The proximity of groundwater is a factor that can destroy a tree or expose it to the risk of constant fungal diseases. The presence of an aquifer located close to the surface of the soil is not a reason to abandon your own garden; it is enough to know how to plant an apple tree correctly if groundwater is close.
- The influence of groundwater on apple trees
- What water level is considered high?
- Apple tree varieties for close groundwater
- Summer
- Autumn
- Winter
- Preparation
- Methods for planting trees if groundwater is close
- Pillow
- Planting apple trees on a hill (hill)
- Care
- Top dressing
- Trimming
- Watering
- Ways to protect apple trees from groundwater
- Specifics of planting for different soil types
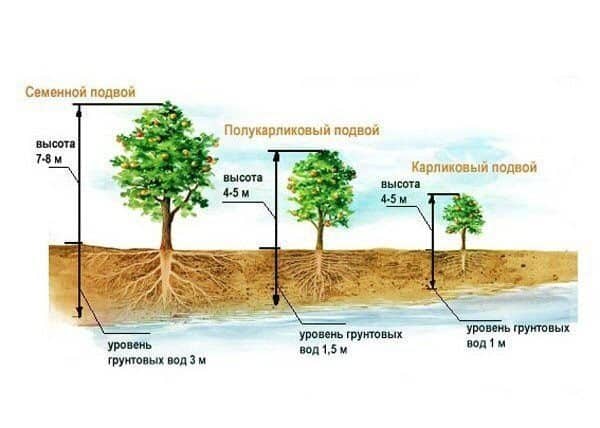
The influence of groundwater on apple trees
What threatens the immediate proximity of an apple tree to groundwater:
- Constant contact with water will lead to rotting of the rhizome, as a result of which the fruit tree will lose its pump, which produces the main portion of food. The tree will be sick for a long time, which will affect fruiting and the quality of the harvest, as a result it will soon die.
- The layer located in close proximity to the roots will be replenished with melt water when the snow melts. During the intensive process of snow melting, a tree can be squeezed out of the ground, which will deprive it of some of the new roots and natural support of the soil.
- Excess moisture received at the stage of fruit ripening will affect the ratio of acids and fruit sugars in the fruit.
- The humid environment near the tree trunk is a favorable microclimate for the proliferation of mosses and lichens, in which pathogenic mycelium feels comfortable.
- Minerals coming in large quantities from an underground source accumulate in the roots of the tree, which will also lead to disease and reduced yield.
In any case, constant contact of moisture with the roots of the tree is harmful. The same attention should be paid to selecting or preparing a site for planting as when building a house.
Attention! Exceeding the permissible norm of sulfates and chlorides in water dictates special planting conditions; such groundwater should be located at a depth of no higher than 3 m from the surface.
What water level is considered high?
When examining the soil before laying the foundation, most amateur gardeners learn about the close occurrence of groundwater and the presence of floating waters on the site, which cause much more damage to the garden than a stable aquifer.
If such studies have not been carried out, then the depth of the water can be determined by the depth of wells installed in the area or based on the depth of the well for home plumbing.
If the documents say “artesian well”, then there is no threat to the garden; the water is at a depth of at least 10 m.
A well or a well on a site, the depth of which is no more than 2 meters, makes one wary for several reasons:
- In temperate climates, this is above the freezing point of the soil in winter.
- The roots of tall fruit trees can go 4-6 meters deep; direct, constant contact with water is inevitable.
- When snow melts, lateral pressure is possible; the more intense the spring natural processes, the greater the threat that the tree will be forced out of loose soil or broken in dense soils.
It is difficult to significantly increase the level of the fertile layer by bringing in soil, sand and clay from a quarry, and this measure is temporary - sand and peat will be washed away by spring waters, which will only delay the contact of the rhizome with water. The only way out is to choose a variety of apple trees with roots that do not reach the aquifer.
Attention! The aquifer may be uneven; its approach to the surface of the earth can be determined by the swarming of midges over a certain area of the ground. Trees cannot be planted in this place!
Apple tree varieties for close groundwater
When choosing a variety for a site located in close proximity to groundwater, it is preferable to choose columnar plants with spreading, horizontally growing roots. Dwarf or semi-dwarf rootstocks are what is needed for low areas near natural reservoirs, shallow wells overlooking the surface of springs.Almost no variety on a seed rootstock is suitable for planting in such an area.
