Many farmers who raise animals are faced with pigpox. This is a serious viral disease that leads to intoxication of the body and the appearance of a rash on the surface of the skin. Before proceeding with the treatment and prevention of such a disease, it is necessary to become more familiar with its features and description.
Pathogen and causes of the disease
Smallpox is a dangerous viral disease that is difficult to treat. Most often, the disease is caused by different strains of smallpox, which can only affect certain types of animals.If we talk about swine pox, its spread is carried out by three types of pathogens:
- cow virus;
- swine virus;
- vaccinia.
There are several ways to become infected with the virus. However, most often piglets get smallpox through the intestines, mucous membranes, skin surface and respiratory tract. The virus enters the body of a healthy animal after direct contact with an infected individual. You can also become infected with carriers of the virus who are in the incubation period. It is worth noting that not only animals carry vaccinia, but also people.
The virus is resistant to many factors. It can only be destroyed when exposed to acids or ultraviolet light. The causative agents of the disease can remain on the skin of animals, in food and on equipment for six months. The virus, which was previously on the surface of the skin with pockmarks, has even greater vitality and does not die for more than a year.
Most often, smallpox appears in pigs in autumn and winter. This is facilitated by a lack of vitamins in the body, poor nutrition and a weakened immune system. Other reasons that may cause the disease include:
- keeping in unsuitable conditions;
- failure to comply with quarantine requirements;
- refusal to disinfect a barn in which cases of virus infection had previously been recorded;
- the appearance on the farm of equipment with pathogens;
- a large number of rodents in the pigsty.
Symptoms of Pig Pox
To determine the presence of a disease in time, you need to familiarize yourself with its symptoms. Immediately after appearing in the body, the virus actively spreads over the surface of the skin and also penetrates the mucous membranes and the digestive system. The incubation period of the disease is several weeks. The initial stage of smallpox has the following symptoms:
- increase in body temperature up to forty degrees;
- loss of appetite and problems with digestion of food;
- inflammation inside the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity and eyes.
Often the above symptoms mislead people, as they begin to think that they have a cold. However, after 2-3 days, smallpox begins to appear much more clearly. The following symptoms appear:
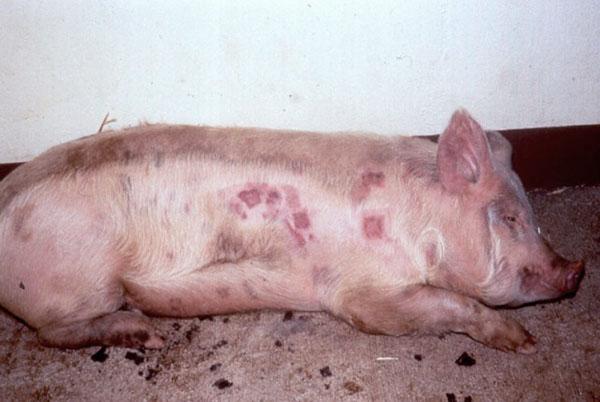
- formation of roseola on the surface of the skin, which have a pinkish tint;
- the formation of papules in the central part of previously appeared roseolas;
- release of exudate from wounds;
- transformation of wounds into vesicles;
- suppuration of wounds;
- the appearance of pus and the formation of a dense crust on the surface.
Some individuals who contract smallpox develop diarrhea, severe itching of the skin and an unsteady gait.
Diagnosis of the disease
It is difficult to determine the diagnosis on your own, and therefore, to identify smallpox you will need the help of specialists. It is necessary to conduct special laboratory tests to check the animal for the presence of smallpox.
During diagnosis, virological tests will be needed. To conduct them, you will have to take sections of the smallpox rash and place them in securely sealed tubes. By conducting such studies, they try to detect the accumulation of smallpox virions. A bioassay is also carried out on piglets that are susceptible to the disease. If the test material contains a virus, it means that pockmarks should appear a week after applying the suspension.
To identify the type of virus, electron microscopy of the material is performed. It is collected from pigs that are infected with the virus and need treatment. Microscopy may reveal smallpox virions.Sometimes protein-type paracrystals are found along with them.
Methods for treating swine pox at home
Piglet pox is considered a serious disease that often leads to the death of animals. This disease is relatively young, and therefore today there is no effective treatment. Therefore, it is recommended to closely monitor the health of your pigs and examine them for symptoms.
If there is a suspicion of smallpox infection, the sick individual should be immediately isolated from other animals. The barn in which the sick piglets were kept must be disinfected.
Although there is no cure, the affected areas of the skin still need to be treated to promote healing. The following means are used:
- two percent sodium solution;
- formaldehyde;
- three percent sulfur-carbon mixture.
To prevent complications from occurring in sick animals, you must do the following:
- Introduce antibiotics to alleviate the piglet's condition. The most commonly used is streptomycin.
- Treat crusts with ointment or neutral fat.
- Apply chloramine solution and iodine to surfaces with ulcers.
- When pus is released, treat wounds with chamomile decoction with potassium permanganate.
Preventive actions
It is necessary to regularly carry out preventive measures to prevent the spread of the disease. To protect pigs from contracting smallpox, farmers need to do the following:
- do not use feed or equipment from disadvantaged farms;
- pigs arriving at the farm must be kept separately from other animals for a month;
- regularly undergo veterinary examinations;
- monitor the condition of the sheds in which pigs are kept;
- organize a ventilation system inside the pigsty for normal air circulation;
- add more foods to your diet that contain many vitamins and minerals.
Conclusion
Smallpox is a dangerous disease that can infect piglets and other farmed animals. Every farmer should familiarize himself with the detailed description and characteristics of such a disease. This will help in the future to diagnose smallpox in time and prevent its occurrence in other animals.