Almost all vegetable lovers are involved in growing potatoes. However, not everyone manages to get a high-quality harvest, since potatoes often get sick and are attacked by pests. Many vegetable growers do not know what to do if the potato tops turn yellow. To prevent the plant from turning yellow, it is necessary to understand the causes of this problem and how to eliminate it.
- Should I sound the alarm if potato tops turn yellow?
- Causes
- Temperature and humidity
- Fertilizer shortage
- Development of the disease
- Fungal and bacterial diseases of potatoes
- Non-parasitic diseases of potatoes
- Viral diseases
- Pest attack
- Potato parasites
- Harmful insects
- Plant protection
- Advice from an experienced summer resident
- Conclusion
Should I sound the alarm if potato tops turn yellow?
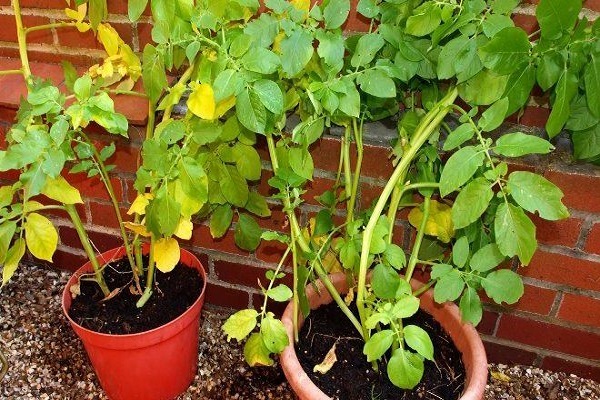
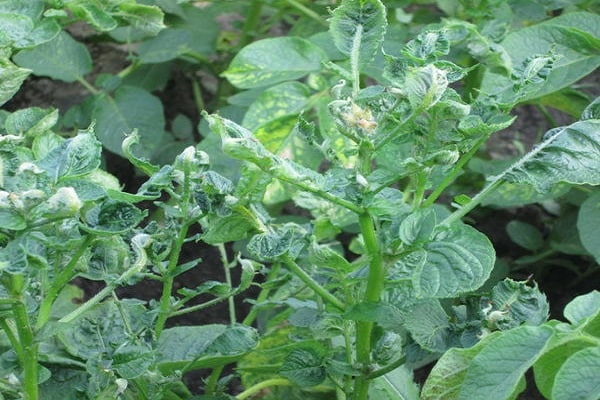
Some people don’t know what to do if potato leaves dry out and whether they should pay attention to this problem. It’s definitely worth it, since the future harvest depends on the health of the bushes being grown. If potato leaves begin to turn yellow, the likelihood of losing almost the entire crop increases by 2–3 times.
If even slight changes in the color of flowers or potato tops It is necessary to immediately determine the causes of such changes and begin to treat the plants.
Causes
It is difficult for inexperienced vegetable growers to independently determine the reasons for the yellowness of the leaves and therefore it is recommended to familiarize themselves in advance with the main factors that cause the tops to dry out.
Temperature and humidity
Most often, the lower leaves of potatoes turn yellow due to lack of temperature control when growing the vegetable. Due to severe drought, the leaves located at the bottom of the bushes turn yellow. Over time, yellowing spreads to the upper leaves. Sometimes drying out of the soil provokes the appearance of diseases and some gardeners have to deal with late blight.
When the air temperature exceeds 30–35 degrees, potatoes have difficulties with metabolism. It is because of this that the amount of harvest is reduced several times.
When growing such a vegetable, you need to ensure that the soil moisture is 60–80%. Therefore, before planting potatoes, an irrigation system is installed on the site. Also, to avoid yellowing of the leaves, you need to regularly loosen the soil.
