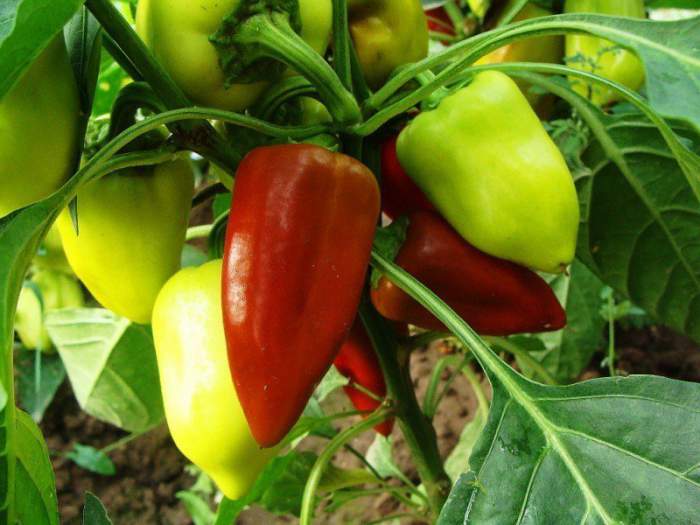
The formation of pepper in a greenhouse is mandatory for all types of this plant. For each variety, this event may be slightly different. For example, when growing sweet peppers, you have to completely remove the shoots and pinch off the top part.
If you have to prune short varieties, then only a small part of the shoots, which are located lowest, is removed.
What varieties need to be formed
Before growing peppers in open ground or a greenhouse, you need to understand what types of plants need it. Gardeners are engaged in growing varieties that can vary in duration of ripening. The following types of peppers are distinguished:
- Ultra-early - technical maturity is achieved in exactly three months.
- Early – the fruits ripen within 100 days.
- Mid-early - the first peppers ripen 130 days after planting.
- Late - ripens five months after planting.
Also, bushes may differ in their height. All varieties can be divided into:
- dwarf - below 40-45 cm;
- short - grow up to 50-60 cm;
- medium-sized - the height of the bushes does not exceed 100 cm;
- tall - the average height of an adult plant is about 200 cm.
The formation of peppers is carried out for all varieties except dwarf ones. They bear fruit well even without pruning the bushes, provided that the planting scheme has been fully followed.
When pinching low-growing bushes, it is enough to trim off weak shoots that grow inward. A tall pepper bush needs a lot of nutrients. If it grows greatly during growth, then ideal conditions will be created for the appearance of dangerous pests and diseases. Therefore, pruning of such bushes is mandatory in order to protect the plant and improve its nutrition.
Formation methods
To understand how to form peppers in open ground, you need to familiarize yourself with the basic methods of pinching. During pruning of many varieties, various methods are used. There are three main methods for pruning bushes.
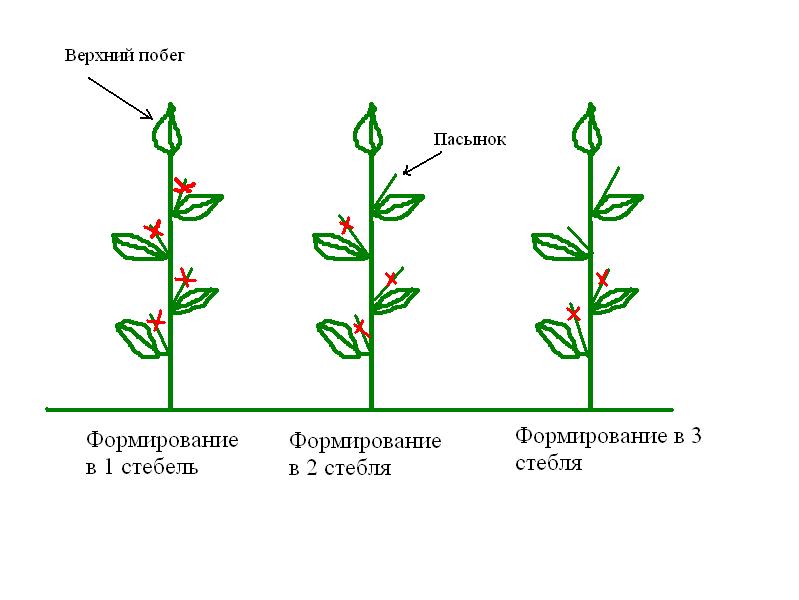
In one stem
Quite often this option is used if a lot of seedlings are planted, but the bed is not very spacious.By forming a bush in this way, the plant will receive more light, since most of the shoots and leaves will be removed.
To form a bush in this way, it is necessary to break out all the stepsons and their twins that appear during the bifurcation of the stems. Only all the flower clusters are left on the plant.
In two stems
This method is the most popular, as it is suitable for many varieties of pepper. In this way, you can get a small and powerful bush that can easily withstand the weight of even the largest fruits.
