Apple trees are traditionally very popular in our country as a garden crop. But these plants grow quite large, and it is rarely possible to plant more than two or three in a limited area. Despite the periodic criticism of columnar varieties, the columnar apple tree is increasingly appearing on plots, and the variety has carved out its niche. However, not everyone knows exactly how to care for such trees. The article will discuss the main aspects.
- Description and features of a columnar apple tree
- Carrying out pre-landing activities
- Conditions
- Landing dates
- Seedling storage
- Planting plan
- Choosing a landing site
- Pit preparation
- Planting seedlings
- Root treatment
- Placement in the landing pit
- Planting and watering
- Rules of care
- Watering
- Fertilizing fruit
- Nuances of pruning
- Grassing of columnar plants
- Protection from diseases and pests
- Protection of columnar apple trees in winter
- Harvest
Description and features of a columnar apple tree
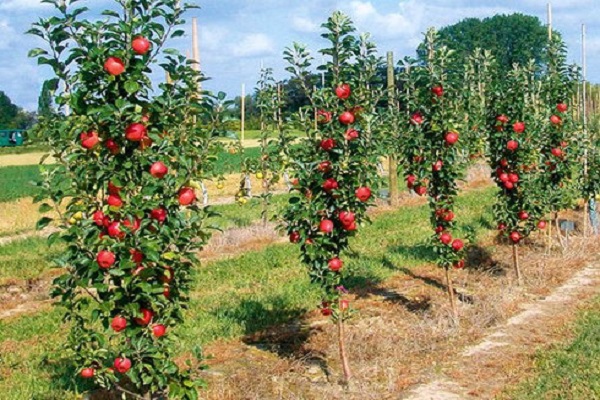
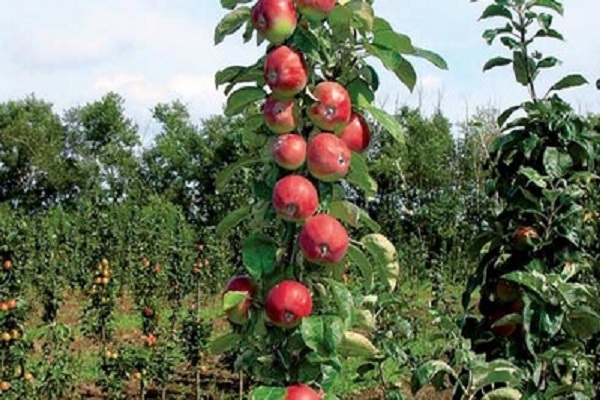
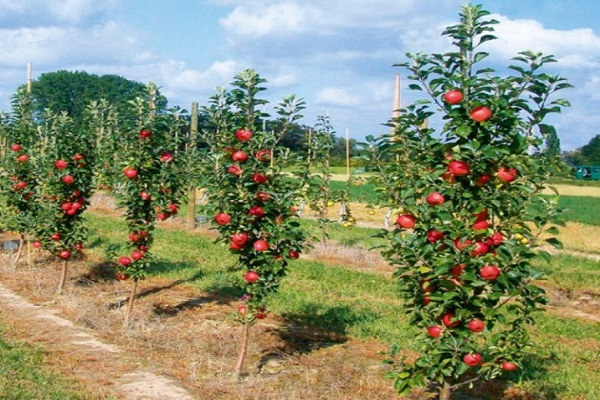
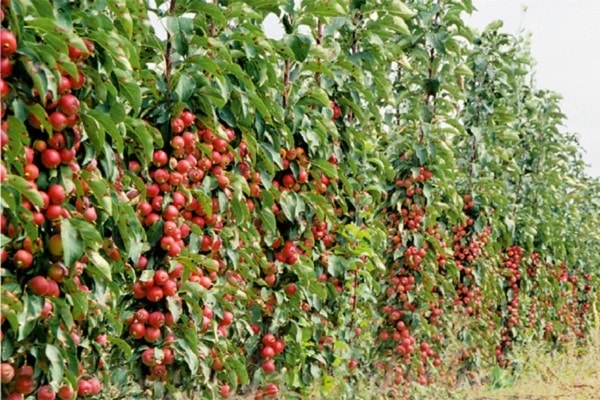
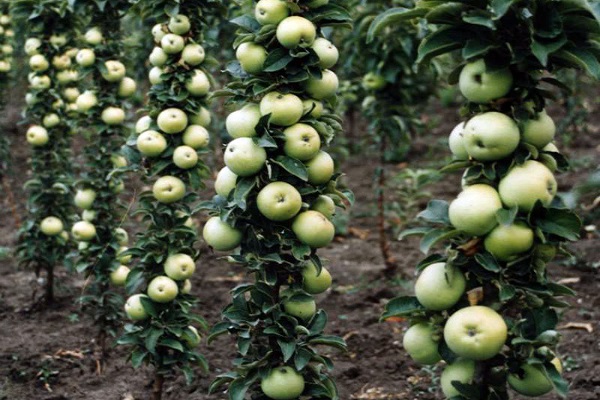
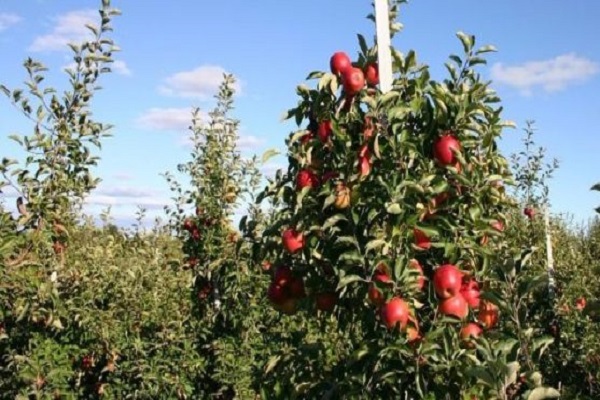
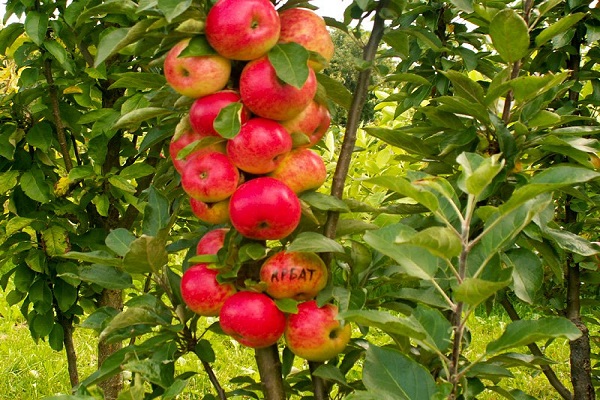
Many summer residents have fallen in love with columnar varieties, which allow, with small trees, to obtain good harvests. If you follow the rules of care and pruning and fertilizing technologies, you can get tasty and beautiful fruits in large quantities, which are suitable both for direct consumption and for canning for the winter.
The special trunk structure of representatives of columnar varieties is associated with a genetic mutation. Due to this, the side branches grow in a certain way, and the central trunk becomes much thicker. The average height of such trees is three meters. Although different varieties of different sizes are cultivated.
