What kind of soil should be prepared for grapes? Beginning winegrowers, amateur and practicing gardeners often ask about this. The soil mixture determines whether the seedling will take root or not, how quickly it adapts and grows. Thematic material with advice from professionals will help you dispel all doubts and make the right choice.
- Soil suitability criteria for planting grapes
- High-quality composition
- Acidity
- Correct pH
- Indicator plants
- Alkali content
- Humidity and tensiometer measurement
- Soil characteristics depending on the planting method
- For cuttings
- For seedlings
- For layering
- Under the shanks
- When grown from seed
- For adult bushes
- For growing different varieties
- Land preparation
- For open ground
- Substrate for greenhouses and greenhouses
- For landing on balconies
- Improving soil quality in different seasons
- in spring
- In summer
- in autumn
- What to look for when choosing soil
- Fertilizing the land
- Manure
- Bird droppings
- Compost
- eggshell
- Yeast
- Mulch
- Sawdust
- Care
- Disinfection
- Protection
- Recovery
- Biological products
Soil suitability criteria for planting grapes
Even experienced gardeners can make mistakes when it comes to factors influencing the development of wine berries. They will probably call:
- variety and its individual characteristics (ripening period, disease resistance);
- climatic growing conditions;
- fertilizing - its availability and frequency;
- natural causes - air, light, watering.
But not everyone will remember the basics - the composition of the soil, its acidity, mineral saturation, fractional characteristics. And this also seriously affects the growth of the vine and its ability to bear fruit.
The subtlety is that grapes do not need black soil in its pure form. A composite mixture of sand, humus, and earth, which is sufficiently air- and water-permeable, is much better suited. Heavy, clayey soils are unacceptable. A place with close aquifers is also not suitable: this will lead to rotting of the roots. Therefore, winegrowers resort to tricks, partially or completely replacing the soil in the selected area with a carefully composed “cocktail” that will satisfy the needs of the finicky vine.
High-quality composition
This is the saturation of the soil mixture with useful substances that the vine will need to form a root system and grow bunches and berries.Grapes need the following minerals (in an ideal situation they should be in the soil or they will have to be “added” as fertilizer):
- Nitrogen. The basis of growth. If there is no nitrogen, the shoots do not develop well. Oversaturation leads to a shift in balance, weight gain of green mass to the detriment of the taste of the berry.
- Phosphorus. The second most important element affecting the vineyard is the speed of fruit ripening, shortening the growing season.
- Potassium. It affects the synthesis of carbohydrates - starch and sugars, therefore, if there is a lack of this component in the soil, the berries will be sour and tasteless. The presence of potassium is also associated with the frost resistance of the bush.
- Magnesium. Its role in the main process - the formation of chlorophyll - is undeniable. Without magnesium, the foliage loses its natural green color, becomes withered and dead.
- Calcium. When there is enough of it, the roots grow in time, supporting the stem, and the berries are tasty and aromatic. An excess of calcium leads to bush disease (chlorosis).
- Iron. Also involved in the synthesis of chlorophyll in leaves.
These are the main elements, but besides them, there are also auxiliary elements - sodium, aluminum, zinc. Therefore, for feeding grapes, experienced gardeners use complex, complex fertilizers.
Acidity
The normal development of seedlings and adult plants depends on the reaction of the soil, its acidity. Soil that is too acidic will have to be alkalized; soil that is not acidic will have to be acidified. In general, in such cases they talk about the acidity balance, the pH indicator, which is determined by carrying out a special analysis.
Correct pH
Each plant has its own acidity requirements. Grapes are no exception. Potatoes and raspberries love an acidic environment; for wine berries, a corridor of 4-8 units has been experimentally established.The maximum value should not exceed 8.2, and only if the soil is not oversaturated with salts.
Indicator plants
Certain plants that choose certain conditions will help determine the acidity of the environment. At the same time, it will become clear why some of them grow and prosper, while others wither. Sorrel, carrots, cucumbers like acidic soils, and irises and lilies like flowers. Moss, sedge or horsetail settle there. If the pH is low, this is evidenced by the rapid growth of gooseberries, blackberries, and thujas.
Alkali content
For normal grape growth, you need the “correct” pH balance, and not just an indicator skewed into an acidic or alkaline environment. The neutral level (5.6-6.0) is determined by lettuce, apple, and pear. It must be remembered that many plants are able to adapt to the acidity of the environment, and some can correct it during the growth process. Clover and nettles grow on low-acid lands; for slightly alkaline ones - quinoa or mustard.
Humidity and tensiometer measurement
More than the presence of nutrients in the soil, only soil moisture affects the growth of grapes. Rare varieties react normally to excessive moisture.
Wineberry prefers well-drained, dryish mixtures. The humidity indicator is determined by a special device - a tensiometer. To learn how to use it, enthusiasm alone will not be enough. It is better to know approximately the level of groundwater and regulate soil moisture by watering.