Fertilizer shortage
Another reason why the lower leaves of potatoes turn yellow is an insufficient amount of nutritional components in the soil. Plants often lack the following elements:
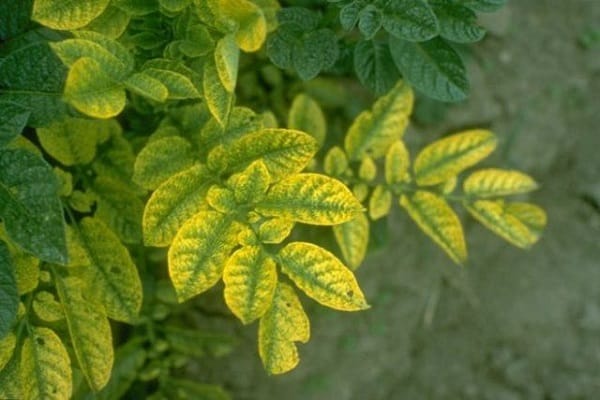
- Nitrogen.Determining the lack of this substance is quite simple. To do this, just examine the potato leaves. With a lack of nitrogen, they turn pale, gradually turn yellow and fall. In order for potato bushes to grow green mass again, it is necessary to restore the supply of nitrogen to the soil. To do this, 50 grams of the substance are added per square meter of area.
- Phosphorus. This substance must be present in the soil, as it is responsible for the formation of tubers and the development of plant roots. If there is a lack of this important microelement, the bushes are less able to tolerate high air temperatures, which leads to yellowing of the leaves.
- Potassium. Potassium-containing substances found in the soil improve the taste of grown potatoes and increase their immunity. If the plant does not have enough potassium, this will cause problems with photosynthesis and the leaves will begin to wilt.
Development of the disease
The reasons why the lower leaves of potatoes turn yellow include common plant diseases. Such diseases not only worsen yields, but also completely destroy potato bushes.
Fungal and bacterial diseases of potatoes
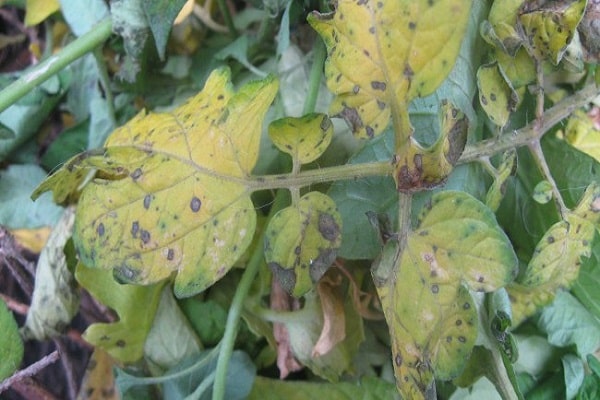
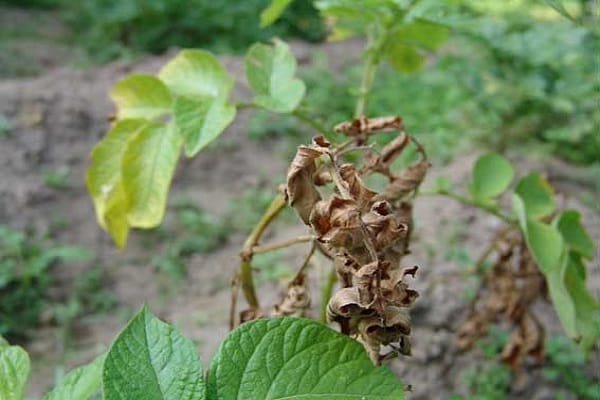
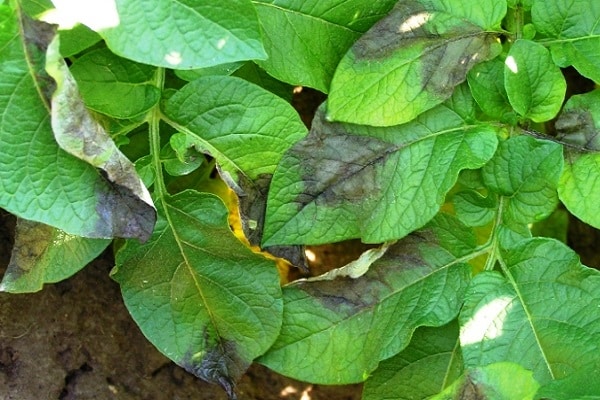
Speaking about why potato tops dry out and turn yellow, we must mention fungal diseases. Most often, plants suffer from late blight, which can completely destroy the plants. Bushes become infected with this fungal disease in two ways:
- through the remains of infected vegetables that remained in the ground from last season;
- through untreated planting material.