The stems of the columnar apple tree are thicker than those of other varieties, while the distance between the buds is smaller. Branching depends on height - the taller the tree, the more branches it has. Moreover, the difference between the smallest representatives and large plants can be up to three to four times.
Upon reaching four years of age, the side shoots stop growing. It can be activated only if the growth point at the apex is injured.
The first full harvest can be harvested within two years after planting. The trees reach their peak yield within five years, then the level remains consistently high, subject to the required agricultural technologies. The type of root system of columnar plants is fibrous. Its development also affects fruiting.
The active life span of a columnar apple tree, when it bears fruit well, is from fifteen to twenty years. After this, the number of fertile buds decreases sharply. The only exceptions are tall varieties. Moreover, in each individual case, the lifespan of a tree may vary. This is due to the fact that to increase the duration of the fruiting period, you can apply fertilizing, as well as pruning for rejuvenation.
The described columnar varieties are good for placing in small garden plots. There are two types of columnar apple trees:
- containing a mutation in the genotype;
- apple trees to which varieties are grafted dwarf apple trees columnar type.
Carrying out pre-landing activities
Due to the characteristics of the rhizome, columnar tree varieties require soil rich in nutrients, well ventilated and moist. If the soil contains a high clay content, additional drainage work will be required. Groundwater should lie as deep as possible. Also, the area should be well lit and drafts should be avoided. Only compliance with all growing conditions will allow you to obtain maximum yields and ensure active growth.
Conditions
When purchasing columnar seedlings, you need to consider the conditions in which they will grow. Therefore, when purchasing, you need to consult with sellers to select the varieties that are most suitable for the existing conditions.