During the formation of the pepper into two stems, not only the main stem is left, but also its first stepson. It is this that develops faster than other stems. All other shoots need to be gotten rid of.
Three stems
This option is used when you have to grow few seedlings on a large plot. To form a bush with three stems, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Two stepsons are left on the plant, which are located below the first flower cluster.
- The bush is carefully examined and another well-developed and strong stepson is selected.
- All remaining stepsons are deleted.
Recommendations
Many people do not know how to grow peppers in a greenhouse. There are a number of specific rules that will help you perform this procedure correctly:
- You should not plant peppers if the weather outside is too hot and dry for several days. In this case, it is better to leave the leaves on the bushes so that they can protect the plant from burning out. The formation of a pepper bush in a greenhouse during such a period can lead to its death. Having removed all excess shoots, the soil and bushes will lose additional protection from the sun.
- Pruning tools can be carriers of dangerous infections.Before the procedure, it is recommended to disinfect them with antiseptics.
- Pepper planting is not carried out if the height of the bush is less than 20-30 cm. This can negatively affect growth and fruiting.
- You cannot form a bush if it is sick. Because of this, he may die.
- It is not recommended to plant peppers if they are planted too sparsely. The distance between each bush should be at least 25 cm. Bushes that have no other plants near them should be left with dense greenery.
Basic Techniques
During the formation of plants, three main techniques are used.
Topping
Pinching is carried out in order to stop the growth process and direct all the nutrients to the young fruits. Pinching is a must. If this is not done, then all useful elements will be spent on the development of stepsons, side shoots and leaves.
Stepsoning
The bushes are pinched to provide the fruits with nutrients. It is necessary to remove only those stepsons that have grown to 4-5 cm.
Trimming
Pruning is done when a large number of unnecessary shoots appear. After pruning, only a few of the most developed stems remain on the plant, which are located far from each other.
Stages of formation
The process of planting peppers in open ground is carried out in several stages. It is recommended to use a clean tool that is not covered with rust.
crown bud
Young bell pepper seedlings have one stem, but over time the plant begins to branch and new ones appear. At the point where new branches form, the first flower is formed. Quite often it is called the crown bud.The essence of the first stage of formation is its removal. This is done in order to accelerate the development of culture.
Sometimes several such buds appear on the bushes at once. In this case, you will have to get rid of all the flowers so that the greenhouse pepper can branch out well.
This procedure is carried out even if the buds appeared before the pepper was planted in open ground.
Extra shoots
The second stage of formation is carried out after the first 10 leaves grow on the bush. In this case, all unnecessary branches are removed from the peppers in the greenhouse and only a few shoots are left that were formed by the fork of the main bud. Weak branches are shortened - the top growth point is removed from them. All remaining shoots will form the basis of an adult pepper.
After removing excess stems, bush peppers should be observed for several weeks. Over time, the shoots will begin to branch and a new bud will appear on each of them. They can also form in internodes. The buds that are there must be removed immediately.
Of all the new stems, you need to choose the strongest one and get rid of the rest. This is done in order to improve the supply of nutrients to the ovaries. This operation should be carried out after each branching of the bush. If weak shoots are not removed in a timely manner, the plant will gradually begin to weaken.
After completing the second stage, the pruned bush should have no more than 25 ovaries.
Barren shoots
After removing all excess stems, the sweet pepper bush in the open ground or greenhouse begins to develop rapidly. Over time, empty shoots begin to appear on the plants, which will have to be gotten rid of.They appear in the lower part of the bush, not far from the branching of the main stem.
In addition, at this stage, the sweet peppers in the greenhouse are covered with extra leaves, which do not take part in feeding the ovaries and create additional shade. Also, sometimes damaged leaves appear, due to which the plant develops various diseases.
If you do not remove excess leaves in a timely manner, the pepper's yield will begin to seriously decline. To do this, it is recommended to follow the following scheme:
- Leaves on the main stem need to be trimmed only after they have reached the stage of technical ripeness. No more than two leaves are removed at a time.
- The second removal should be carried out after the formation of the second cluster of peppers.
- The last stage of removing leaves is carried out 1-2 months before the fruits are fully ripened.
Topping
To form sweet and large fruits, the bushes will have to spend quite a lot of effort, which is often spent on maintaining new and unnecessary ovaries. Most novice gardeners make the same mistake - they leave a lot of ovaries that the bushes cannot feed.
At a late stage of pepper development, many new flowers appear. However, they do not increase productivity, but only weaken the newly formed fruit. It is because of this that the fourth stage of bush formation is carried out, during which growth points on all branches are pinched. Thanks to this, the plant spends all its energy on the development of new peppers.
Conclusion
To understand how to form peppers in a greenhouse or open ground, you need to familiarize yourself with some recommendations. A video will also help when forming peppers in a greenhouse, with which you can familiarize yourself with the features of this process.