Soil is the basis of human well-being because crops depend on it, as well as, in many respects, the climate of the entire planet. Nutritious soils support the life of millions of plants, and they, in turn, provide food for both people and animals. In order to maintain high soil characteristics, it is necessary to know what factors influence the process of soil formation and whether they can be controlled.
Factors influencing the process
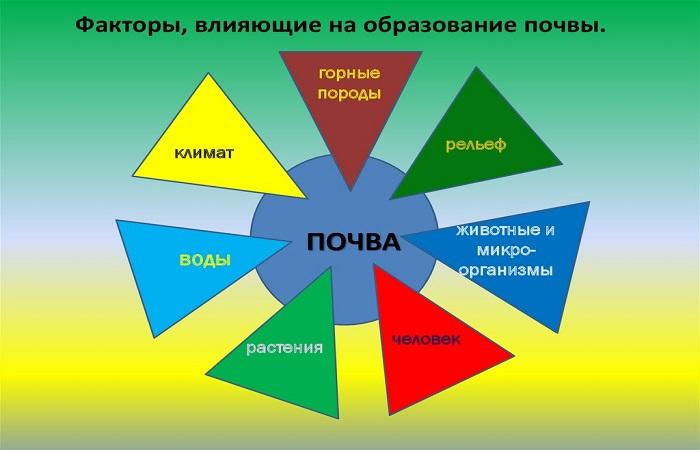
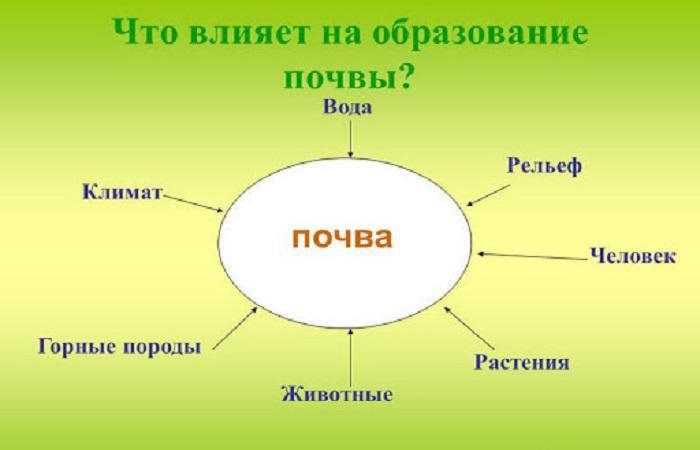
Soil formation is influenced by five different factors (according to Dokuchaev):
- Soil-forming (mother) rock.
- Climate.
- Plants and living organisms.
- Relief.
- Time.
Now they have been supplemented by two more factors: water and human economic activity.
There are many definitions and interpretations of the factors that influenced the process of soil formation, but the main one in the formation of fertility is always biological. Without microorganisms, plants, animals and other products of the kingdom of Flora and Fauna, any soil is just a collection of minerals. Only through long-term and complex interaction with living organisms does it acquire fertility. Biological impacts have the greatest impact on soil fertility.
This process requires a lot of time and certain favorable conditions. To understand what components of nature the properties of soils depend on, you need to understand that fertility is the most important indicator of soil quality.
The following components are considered the main ones:
- Moisture and its level of evaporation.
- Presence, quantity and level of groundwater.
- Prevailing winds.
- Annual temperature regime.
- Climate (climatic zone).
- Main herbal composition.
Soil is part of the earth's lithosphere and is one of its main components. All shells involved in the formation of soils are involved, for example, water in the form of precipitation or soil flows, the remains of living organisms, plants and animals converted into humus by microbes of various types and types.
So this complex action involves not only individual components, but also such global shells as the lithosphere, biosphere and hydrosphere of the Earth.
How does soil form?
The formation of soil is a long and complex process.It involves many factors that are interconnected by a unifying basis - time. It takes not years or even centuries for more or less fertile soil to emerge from the parent rock. Nature spends thousands and millions of years on the process of its formation. That is why it is important to realize the value of the land and try to preserve it at all costs.
