Acidity is one of the most important characteristics of soil. It affects the conditions in which plants will grow, their condition and productivity. Let's look at the soil acidity standards for plants in the table, how and by what means we can increase or decrease it if it deviates greatly from normal. What are the dangers of disturbing the acid-base balance of the soil?
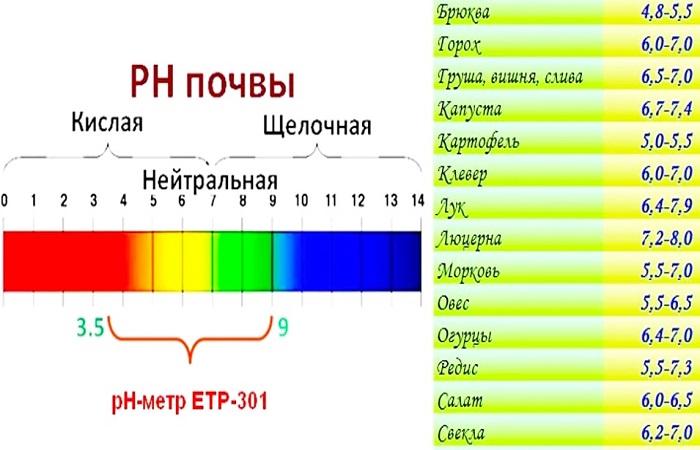
Acidity standards for different plants
For each type of garden and garden plants, the acidity of the soil should be different.The reaction of the soil environment, which is measured in pH, depends on the amount of hydrogen ions dissolved in the soil complex, and serves as an indicator of how acidic or alkaline the soil is.
The average value of the soil environment scale is 7, which indicates a neutral reaction. It is preferable for vegetable crops, fruit trees, shrubs and most flowers. A reaction from 7 to 3.5 indicates acidic soil and the lower it is, the more acidic the soil. From 7 to 11 – alkaline. A decrease or increase in pH by one means a decrease or increase in acidity by 10 times.
On the ground with what acidity different crops prefer to grow, you can see in the table:
| Culture | Acidity |
| Wheat | 6-7,5 |
| Corn | 6-7 |
| Peas | 6-7 |
| Sunflower | 6-6,8 |
| Potato | 5-5,5 |
| Sugar beet | 7-7,5 |
| Cabbage | 6,7-7,4 |
| Table beet | 6,8-7,5 |
| Tomatoes | 6,3-6,7 |
| Radish | Above 5.5 |
| Carrot | 5,5-7 |
| cucumbers | 6-7,9 |
| Salad | 6-7 |
Ways to increase acidity
To acidify sandy or sandy loam soil, you need to add humus, manure, compost, rotted sawdust or pine needles, that is, any organic fertilizers. The acidity will not change quickly, acidification will occur slowly and gradually, but the effect will last a long time. This happens because acidifying substances are produced by bacteria that process organic matter. To make alkaline soil slightly acidic, you need to add organic matter for several years in a row.
On clayey, especially waterlogged soil, the addition of organic matter increases acidity faster, since the activity of microorganisms in it is higher.
Many mineral fertilizers, nitrate, urea, and potassium salts, that is, those that are used everywhere, have an acidifying effect. Their action is also gradual; they cannot quickly change acidity.It is also impossible to exceed the application dose in order to influence acidity.
In addition to traditional fertilizers, colloidal sulfur, iron or aluminum sulfate have an acidifying effect. Substances must be dosed accurately; exceeding the permissible dose will harm the plants. Sulfur is added at the rate of 4 g per 10 liters of soil, iron sulfate - 50 g per 1 sq. m, aluminum sulfate - 75 g per 1 sq. m. m.
Sphagnum peat acidifies the soil well; it is added for digging at a rate of 1.5 kg per 1 sq. m. m and mixed with soil. In addition, peat perfectly loosens the soil and makes it permeable to air.
There is a popular way to quickly increase acidity - the use of organic acids - malic, citric or acetic. Dissolve 1-2 tsp in a bucket of water. acid and water the solution on the ground, using a volume of 1 bucket per 1 square meter. m.
Green manures can slightly acidify the soil: oats, white mustard and rapeseed. The roots of these plants release organic acids into the ground. Legumes (lupine, soybean, vetch) are able to maintain pH balance.
How to reduce soil acidity
Soils with acidity, weak or strong, are more common than alkaline ones. A common method of leveling acidity is liming, that is, adding fluff lime (slaked) to the soil. In addition to lime, chalk and dolomite flour are used. They spend, on average, 0.5 kg per 1 sq. m. on the ground with a weakly acidic reaction and up to 1.5 kg - with a strongly acidic reaction. Lime should be applied in the fall or spring, at least 3 weeks before sowing or planting plants.
Sand and sawdust need to be added to heavy clay soil to make it more permeable to air. Waterlogged soil must be drained by creating a drainage system on the site.
What is dangerous about the disturbed acid-base balance of the soil?
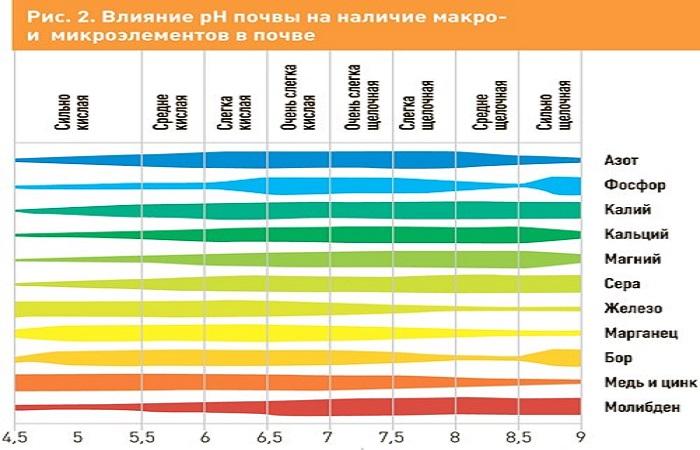
Most species of cultivated plants prefer a neutral or slightly acidic reaction; some flowers and conifers prefer an acidic reaction. More often, increased acidity leads to oppression of plants, they develop poorly and reduce productivity. In an acidic environment, mineral elements transform into forms that are difficult for plants to assimilate, and the activity of soil microorganisms slows down.
With high acidity, not only depression can be observed, but also the death of plants for seemingly no apparent reason. They get sick more often and are attacked by pests, and freeze out in winter.
Slow growth and poor development of plants are also observed in alkaline soils. Many microelements in them are also inaccessible to plants due to the fact that they are in the form of insoluble hydroxides. The lack of mineral elements affects the appearance of plants; they quickly turn yellow because they do not receive enough nutrition.
Soil acidity and its level affect the development and condition of plants and, first of all, agricultural ones. A large deviation from the average value is not favorable conditions for their normal development and obtaining a harvest from them. When growing plants, it is customary to take measures to reduce or increase acidity in order to make the soil more convenient for plant life.