Fungal diseases are frequent guests of gardens and vegetable gardens. They spread quickly and often cannot be treated. For preventive purposes, we developed the Bravo fungicide, which prevents the development of fungal diseases. The use of this contact composition completely saves the harvest. Let's consider its properties and field of activity.
- Composition, purpose and release form of Bravo fungicide
- Operating principle
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Method of preparing the solution
- Processing method and time, consumption
- Wheat
- Barley
- Potato
- Tomatoes
- Grape
- Onion
- Protection period
- Precautionary measures
- Degree of toxicity
- Compatibility with other drugs
- Shelf life and storage conditions
- Analogs
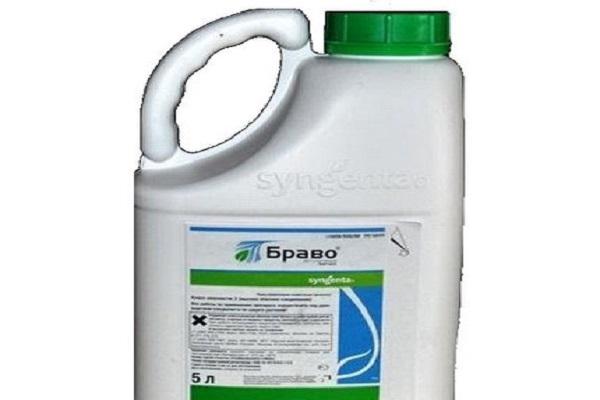
Composition, purpose and release form of Bravo fungicide
The main component of the Bravo fungicide is the low-toxic pesticide Chlorothalonil, which has the main functions of combating fungal spores. After spraying, the product lingers on the foliage for a long time and does not allow fungal cells to germinate, which prevents infection.
The pesticide content in the product is 0.5 kg per liter of product. The product is available in the form of a suspension. Plastic packaging contains 20, 100 ml or 1-10 liters. Used in the form of a concentrated solution.
The fungicide has a shelf life of 3 years at temperatures from minus 5° to plus 35°.
Operating principle
In addition to the pesticide chlorothalonil, Bravo contains additional substances that regulate the distribution of the fungicide over the surface of the plant and ensure its adhesion. A protective layer is created that prevents the fungus from reaching the culture tissues.
Attention! Fungicide Bravo performs a protective function, but does not cure.
Advantages and disadvantages
Positive qualities of Bravo:
- preservation of properties after watering or precipitation;
- instant action;
- lack of phytotoxicity;
- massive area of lesions;
- compatibility with other drugs for protection against fungus;
- quick payback;
- lack of addiction in pathogenic microbes;
- long lasting effect.
Disadvantages of the fungicide:
- long stay in open waters;
- danger to fish and insects;
- compliance with safety regulations is required;
- an ineffective drug for mass infection.
Method of preparing the solution
Before use, the suspension is diluted with water. To obtain the required concentration, use the instructions.
The tank is washed with cold running water to remove any remnants of previous preparations. Then fill halfway with water and add the drug according to the instructions.The composition is thoroughly mixed, the rest of the water is added and mixed again until the liquid has a homogeneous consistency. Having achieved success, a sprayer is put on the tank.
The finished composition is used within 24 hours. When spraying, the tank is constantly shaken to prevent sediment from forming.
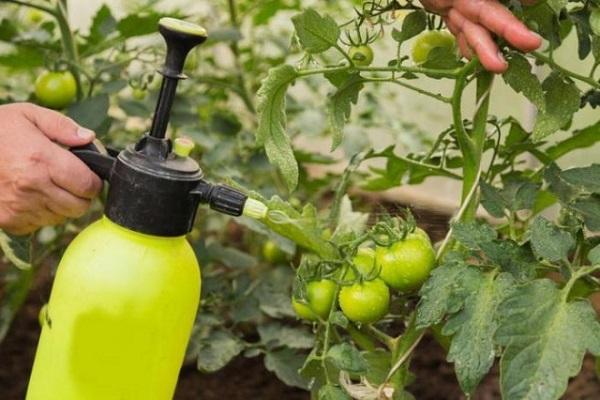
Processing method and time, consumption
The resulting working solution is consumed within 24 hours. Norms are not the same for different cultures. In order not to harm the crops, use the instructions for using the fungicide, depending on the crop.