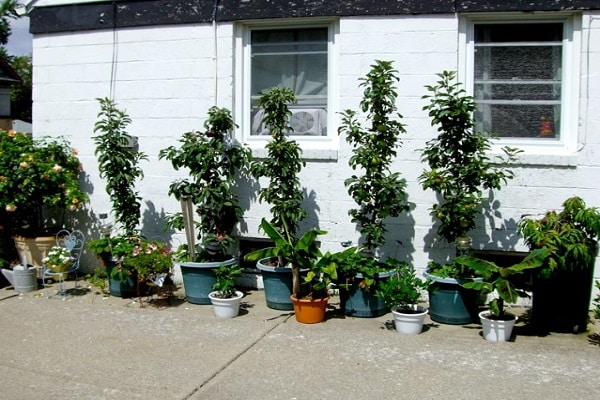
To grow healthy, fruit-bearing columnar trees, you will need a well-lit, draft-free area with well-moistened soil. Do not forget that columnar varieties are available for cultivation in greenhouse conditions.
Landing dates
For planting, you need to choose the right season so that the seedlings take root better and suffer less pain.In the Moscow region this is mid-spring and autumn.
Experienced gardeners advise planting in early spring weather:
- before active sap flow begins;
- when the soil has already warmed up sufficiently.
In the autumn, planting should be done:
- after the leaves have fallen;
- in the period before the first frost, so that the plant has time to get used to it.
Planting apple trees in summer is not recommended.
Seedling storage
The root system should not dry out. Before planting, it is better to temporarily dig the tree into loose soil and water it. If the rhizome is closed, moderate watering will be required every two days. Moistened wood shavings are also suitable for storage.
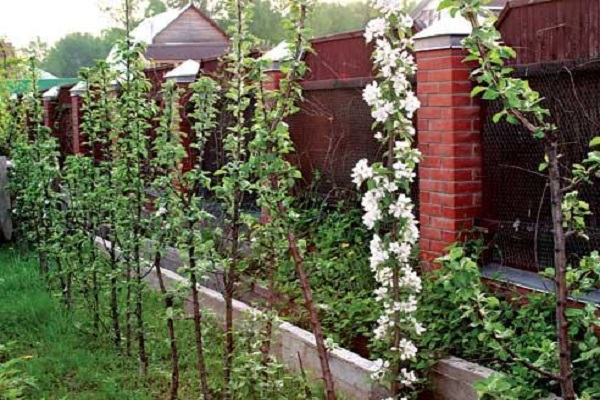
Planting plan
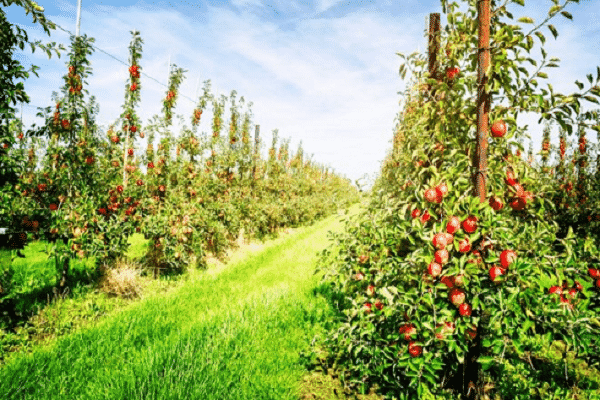
Before planting, you should consult the advice of professionals. If planting involves a large number of trees, then it is better to draw up a diagram that takes into account the necessary distances between individual seedlings. They depend on the specific variety and further growth.
Columnar plants are planted in such a way that in adulthood they do not interfere with each other’s growth.
Choosing a landing site
Experts recommend protecting the area for planting columnar apple trees from gusts of wind in advance. In this case, it is necessary to ensure sufficient illumination and the absence of shadow areas. Fences and fences are suitable as shelter from the wind. You also need to take into account that even though the plants are small, they will still need more space as they grow.
Pit preparation
The seats are prepared as follows:
- Grooves for group plantings can be up to half a meter deep.
- For spot planting, holes of the same depth are dug.
- It is recommended to dig up in advance so that they can stand for at least two to three weeks.
- Dimensions are determined based on the rhizome.The greatest depth can be up to ninety centimeters, the radius can be up to half a meter.
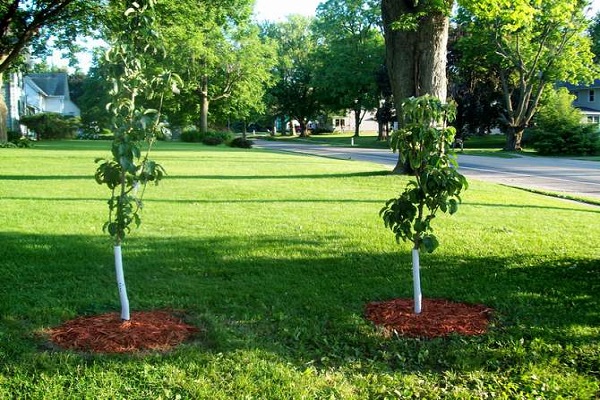
Planting seedlings
It is better to plant specimens no older than one year. Despite their small size, compared to older seedlings, they will be better accepted, which will have a beneficial effect on further cultivation. Planting is best done in the spring, before sap flows and buds begin to bloom.
