Based on the morphological characteristics of soils, one can determine their origin and properties, which will indicate the characteristics of their economic use. Let us consider what this concept means, the main features of soil morphology (the structure of the soil profile in a vertical section, soil color, soil structure and their significance, new formations and inclusions).
The essence of the concept
The soil acquires morphological characteristics over time as a result of formation. They indicate the genealogical origin of soils, their development, composition, chemical and physical properties.Some morphological characteristics can be determined visually; laboratory tests are required to determine others.
Main morphological characteristics of soils
Among the important features are the following characteristics: the structure of the soil profile, soil structure, color, inclusions and new formations.
Soil profile structure
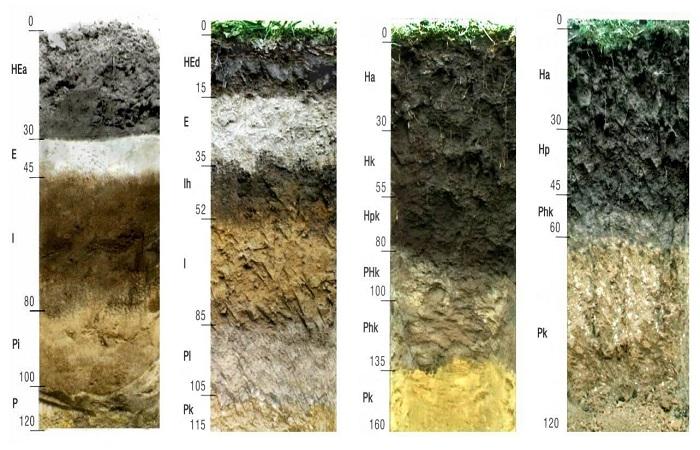
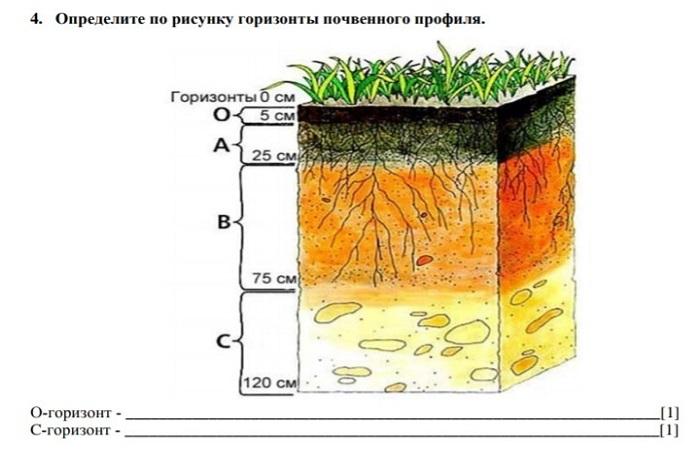
The soil in its vertical section is heterogeneous and has a layered structure. The profile of a well-developed soil is divided into 3 main layers or horizons, going from the surface inwards and having their own characteristics. Each layer throughout remains predominantly the same in mechanical, chemical composition, physical properties, structure, color, mineralogical composition and other characteristics. But all horizons within the profile are connected and influence one another. The total thickness of the soil, including all layers, can vary from 0.5 to 1.5 m.
The soil layers separate gradually during its formation, but even after the formation is complete they do not have a clear boundary; a transition layer is visible at the confluence. The main layers of the profile: upper soil, which determines the fertility of the soil, parent or soil-forming rock and underlying rock. In the layer from the surface to the parent rock, processes occur that determine the fertility of the soil and its value for agricultural use.
Soil coloring
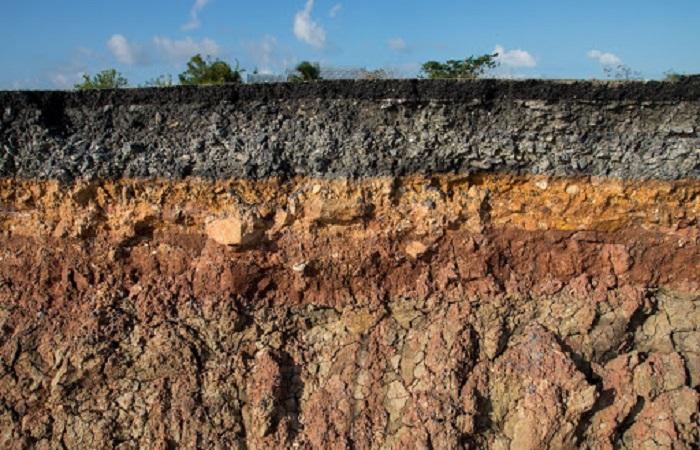
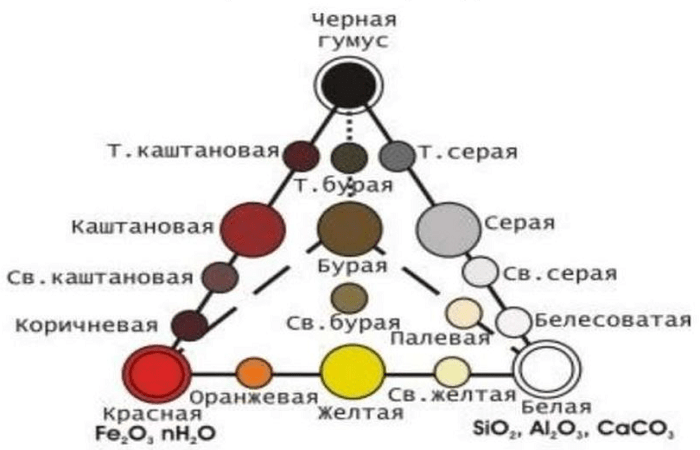
Based on this feature, it is possible to determine the profile horizons and their boundaries. Color is a general term that defines the heterogeneity of the color characteristics of horizons. The color depends on the predominant substances that appeared during the process of soil formation. In accordance with this external characteristic, some types of soils were named: chernozems, red soils, gray soils, and so on.