Soil characteristics depending on the planting method
Before planting grapes in one way or another, determine the location, soil composition, its moisture content and fertilization. It will be different for cuttings and seedlings.
For cuttings
For planting cuttings in cups or pots, mixtures are prepared according to the following “recipes”:
- About 1 part humus, the same amount of turf and sawdust, half a part sand.
- Peat and stale (not fresh) manure taken in equal proportions.
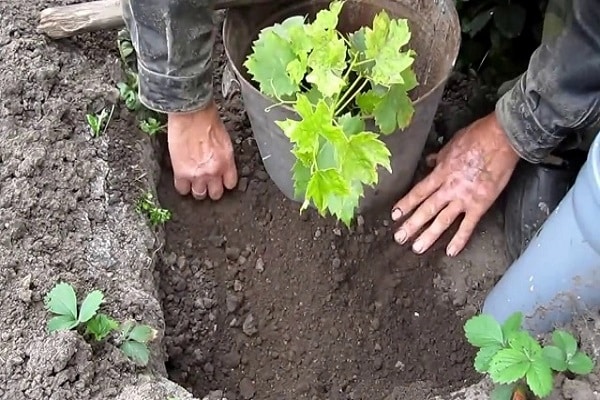
For seedlings
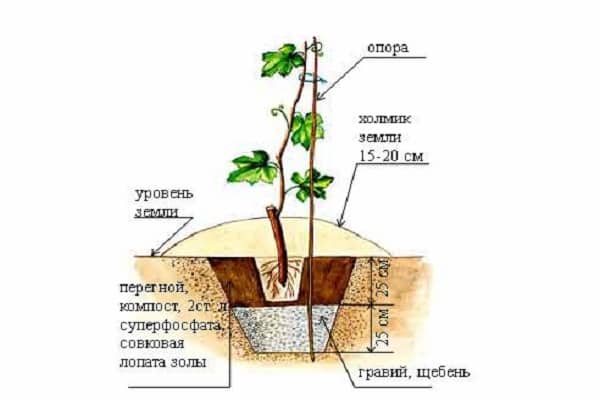
The soil for seedlings is prepared using different methods, but they begin to do this in the fall: they dig, loosen, fertilize, remove old plants (if there were sick ones, it is better not to plant grapes in such a place to avoid infection).
For better drainage, crushed stone is added to the soil under an already planted bush; for seedlings, coarse material is placed at the bottom of the dug hole - stones, bricks, sometimes pieces of pipes with holes are dug in to supply water and fertilizers to the roots through them. Depending on the composition of the soil, it can be “diluted” with sand, mixed with peat or humus.
For layering
Layering on grapes is carried out from an already mature plant; no special preparation is required, since the same soil is used. Depending on the chosen technique, a trench is dug, a vine or a fresh shoot is placed in it, and sprinkled with earth. It is allowed to add peat, compost, and mulch the planting.
Under the shanks
It is best to start preparing in the fall: this way the earth will settle and be saturated with fertilizers. Digging is required, but without fanaticism, so as not to grind the soil to the state of sand. You can add mineral fertilizers or organic matter (regular manure).
Each experienced winegrower has his own technique, for example, this: when digging a hole, the soil from it is divided into an upper and lower layer. Next, the “top” is mixed with humus and again placed in the hole, then adding the remaining “bottom” soil.
It is recommended to use any large fragments - bricks, stones, crushed stone. They will increase permeability to air and water, which is so important for grapes.
When grown from seed
Growing from seed is one of the most difficult methods. It will require well-fertilized, pH-balanced soil (you can take a ready-made soil mixture for flowers). Peat and dosed mineral fertilizers are welcome. The main task is to maintain the required level of humidity and temperature.
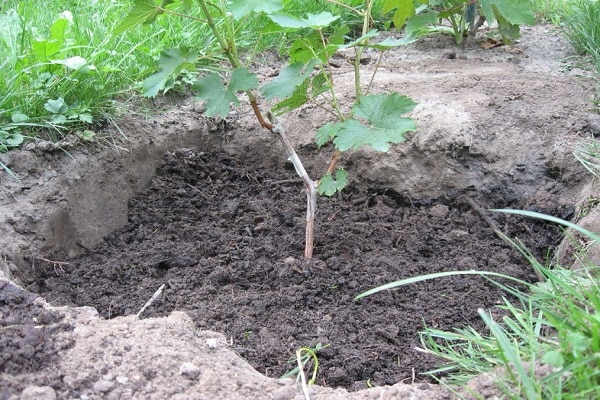
For adult bushes
The transplant itself is a serious shock for the bush; it is not recommended to do it unless absolutely necessary, with old plants. It is better to think about other options, but if replanting is inevitable, then prepare the soil a month before the procedure, in the fall.
There is nothing new in this: digging, fertilizing, watering. Autumn replanting is preferable, since the bush will grow in winter, under the snow, and by spring it will definitely get stronger and take root in a new place.
