worker bees had to change their diet. This allows females to lay eggs. However, they do not have a spermatheca, and therefore the eggs are unfertilized. Only males can be born from them.
In the uterus, the ovary contains about 150 tubes, each containing one mature egg. In this case, the vagina is connected to the ovaries by a paired oviduct. The spermatic receptacle is also connected to a narrow fragment of the vagina. There is also a channel there that functions as a kind of dispenser. He lets several sperm pass at the right moment.When fertilized, the egg will hatch into a worker. If it doesn't happen, a drone will appear.
Sting
This element represents a means of protection or defense for the bee. It also assists in laying eggs. The sting is characteristic only of females. In appearance it resembles a needle and is an ovipositor.
The sting is located at the end of the abdomen. It is covered by the outer segments. In this part of the body there are 3 systems of glands - small, lubricating and large poisonous. The sting itself resembles a saw in appearance. This allows it to get stuck in enemy tissue. However, the bee loses it and dies.
The longer the sting is in the victim, the more poison enters the enemy’s body. The poison is a clear liquid that has a special aroma and bitter taste. When exposed to air, it quickly acquires a crystalline structure.
Genome
The honey bee is considered the third insect to have a known genome. It contains 300 million DNA base pairs. According to the first studies, this species appeared in Africa, after which it migrated to Europe in two waves. However, a later study of the bee genome showed that they arrived from Asia about 300 thousand years ago and rapidly spread throughout Africa and Europe.
Digestive system
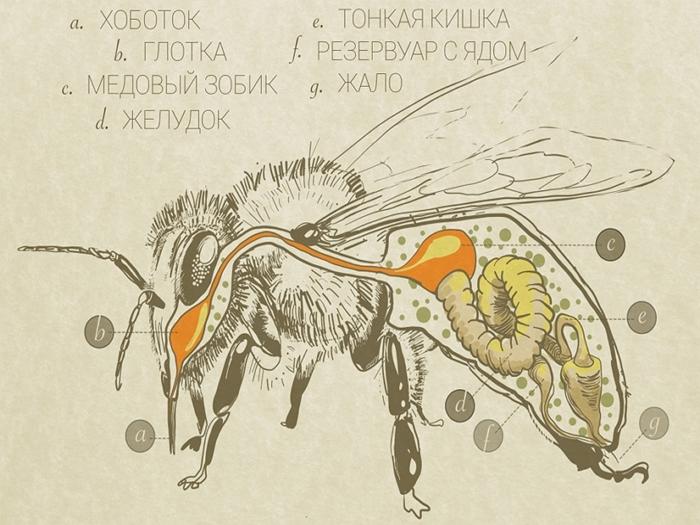
Such a system is divided into 3 fragments:
- the first - includes the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, honey crop;
- second - this section includes the stomach;
- the third contains the intestines.
The absorption, digestion and transformation of nectar into honey is carried out by glands located in the head and thoracic region. The esophagus is an extension of the pharynx. As it expands, it forms a crop to store honey.
Then the stomach is located. Essentially, it is the intestine in which food is digested.The third section is the intestine. It includes 2 intestines - small and rectal.
Respiratory system
Insects are distinguished by a powerful respiratory system, which covers almost the entire body. Inhalation is made through many sections in the body - 3 pairs on the chest and 6 on the abdomen. In the spiracles, air passes through the hairs, is purified and enters the air sacs, which are connected to each other. After which oxygen is distributed through the trachea throughout the body. Exhalation is made through the third pair of spiracles, which are located in the thoracic region.
The structure of the bee's body differs in a number of important features. All the characteristic features of these insects are aimed at successful honey collection.