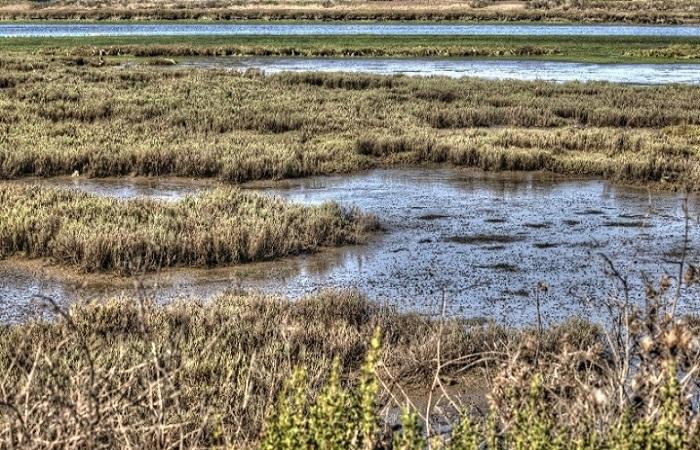
Swamp soil types are most often found in the tundra and taiga-forest zones. They are also common in the forest-steppe and other areas. The formation of this type of soil is caused by waterlogging of land or peaty water bodies. This process is accompanied by peat formation and gleying of the mineral part of the soil profile. The development of such soil is possible only in conditions of increased moisture.
Formation conditions
Swampy soil is a soil that contains a lot of undecomposed or semi-decomposed plant debris.They accumulate under the influence of prolonged increased moisture.
The formation of bog soil types is caused by the influence of a special soil formation process, which is accompanied by increased moisture. This is due to the influence of atmospheric and stagnant groundwater.
The components of the formation process of such types of soil include peat formation and gleying. The first concept implies the accumulation of plant residues and humus, which leads to oxygen deficiency and the development of anaerobic processes.
Gleyization is understood as a biochemical process that is associated with the reduction of iron and manganese. It necessarily involves various fungi and bacteria. At the same time, the soil is characterized by a dark shade.
Basic soil-forming processes
The soil-forming process is accompanied by the accumulation of peat in the soil structure and gleying of mineral compounds. This process develops as a result of constant waterlogging, which is caused by the influence of ground and surface water flows.
When flooding occurs, which is associated with relief degradation and the influence of precipitation, water stagnates. However, this type of soil can also occur in places with flat terrain. This is due to the presence of a waterproof soil layer. If groundwater lies high, the upper layers are oversaturated with moisture, and plants develop well on them.
This organic matter gradually decomposes in swamps and represents a base of fertile soil fragments. After some time, a thick layer of peat forms.
In this case, the main impact factor is considered to be the natural area itself, which is characterized by certain conditions and climate. It itself is conducive to waterlogging and peat formation.
In fact, swamp soil is a peat bog, which alternates with gleying zones. The composition, structure and appearance of the soil depend on the type of waterlogging.
Profile structure and classification
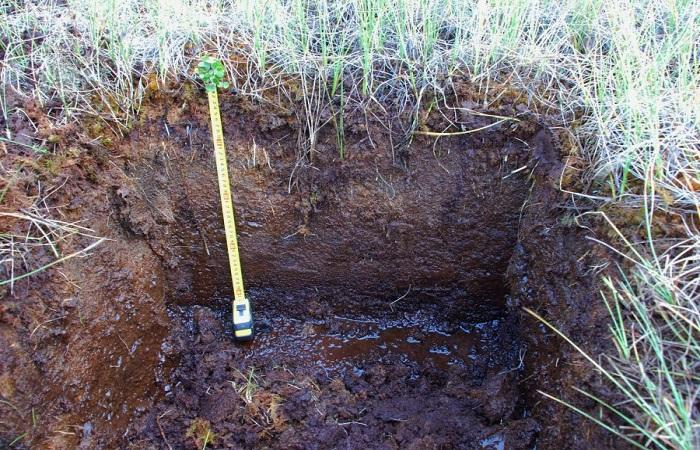
The bog soil profile has several genetic horizons that differ in their characteristics and humus content:
- a thick layer of forest litter or moss, which is the surface layer of moss vegetation, untouched by decomposition;
- peat horizon, which is divided into subhorizons;
- gley horizon.