The drainage substrate can be made from fine crushed stone and a sand mixture up to a quarter of a meter thick. Drainage is made of coarse crushed stone and sand in a layer of at least 20-25 centimeters. The extracted soil is mixed with compost components, and fertilizers are added. Phosphates and potassium salts are suitable.
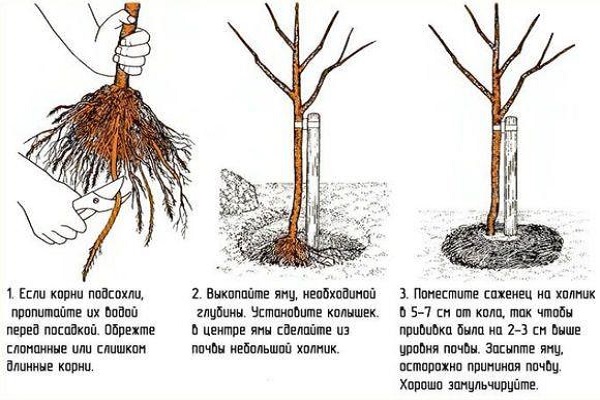
Root treatment
Before planting, the roots are immersed in water for some time. For better survival, growth activators are used. To do this, the rhizome is placed in the solution for half a day. Before planting, the rhizome is treated with a clay mixture.
Placement in the landing pit
The plant is leveled perpendicular to the surface of the earth, the rhizome is straightened, and a support peg is installed. The roots are straightened so that there are no tangles or kinks. The hole is filled carefully so as not to damage the roots. Start from the edges and move towards the stem. The hole filled to the middle is tamped down a little.
We water with five liters of water taken from the home tap. After all the liquid has been absorbed, we check the location of the grafting scar. We place it three centimeters above ground level.
Next, the hole is completely buried and compacted without much pressure. A depression is left around the trunk for subsequent watering. Water and add mulch.
Planting and watering
Planting a seedling is not enough.After digging, the soil is compacted and watered. One hole takes up to twenty liters. Then mulching is carried out.
Rules of care
After planting is completed, the seedlings are fed, watered, and pruned.
In the spring, the branches are pruned and a compound is applied to prevent disease and pest damage. This is done before the sap begins to flow. Nitrogenous fertilizers are also added.
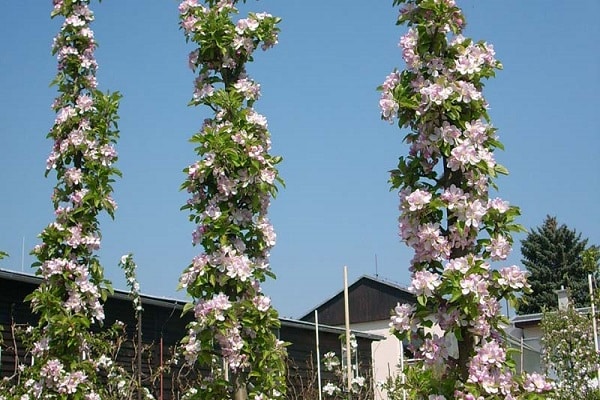
In the first year after planting, flowering buds are removed from the plants. In the second year of life, about ten buds are left. Over time, more and more flowering shoots are left.
Watering columnar apple trees regularly, as the soil dries out. Loosen the resulting crust. We loosen carefully and shallowly so as not to touch the roots. Sometimes we use tinning holes around the seedling. The use of such agricultural technology makes it possible to avoid loosening and, thereby, keep the roots intact.
Feed in early summer with inorganic fertilizers. The pollinated inflorescences that appear are partially removed so that the plant is not overloaded. When the small apples reach one and a half centimeters in size, only two fruits are left on each inflorescence. Subsequently, the smaller of the fruits is also removed.
In summer, it is easier to care for columnar apple trees, but prevention of pests and diseases is required. If symptoms of disease or traces of parasites are detected, urgent measures are taken. Trees are treated with special compounds. Also, for preventive purposes, they are sprayed with chemicals before and after flowering. The last treatment can be carried out no later than a month before harvest.
At the end of summer we apply fertilizing containing potassium salts. From them, young shoots form faster and will not freeze in winter.