The fungicide is intended for preventive measures, therefore the first spraying is carried out when the fungal disease is at the apogee of development, but infection of cultivated plants has not yet begun. A week later, the treatment is repeated when necessary. If the plant has become infected, choose a curative fungicide.
The best hours for spraying are early morning or evening, with a maximum wind speed of 4-5 meters per second.
Wheat
The culture is susceptible to diseases:
- powdery mildew;
- rust;
- septoria.
For safety reasons, spray twice a season, with an interval of one and a half months. 300 liters of solution containing 2.5 liters of product are consumed per 1 hectare.
Barley
To protect a cultivated plant from rust (stem, dwarf), spotting and powdery mildew, one treatment per season is recommended at the stage of mild or moderate disease. To prepare 300 liters of working solution, take 2.5 liters of fungicide per 1 hectare.
Potato
The culture is threatened by late blight and alternaria. Spray potatoes 3 times per season. The first procedure is carried out if there are signs of the disease. The treatment is repeated after a week and a half.For 1 hectare, 400 liters of solution containing 2.5 liters of fungicide are consumed.
Tomatoes
Tomatoes are afraid of the diseases late blight and brown spot. To prevent their development, use 3 liters of product per 500 liters of working fluid. According to the instructions, carry out 3 sprayings with a difference of 10 days. The first procedure is performed under conditions favorable for the formation of diseases (high humidity, low temperatures, dense plantings).
Grape
Grapes are often infected with the following diseases:
- oidium;
- mildew;
- anthracnose.
To avoid damage, bushes are treated with Bravo. Combine 10 liters of water and 25 g of product. Per 100 sq. m account for 4-5 liters of such a solution. Grapes are sprayed in early spring. But the last 3 weeks before harvesting are not treated with fungicide.
Onion
The fungus peronosporosis, which appears during the rainy season, is terrible for the crop. At the first signs of disease, onion processing begins and continues 3 times per season, every tenth day. Consumption per 1 hectare: 3 liters of product per 350 liters of working solution.
Important! Fruit trees are treated with Bravo fungicide against scab and alternation blight. Apple trees and apricots are sprayed with a solution prepared from 20 ml of suspension per 10 liters of water.
Protection period
The exposure period lasts 1-3 weeks. It depends on the plant being sprayed, the degree of infection, and the weather forecast. Manual work is carried out after spraying after 10 days, mechanized - after 3 days.
Precautionary measures
A person working with a fungicide and not following safety precautions may become poisoned. It is necessary to wear a protective mask, gloves, and goggles. If the product gets on the skin, remove the drops with a cotton pad or napkin, and wash the skin area with soap.If the eyes are affected, rinse them with running water for 10 minutes.
In case of fungicide poisoning, a person is provided with a flow of fresh air, a large volume of water, along with activated carbon. And they call service 03.
Degree of toxicity
Fungicide Bravo has level 2 toxicity for animals and humans, level 3 for bees and poultry. The active substance is dangerous for the inhabitants of water bodies, in particular fish. Therefore, processing is carried out away from bodies of water.
During treatment, the drug can get on nearby plants, therefore, it is not advisable to spray in windy weather.
Compatibility with other drugs
Bravo is used in mixtures with insecticides, arcacides and fungicides of other names. Before combining the drugs, control mixing is carried out. Incompatible drugs leave sediment at the bottom of the vessel. It is not recommended to mix Bravo with other products that differ from it in the frequency of treatments.
Shelf life and storage conditions
Bravo fungicide is stored in a dry, isolated room, where children and animals have no access, and where food and medicines are not kept. Shelf life is 36 months from the date of production of the drug.
Analogs
Modifications of the fungicide Bravo that are similar in composition are produced under the following names: Bravo (500; 720; F).
Daconil (2787 B-75, 2787, B-75) has similar properties. These drugs have the same active ingredient as Bravo. Only the names are different.
Fungicide Bravo is excellent for personal and farm agricultural land. Based on its properties, it is possible to create a worthy barrier to fungal diseases.