For growing different varieties
As such, there is no selectivity among different species according to soil type - grapes need drained, moderately acidic, dry soil containing potassium, nitrogen and phosphorus. If you have doubts about the choice of soil for a specific variety, it is better to check with the seedling seller or familiarize yourself with the material yourself by studying thematic materials.
Land preparation
Careful selection of the planting site and soil mixture account for 80% of success. Even the strongest seedling will not grow on poor, clayey, too wet soil. Therefore, experienced gardeners even in difficult conditions use soil replacement (full or partial) to compensate for the shortcomings of natural conditions.
For open ground
The simplest methods of fertilizing the soil are no less effective than complex ones. It is enough to add organic matter to the soil - compost, humus, use mulching, feed with ash to lay the foundation for the growth of the vine.
Cattle or bird manure must be fermented and left to rest so that it does not burn the tender roots of the grapes. In the case of compost, grass, leaves, small branches, fruit remains and kitchen waste are sequentially placed in the pit, and after a few years a ready-made home-made complex fertilizer is obtained.
Substrate for greenhouses and greenhouses
In cold climates, to accelerate the growth of seedlings, they are grown in a greenhouse. To do this, use a ready-made substrate, purchased in agricultural stores or mixed yourself. In the first case, you don’t need to worry about the pH level or the presence of minerals - they are already there. Otherwise, there will be painstaking work of adding peat, humus, thoroughly mixing and distributing the soil throughout the greenhouse.
For landing on balconies
The ideal option is to plant ornamental grapes in a soil mixture, which is sold in stores for growing indoor plants: it has a balanced composition, and at the same time you can choose the desired acidity level.
Improving soil quality in different seasons
Not everyone is equally lucky - some have to painstakingly enrich the soil on their plot in order to create the required conditions for the grapevine. But this is also possible.
in spring
Each application of fertilizing has its own season. In the spring, the first digging is carried out after the cold season, mineral complexes containing nitrogen and its derivatives are added.
In summer
During hot weather, they loosen the soil, remove weeds, apply nitrogen fertilizers, and use foliar fertilizers.
in autumn
At this time, dig up the soil, remove damaged parts of the plant, and add potassium mineral complexes. At the same time, manure, compost and mulch are added - this way they are better absorbed by the plant.
What to look for when choosing soil
When deciding on a site for planting vines, they note what indicator plants grow there and how deep the groundwater is. The vine will reach the lower moisture-bearing horizons on its own, putting out long roots; in the case of a superficial location, the situation is worse. It may be necessary to drain the fluid, install a drain, or choose another location.
Fertilizing the land
Grapes urgently need nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus - the growth of the vine and the taste of the berries depend on this. You can fertilize the soil using simple improvised methods.
Manure
Cow humus is a wonderful organic fertilizer. It’s just important not to overdo it, add humus in doses and it’s better in the fall than in the spring. Experts advise using horse manure, but applying it once every 2-3 years.
Bird droppings
Bird guano can compete with other organic substances in its balanced composition, but there is one subtlety: due to its high energy value, the droppings must “burn out” and stand so as not to burn the roots of the grapes. You can reduce the concentration by diluting it with water.
Compost
Organic fertilizer of natural origin. Prepared from leaves, food waste, grass. A significant drawback is that such a complex takes a long time to prepare. It is applied in doses, once a year, usually before winter.
eggshell
The shell contains an important mineral for grapes - calcium, which affects the ripening and taste of the berry. It is crushed and added to the soil in small portions, trying not to exceed the norm.
Yeast
Regular yeast helps balance the microflora. The method of preparing top dressing is simple and straightforward: yeast (100 grams) is diluted in a bucket of warm water (10 liters) and left overnight.One bush requires up to 2 liters of nutrient solution.
Mulch
Mulching helps retain moisture and nutrients in the soil. To do this, after planting and watering the seedling, the root zone is covered with small branches, straw, foliage, in a layer of up to 5-7 centimeters. This protection is said to inhibit the growth of weeds.
Sawdust
Ordinary sawdust can play a dual role - mulch the soil and, over time, turn into fertilizer and rot to saturate the soil with useful substances.
Care
Care measures for planted vines include timely watering, treatment with chemicals against diseases and pests, fertilizing and shelter for the winter.
Disinfection
It is carried out in the spring or several times during the summer season, for prevention. They use preparations to kill insects and pathogens by spraying the grapes with a garden sprayer.
Protection
Some varieties are actively eaten by wasps and birds - effective protection of the future harvest is necessary. To do this, use traps, insecticides, special nets or caps. In the case of protection against common garden diseases, spraying with Bordeaux mixture, complex-action preparations, is used.
Recovery
To push the bush after a long winter period and make it grow more actively, pruning dead areas and forming sleeves are widely used. For some varieties, due to the abundance of fast-growing stepsons, this is an extreme but necessary measure.
Biological products
Serve as an alternative where chemistry is not effective or cannot be used. Based on special strains of biocultures that suppress the activity of gray rot, mildew, and fungi.Absolutely harmless to humans: processed fruits can be eaten without fear of poisoning (unlike pesticides).