Sometimes in late autumn, after harvesting, we feed and treat them against pests and diseases. We cut off excess shoots.
Watering
Regular irrigation makes the fruits juicier. Gardeners ensure that plants are sufficiently watered throughout the season. To effectively distribute moisture, trees are dug in and holes are formed to prevent water from spreading. One tree requires up to twenty liters. After watering, the surface is mulched. The frequency of watering depends on how regularly it rains, as well as the type of soil in which the seedling is planted. On average, plants are watered twice a month.
Fertilizing fruit
After the buds open, gardeners feed the apple trees. Fertilizers are applied in the spring, when sap flow begins. The procedure is repeated two more times, every half month.
Most often used:
- chicken manure;
- cow dung;
- urea solution;
- saltpeter;
- fertilizer complex.
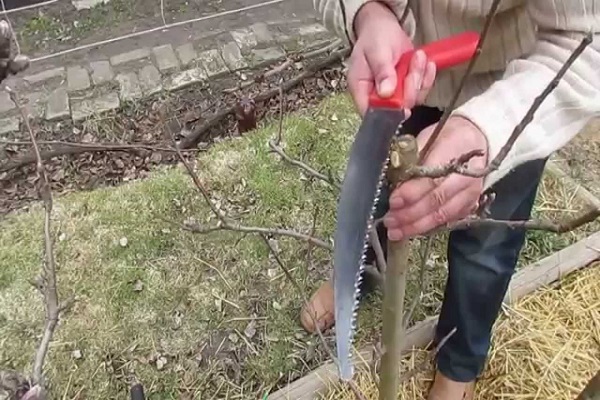
Nuances of pruning
There is an opinion that columnar varieties do not require pruning, since they do not produce distillations. But that's not true. Sometimes, under unfavorable development conditions, lateral shoots grow, which spoil the crown. Whether to cut them or not is up to everyone to decide for themselves.
The most favorable periods for pruning are spring, early summer and autumn. Pruning is carried out over several years.
Each year required:
- First year. We cut off all the shoots on the side, making the main stem shorter.
- Second year. We trim new shoots, leaving no more than thirty centimeters.
- Third year. The top is shortened to twenty-five centimeters, leaving forty centimeters on the side.
- Fourth year. We remove excess and bad shoots from last year.
- Fifth year. The trunk is trimmed so that the total length of the tree is no more than three meters.
- Subsequently, unnecessary shoots are removed.
Grassing of columnar plants
The rhizome of columnar apple trees is designed in such a way that it is very afraid of drying out the soil. Therefore, constant hydration is required. To do this, add mulch or peat crumbs. But the easiest way is to tin the surface around the trunk.
Sowing with lawn grasses or other types of low-growing vegetation creates protection from the sun, the roots are sufficiently moistened. At the same time, the grass does not inhibit the growth of the tree. The grass cover is mowed periodically.
Protection from diseases and pests
There are many diseases and parasites that can harm columnar apple trees. These are insects, fungi, mold, microbes and viruses. Periodically, the crown and bark of plants are treated with special compounds to combat pests. Otherwise, it will be difficult to get a good harvest.
Protection of columnar apple trees in winter
Columnar apple trees need protection during the frosty period. We remove the mulch from the straw to prevent rodents. The trunk is covered, snow is best. It is important to prevent the trunk and buds from freezing, which occurs when they get wet and freeze.
We wrap the growing point especially carefully to prevent it from freezing. We prepare a pole to which the tree is tied so that it does not break from the wind.
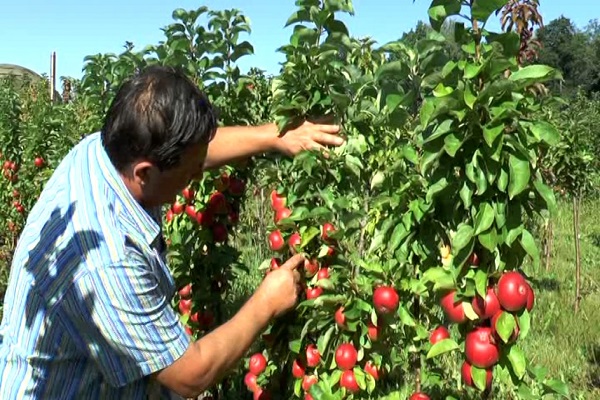
Harvest
Since columnar apple trees are not tall, special tools and equipment are not required for harvesting ripe fruits. Fruit picking begins as it ripens. It depends on the variety. Depending on the purpose of use, the fruits are either stored in the basement or prepared for further processing.