The top layer is colored with humic substances; they are dark in color; the more of them, the darker the soil. Brown and red tones give it a high content of iron and manganese. The whitish color of the soil in which podzolization processes took place, that is, the processes of leaching of minerals, is the same color of brackish and carbonate soils, due to the content of salts, chalk, gypsum, kaolin, and silica in them. A bluish color appears in waterlogged soils that contain iron oxide minerals. The lower soil horizons are colored in color, which is determined by the composition of the parent rock and the degree of weathering.
The intensity of color depends on soil moisture and the degree of illumination; it is determined using a sample of completely dry soil in diffuse daylight.
The shades of soil color clearly display the features of the processes that form the soil. The following 3 groups of substances are considered to have the most influence on color: humus, lime carbonate, silicic acid and kaolin, as well as iron compounds. The color can be uniform and uneven, that is, spotted, striped, speckled.
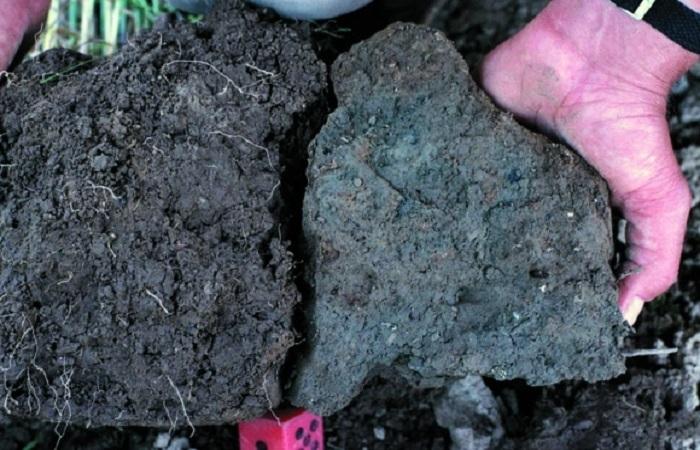
Soil structure
Soils consist of individual structural elements, so-called soil aggregates, which are glued together by humus or silt particles. The size and shape of aggregates, their strength depend on the processes that occur in the soil.
The moisture and breathability of the soil and its resistance to erosion processes depend on this characteristic. The structure of the soil is affected by soil microorganisms, plant roots, periodic drying and waterlogging, heating and cooling, freezing and thawing.
The soil particles are glued together by humus, silt components, iron and aluminum hydroxides. Sandy soils, where there are few clay particles and humus, have a weak structure.In the structuring process, plant roots play an important role, which creates a lumpy structure.
According to their shape, structural particles are divided into 3 types: cuboid (approximately equal in size in 3 directions, which gives them the appearance of polyhedra), prism-shaped (when elongation in height dominates, due to which the structural particles acquire an elongated shape) and plate-shaped (particles acquire flattened shape). Different types of soils and horizons are characterized by a special type of structure, for example, granular, lumpy, lamellar, blocky and others.
Changes in soil formation conditions are also reflected in the structure. The strength of the structure of the fertile layer is important for agriculture. Of particular importance is the characteristic of water resistance, that is, the ability to form individual particles that are not eroded by water. Soils with a water-resistant structure also have mechanical properties and moisture-air conditions favorable for the growth of agricultural plants. The less structured the soils, the worse their characteristics; they quickly become impermeable to air and moisture, float, and when they dry out, compact and crack.
The weight ratio of particles of different sizes determines the mechanical composition. Size is determined by the specific diameter of the particles, which determines their ability to retain moisture. The stony fraction with a particle diameter greater than 1 mm cannot retain moisture and is therefore considered inactive in this regard. Sand holds water poorly; dust particles of clay retain moisture best.
Features of the mechanical composition affect the physical properties of the soil: moisture capacity, water permeability, thermal and air conditions, and others. Sandy soils do not have a cohesive structure; they crumble even when wet. Dry sandy loam soils are loose and also have no structure; wet soils easily roll into a ball, but they cannot be pulled out into a “cord”.
Loams are dry, moist, plastic and roll freely into a “cord”. The thinner it is, the more clayey the soil. Wet clays are rolled into a thin “cord” that can be rolled into a ring without cracks. The general name of the soil is given by analyzing the top layer 0-25 cm high.
Neoplasms and inclusions
This is the name given to isolated substances that differ in composition and structure, and which are locally included in different types of soil. The formation of new formations occurs under certain conditions, therefore, by their appearance, one can determine the type of soil-forming processes that occurred before or are ongoing now. They are an important feature in determining soil classification.
New growths vary in shape, color, mineralogical and chemical composition. They look like spots, veins, plaque, located near the roots of plants or animal passages; they can be nodules or glandular layers. Biological new formations are molehills, earthworm tunnels and their waste products.
Inclusions are foreign bodies whose appearance in the soil was not caused by the processes that formed it. These can be fragments of rock that are not identical to the parent rock, crushed stone, large stones, bones and shells of extinct animals, objects left over from human activity.Based on inclusions, one can understand the origin of the parent rock and determine the age of the soil.
Morphological characteristics of soils help to correctly characterize them, establish their origin, the processes that led to their formation, age and value for economic use. In agricultural terms, morphological features help determine how to improve and refine the soil so that it is more suitable for growing plants and becomes more fertile.