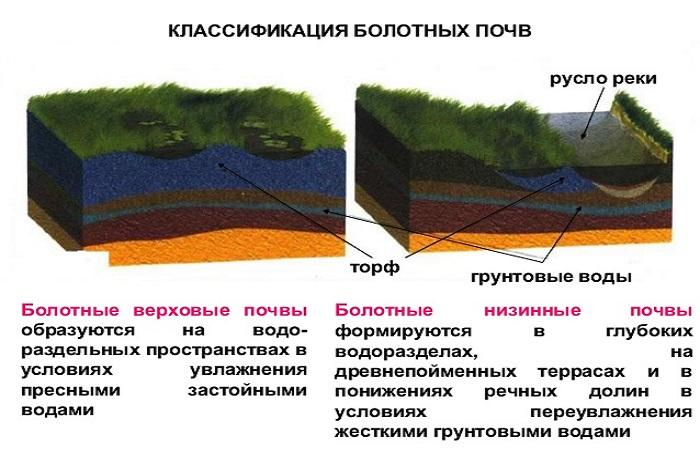
Depending on the process of formation and natural zones, wetlands are divided into 2 groups - upland and lowland. The first category includes the following varieties:
- ordinary - they are also called organogenic;
- transitional - include fragments of moss and grass;
- located on sandy layers - they are called humus-iron.
Peat-bog soils are found in the taiga regions of Siberia, Kamchatka, and Sakhalin. They are characterized by a high degree of acidification, low ash content, and significant moisture capacity.
In addition, marshy soils are divided into the following groups:
- According to the level of development of peat formation processes. The formation and decomposition of peat and gleying provoke the formation of fertile soil types with varying contents of humus and humus. They also differ in the degree of acidification. According to this criterion, soils are divided into highland, lowland and peat-gley.
- From an economic point of view. This criterion involves consideration of soil properties depending on the type of swamp.High soil types in which the substrate is not completely decomposed are considered not very suitable. They are acidic and contain few nutrients.
Lowland swamps are more suitable for development and adaptation to agricultural needs. They are distinguished by neutral acidity parameters and high-quality peat decomposition.
Composition and properties
The composition, characteristics and fertility of marshy soils are influenced by the structure of the peat horizon. The composition of gley horizons is varied. It is largely determined by the granulometric, mineralogical and chemical composition of the rocks on which peat types of soil are formed.
Common features include unfavorable physical characteristics, such as disaggregation and compaction, and the presence of ferrous varieties of iron. Agronomic and genetic assessment of peat soil types is carried out taking into account the thickness of the peat layer. It is also worth considering the following peat parameters:
- level of decomposition;
- botanical composition;
- structure of organic matter;
- nitrogen content;
- ash content and composition of such components;
- physical characteristics.
How to improve?
To improve the composition and structure of bog soil types, it is recommended to use a whole range of actions:
- First, drain the soil. To drain water, reservoirs are erected and sluices are constructed. This contributes to increased mineralization of organic elements, increased soil aeration, and oxidation of ferrous components.
- Systematically add nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus to the soil. It is especially important to do this in the first years after drainage.
- Add copper regularly. Swamp soils contain little of this component.
- For raised and transitional soils, carry out liming.This procedure helps reduce acidity parameters.
- Remove weeds, as their root system causes soil compaction.
Usage
Lowland peat can be used as an organic fertilizer. This fertilizer is perfect for turf and podzolic soil types. The moss variety of this product is used for pet bedding because it is excellent at absorbing gases and manure, reducing nitrogen loss. Peat horizons are used for composting. This helps to obtain high-quality fertilizers.
Vegetation
Heather shrubs and sphagnum mosses usually grow in raised bogs. There are also dwarf varieties of birch and pine. Lowland bogs can be grassy, hypnotic or wooded. In the first case, they contain sedges, cotton grass, and reeds. The hypnotic types are characterized by a predominance of mosses, while the forest types have a stand of black alder.
Swamp soils differ in structure and composition. This must be taken into account when using soils for agricultural purposes.