It is advisable to prevent diseases of domestic pheasants using preventive measures or treat them in the initial stages. These captive birds have good immunity. Pheasants rarely get sick. Problems arise if birds are fed low-quality feed or kept in poor conditions. Pheasant diseases can be infectious (contagious) or non-contagious.
Infectious diseases of pheasants and methods of their treatment
Infections (bacteria and viruses) can reduce the number of pheasants in a short period of time. Birds can become infected from sick relatives, rodents, insects, or through food, water, soil, droppings, bedding, and equipment.As a preventive measure against infectious diseases, pheasants are vaccinated or fed with feed antibiotics immediately after birth.
Main diseases and their treatment:
- Smallpox. The mortality rate is 70 percent.
- Symptoms: conjunctivitis, pockmarks on the head and legs, refusal to eat, depressed state. As a preventative measure, livestock are immunized against smallpox in unfavorable regions.
- Treatment: the birds are given vitamin pharmaceutical preparations, pockmarks are lubricated with disinfectants. Sanitary services recommend disposing of sick individuals.
- Pseudoplague (Newcastle disease). A viral disease that leads to the death of birds.
- Symptoms: depression, nasal discharge, cough, diarrhea, nervous spasms, paralysis of the limbs.
- Therapy: vaccination of healthy pheasants; sick individuals are sent for disposal.
- Marek's disease. The causative agent of the disease is a virus from the herpesvirus genus.
- Signs: weakness, depression, refusal to eat, paralysis of the legs and wings, the color of the iris changes, and blindness develops.
- Treatment: patients are sent for disposal. As a preventive measure, it is recommended to immunize day-old chicks with a virus vaccine.
- Pasteurellosis. The disease is called "bird cholera".
- Signs: rhinitis, conjunctivitis, suffocation, refusal to eat, intestinal upset.
- Treatment: antibiotics are prescribed (Levomycetin). Vaccination is recommended as a preventive measure.
- Salmonellosis. A dangerous bacterial disease that leads to the death of birds.
- Symptoms: indigestion, abdominal enlargement, diarrhea, refusal to eat, lethargy.
- Treatment: antibiotics (Levomycetin, Furazolidone) and probiotics are prescribed. Vaccination is recommended as a preventive measure.
- Infectious laryngotracheitis. Deadly viral disease.
- Signs: cough, conjunctivitis, suffocation, depression, loss of appetite.
- Treatment: not carried out. To prevent the disease, birds are vaccinated with a virus vaccine.
- Colibacillosis. Bacterial intestinal disease.
- Symptoms: diarrhea, refusal to eat, rhinitis, lethargy.
- Treatment: oral antibiotics (Lexoflon) are prescribed. To prevent the development of the disease, pheasants are vaccinated.
Non-contagious diseases of pheasants
Birds can get sick due to poor feeding and non-compliance with the conditions of their keeping. Pheasants are often injured in fights and during mating games.
List of non-communicable diseases and their treatment:
- Dermatitis. Skin diseases occur due to wounds on the body.
- Signs: redness of the skin area, compaction, formation of pimples, wounds.
- Therapy: wounds are treated with an antiseptic, lubricated with synthomycin ointment, and sprinkled with streptocide.
- Frostbite. In severe frosts, the limbs of birds freeze, which they peck.
- Therapy: wound healing ointments (Levomekol), compresses, dressings.
- Fractures. Occurs due to injury or lack of calcium in the body.
- Therapy: applying a bandage to the wing, limb, torso (carried out in a veterinary clinic).
- Crop blockage. Blockage occurs due to overfeeding with raw grain or when birds swallow stones, pieces of tow, or wool.
- Therapy: the pheasant is given vegetable oil, water, and the crop is massaged. In severe cases, they go to a veterinary hospital (they perform an operation to open the goiter).
- Cloacite. Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cloaca occurs as a result of frequent constipation and lack of vitamins in the body.
- Symptoms: redness of the cloaca, diarrhea, depression, thirst.
- Therapy: antibacterial ointment “Levomekol” is prescribed to lubricate the cloaca, a few drops of castor or vegetable oil are dripped into the beak.
Invasive diseases
A number of pheasant diseases are caused by parasites. Birds can become infected through someone else's droppings, dirty bedding, contaminated food, or soil. As a preventive measure, they try to keep pheasants clean and avoid contact with sick individuals.
List of invasive diseases and their treatment:
- Scabies. The disease is caused by small mites that infect the skin and feed on blood.
- Symptoms: epidermal crusts appear in places where parasites accumulate, birds experience severe itching, peck at the affected area of skin, and tear with their claws until they bleed.
- Therapy: applying birch tar, Frontlay spray, boric vaseline to the affected areas.
- Mites in the respiratory system.
- Symptoms: cough, shortness of breath, suffocation, loss of appetite.
- Therapy: Milben Zerst spray (for spraying feathers) and Ivermek (for internal use) are prescribed.
- Lice and lice. Parasites that live on feathers and body.
- Signs: pheasants lose their feathers, become restless, and scratch their bodies with their claws until they bleed.
- Therapy: spraying with Milben Zerst, Frontline sprays.
- Helminths. Parasites settle in the intestines of pheasants and feed on partially digested food.
- Symptoms: digestive disorders, abdominal enlargement, diarrhea, loss of appetite, sudden weight loss.
- Treatment: depending on the type of parasites, Febtal, Phenothiazine, Avatek, Filixan, Levamisole or Piperazine are prescribed.
Metabolic disease
Metabolic disorders can occur due to poor feeding or when birds are kept indoors.To prevent the development of diseases, it is recommended to give vitamin and mineral supplements to pheasants.
List of diseases and their treatment:
- Hypovitaminosis (lack of vitamins A, D, E, group B). The disease occurs if there is little greenery, fresh vegetables (carrots), or spruce branches in the pheasants' food.
- Prevention: vitamin-enriched feeding, pharmacy vitamin and mineral supplements.
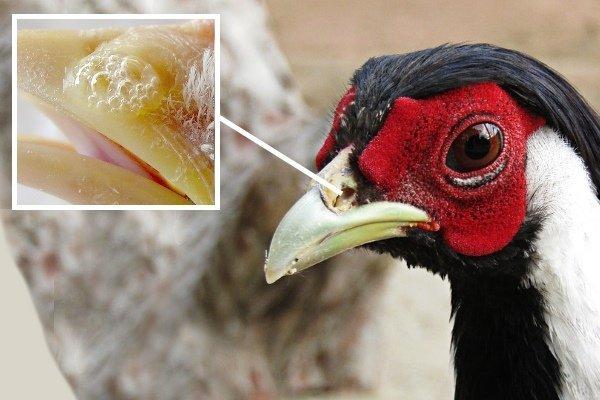
- Gout. Occurs when kidney function is impaired.
- Signs: yellowish nodules on the extremities, from which a cheese-like exudate flows when opened.
- Therapy: carried out in a veterinary hospital (opening nodules, washing wounds).
- Pecking (cannibalism). Occurs when there is a lack of nutrients in the feed (chalk, bone meal, herbs, fresh vegetables, salt, vitamins). The cause of cannibalism may be too dense planting of birds.