Summer
President, Ostankino, Malyukha, Medok are the best early ripening varieties for growing in a continental climate with a high level of aquifer.
Autumn
The garden plot should have apple trees of different ripening periods; if necessary, plant a garden with autumn varieties of apple trees, the roots of which will not go many meters deep into the ground, you should consider the following varieties:
- Vasyugan;
- Dialogue;
- Iksha;
- Chervonets;
- Amber necklace.
Iksha is distinguished by its increased shelf life - up to 3 months, and Chervonets amazes with the gigantism of its fruit - up to 350 g.
Winter
All that remains is to supplement the garden with winter varieties, choosing for the Moscow region from several possible options that have received the most positive reviews from gardeners:
- Currency;
- Victoria;
- Coral;
- Moscow necklace;
- Natalya.
All of them belong to late-ripening varieties and are stored for several months without losing their taste and presentation.
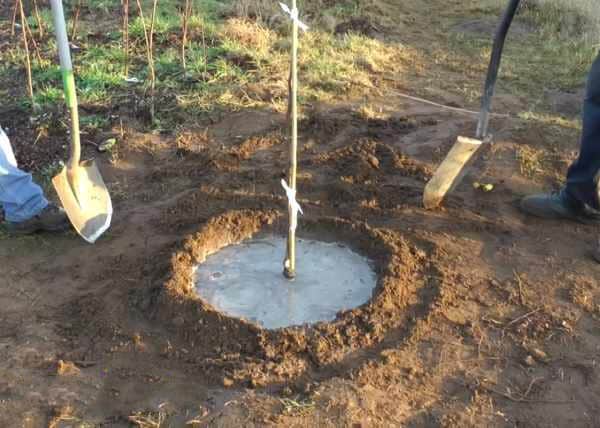
Preparation
In an area where there is a threat of a spring rise in groundwater, a drainage system is needed to drain water from tree trunks. The best option is if the drainage is carried out not into a ditch or a nearby ravine, but into a special reservoir - a septic tank, a container for rainwater located under the drain from the roof of the house, a deep concrete well - a sump, or an isolated cesspool.
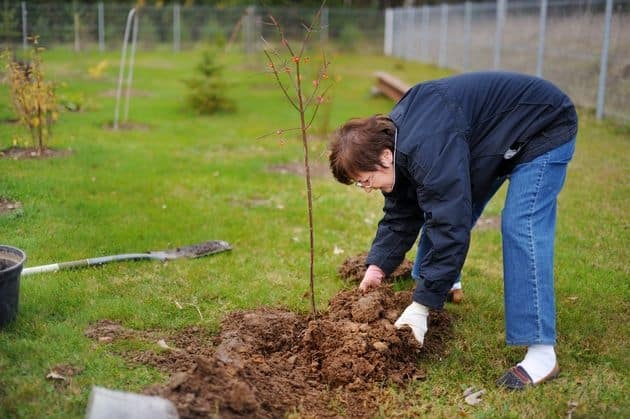
Methods for planting trees if groundwater is close
Raising the level of the area for planting an apple tree by leveling the neighboring hill is also an option if the soil is loamy or sandy loam.With less technical and physical costs, it is possible to raise only the site of future planting of apple trees by compacting the top layer with crushed stone, on top of which there will be a fertile layer of soil. This method is used when planting tall trees, but it imposes additional obligations on the owner to care for the plant - periodically replenishing the layer of soil next to it.
Finding fertile land in the Moscow region is an impossible task. Organic fertilizers are not suitable for all types of plants; it is easier to take the path of least resistance - choose a few low-growing apple trees for planting. Of course, with each of them the harvest will be several times less than with one tall one, but such plantings have a number of advantages:
- Different ripening periods and taste characteristics.
- The area for planting 18 columnar apple trees will be required the same as for placing one tall apple tree with a spreading crown.
- Columnar plants are distinguished by early fruiting; you do not have to wait 7 years for the first harvest.
Using the same principle as a mound for a tall apple tree, a planting hole is prepared, only significantly less materials are required for this. To enrich the soil with organic matter, you can always dig a compost pit behind an outbuilding. In this situation, you won’t have to transport weeds, fallen leaves, spoiled fruits off site, and you won’t have to think about the disposal of human waste. This is how our ancestors acted; there was no dirt or unsanitary conditions on the plots of the zealous owners.