Weathering of rock
This term refers to a broad impact on rocks, associated not only with the direct influence of winds. Weathering of rocks occurs due to the complex influence of a group of factors, resulting in the formation of crust and weathering products.
The following types of weathering exist:
- Mechanical or physical.
- Chemical.
- Organic or biological.
- Ionizing or radiation.
The extent of the effects of these types of weathering can vary significantly between the formation of different types of soil.
Physical
This type of weathering is associated with the effects of temperature changes, water, natural disasters, wind erosion and other factors. Water undermines rocks and transports them over long distances, freezing at night and intense heating during the day cause cracking and destruction, earthquakes, floods and mudflows mix minerals, and the process of further transformation is complemented by winds.
The process of soil cover formation begins with mechanical weathering.
Chemical
This type of weathering refers to a sequence of various chemical processes that continue the process of breaking down rocks, and also trigger their transformation into completely new compounds and minerals.Gradually they acquire special qualities and properties and form minerals that are fundamentally different from the starting substances.
Biological
This type of weathering is “triggered” by living organisms. These include microorganisms (bacteria, viruses and fungi), protozoa, fungi, lichens, lower and higher plants, as well as a number of animals that affect the soil, such as those that dig holes, feed and live underground.
Primary soil formation
This is a long period of development of the process of earth formation on exposed rock, which is a complex of physical, chemical and biological processes that occur simultaneously.
As a result of the action of such a complex of processes, the basis of the earth is formed, which is characterized by a specific composition and characteristics. They will further deepen, change and develop.
Soil development
At this stage, the main formation processes continue, to which is added the intense influence of biological factors. Terrestrial ecosystems are becoming more diverse and complex, which leads to the accumulation of fundamentally new compounds and components, that is, the soil itself is formed. It becomes the basis for the life activity of the next generations of living organisms, which continues the process of development and improvement, as well as the emergence of different types of soil.
Equilibrium
A state of stability occurs when soil formation has completed and reached maturity. In this case, fundamentally different connections and relationships appear and are established between the mineral component of the soil and living organisms.
The earth reaches equilibrium with climate conditions and vegetation cover.
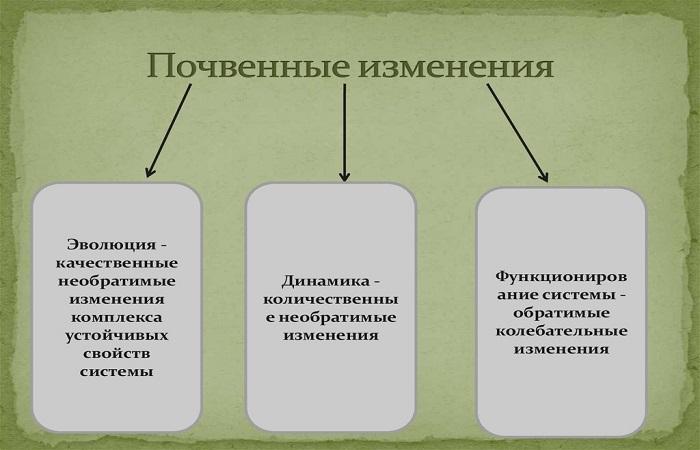
Evolution
These are changes in already formed, mature soils under the influence of environmental evolution. This is how new types or subtypes of soil appear. Evolution occurs as a result of the self-development of soils, the accumulation of changes in their composition and structure, and includes the following cycles:
- Biogenic (biological).
- Biogeomorphological.
- Bioclimatic.
- Anthropogenic.
Over the past two centuries, the role of the anthropogenic factor has grown sharply. This significantly increased the load on the soils and led to their qualitative and quantitative changes.
The role of living organisms
Wildlife influences not only the quality, but also the composition of soils. In addition to saturating them with animal and plant remains, which are processed by microorganisms into humus and increase fertility, other interactions are also observed. Living organisms can lead to changes in the mineral composition of the soil; for example, some microorganisms have this property.
In the formation and development of soil fertility, it is impossible to single out individual factors. They work together to give soils their uniqueness and diversity.