Pillow
One of the most important preparatory stages before planting is creating a cushion on which to place the seedling. The first layer, the strongest and most unshakable, will be crushed stone, filling the recess by a third.Part of the soil selected from the planting hole is thoroughly mixed with 3/5-year-old humus. It is poured into the hole as a mound, which in turn is covered with a layer of ordinary soil. On top of it, after 2 weeks (during autumn rooting), you need to plant an apple tree.
Let the top layer of soil not be as dense as the roots of the apple tree will have to overcome over the next few years, but even such an obstacle will force them to reach for nutrients, overcoming the barrier.
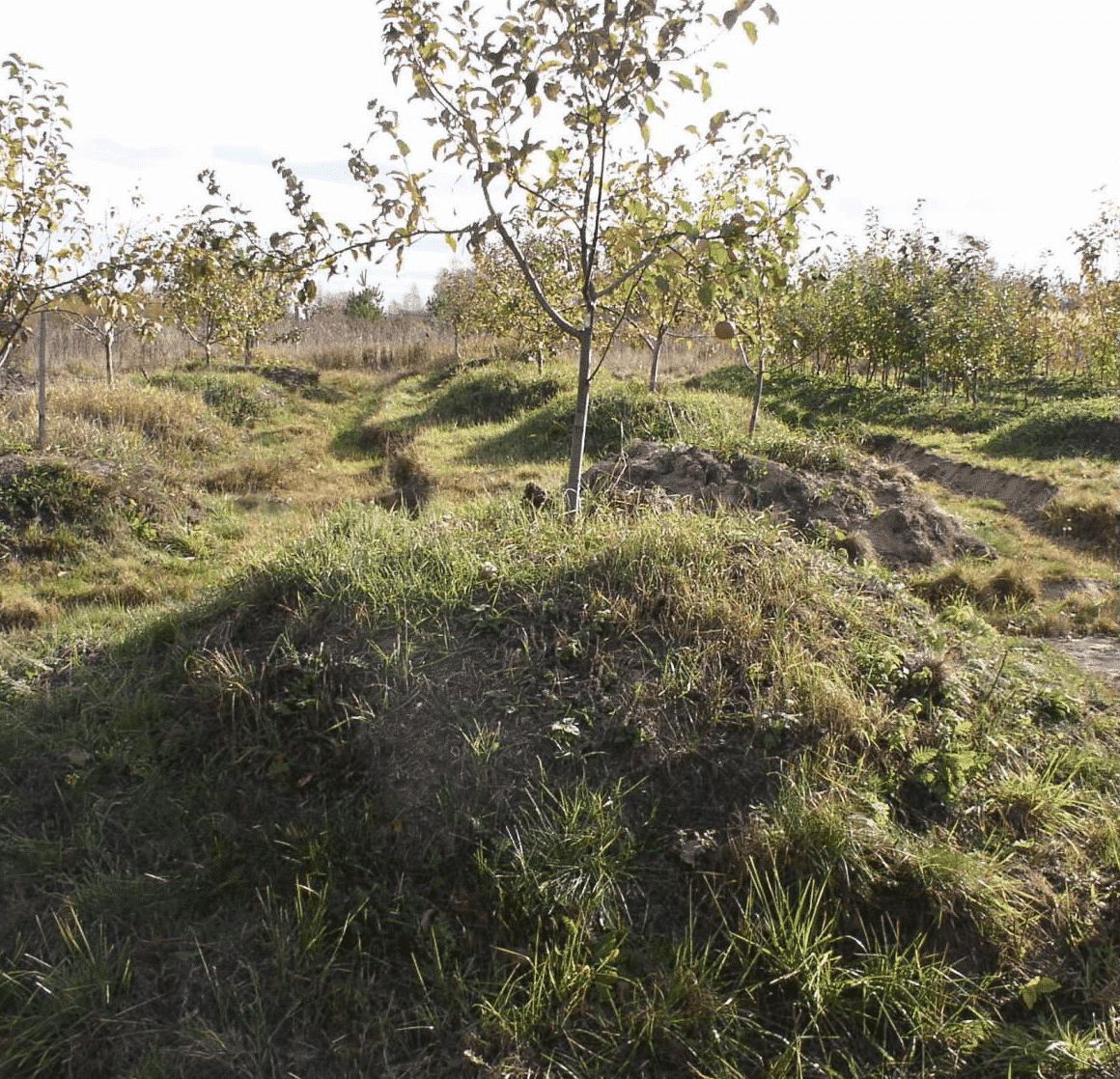
Planting apple trees on a hill (hill)
A small mound in an area where groundwater lies quite high is one way out if necessary plant an apple tree. Apple tree varieties for temperate climates are mostly adapted to the local climate with sharp temperature changes, cold Baltic winds, and constant storms.
Nevertheless, taking care of the straightness of the trunk, when planting a fruit tree on a mound or hillock, it is necessary to consider protecting the fragile apple tree on the leeward side, so the plant will develop organically, and not one-sidedly, as happens with constant exposure to cold air currents moving in one direction.
The preparation of the planting site follows the general rules - drainage, nutrient layer, simple layer. If there is no natural hill, it can be created artificially by adding layers of sand, ash, and peat.
Care
Each selected apple tree variety has its own care characteristics, but all have common stages:
- Loosening the soil in spring.
- Crown trimming.
- Adding nutrients.
- Spraying with insecticides.
- Watering and draining the soil.
- Mulching the soil and painting the trunk.
For all low-growing trees, a garter to a vertically installed support is necessary; this will set the vertical direction of the trunk, which fragile roots are not able to hold in this position on their own during the first 2-3 years after planting.
Top dressing
Feeding is carried out as planned and as needed. The application of foliar fertilizing is dictated by the need for microelements for the development of the plant and its gaining strength. Each apple tree requires nitrogen in the soil at the flowering stage and the formation of ovaries. This element makes the soil more loose and breathable.
For maximum quality and weight of fruits, substances such as phosphorus, potassium, and magnesium are required. They are introduced into the soil in dissolved form or scattered in doses near the plant trunk. These are necessary measures, because the apple tree needs microelements in small quantities; their excess will worsen the harvest in terms of taste and overall weight of the fruit, while individual apples will be gigantic in size.
Trimming
A mandatory preventive step is pruning branches and weak shoots on thickening crowns. The need for unscheduled pruning arises among gardeners after harsh winters, if the trees have suffered frostbite. Long shoots of tall trees are shortened in autumn to 60 cm of fresh growth. For dwarf apple trees, pruning is used to plan next year's harvest.
When an apple tree is damaged by fungal diseases or insect pests, unscheduled pruning is performed at any stage of plant development, no matter how painful such a surgical intervention is for it, it is necessary to save the tree as a whole.
Watering
Different varieties of apple trees react differently to drought and rain.For young trees, watering during prolonged dry periods is simply necessary. On sandy loam, watering is carried out once a week at the rate of 10 liters of water for each meter of trunk height. On sandstones, watering is more sparse, but frequent - once every 3-4 days.
Moisture intensively and evenly evaporates through the leaves of the apple tree on hot days. If there is an excess of it, the plant can get sunburned, so watering is done at sunset or sunrise.
Ways to protect apple trees from groundwater
At planting a dwarf apple tree it is not necessary to use open ground; it can be placed in a tall box made of boards filled with fertile soil mixed with compost. In areas with prolonged rains, this method of planting apple trees has its own reason - the outflow of excess moisture. The disadvantage of this planting is that the box freezes quickly, which is a threat to the root system. Slate or roofing felt should be used as a waterproofing and insulating material. These same roofing materials will help maintain soil moisture during drought.
It is much easier to create a favorable microclimate for a short-growing plant than for a tall one - this is another argument in favor of columnar varieties of apple trees.
Bituminous and pressed covering materials are not of interest and repel rodents, which again speaks in favor of growing fruit crops in high boxes with a wall width of 2 by 2 m on bulk soils.
Specifics of planting for different soil types
When preparing a planting site, it is extremely important to take into account the characteristics of the soil. If it is sour, then this will lead to the reproduction of midges near the trunk of the fruit tree. Accordingly, the larvae will be deposited in the bark of the apple tree, on the leaves, and fruits.Such a dinner will attract birds long before the apples ripen, and the harvest will be spoiled. The way out of this situation is to reduce the acidity of the soil using special chemical compounds or stove ash.
Dense soils for fruit trees are a drawback that does not allow the root system to receive sufficient water and air. Before planting, such soil is mixed with a nutrient mixture and sand to fill the planting hole, which makes the soil looser. From time to time you will have to add sand under the apple tree, on the soil above the root system; the sand, along with moisture, will go into the soil, loosening it naturally. Sandy soils, on the contrary, will have to be compacted with limestone and clay before planting an apple tree.