To protect potatoes from fungal diseases, all tubers are treated with fungicides before planting.
Non-parasitic diseases of potatoes
Sometimes potato tops and tubers wither due to non-infectious diseases that appear due to unsuitable growing conditions for vegetables.
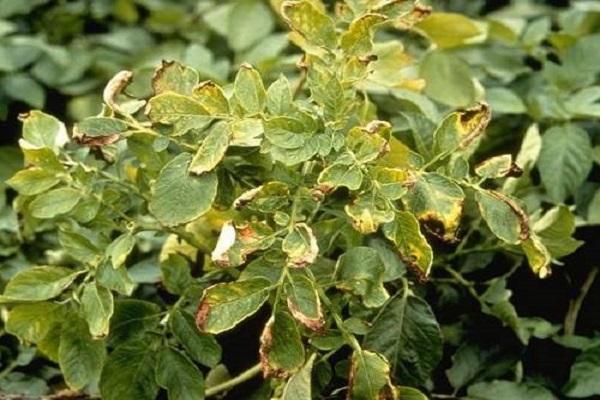
The most common non-parasitic disease is glandular rust, due to which the leaves and fruits of potatoes begin to quickly turn yellow. The disease occurs and actively develops at low humidity and high air temperatures. Also during plant development, the disease appears due to a lack of aluminum or phosphorus.
Viral diseases
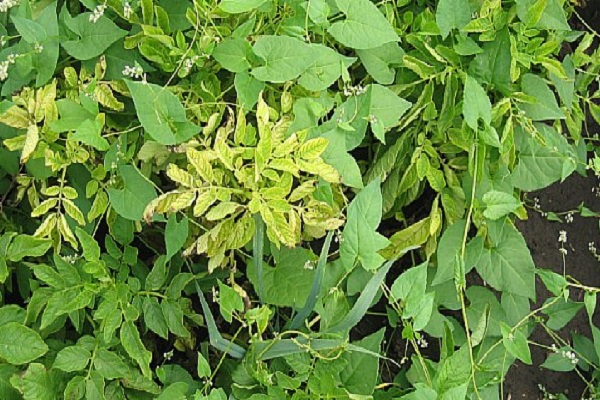
Viral diseases are the most common diseases that can cause potato tops to turn yellow. To identify a viral disease, you need to familiarize yourself with the main signs of such diseases. These include wilting, yellowing and curling of leaves. However, symptoms may vary depending on the type of disease and potato variety.
Potatoes are infected with viruses due to parasites or contact with already infected vegetables. Often healthy planting material becomes infected with mosaic alfalfa, due to which the amount of chlorophyll in the tops decreases. To prevent the plant from becoming infected with mosaic alfalfa, all tubers are disinfected before planting.
Pest attack
The main reasons why potato bushes turn yellow include attack by harmful insects.
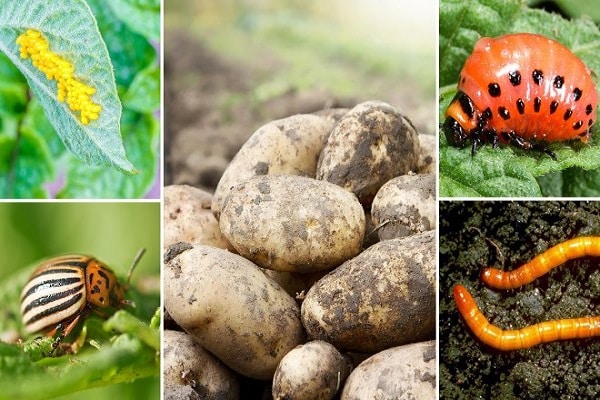
Gardeners often encounter nematodes that attack the plants they grow. These pests live in the ground and feed on potato juice from tubers. When insects suck out large amounts of sap, the plants turn yellow and gradually die.
Another pest that every vegetable grower has to fight is the Colorado potato beetle. This insect also lives in the soil and feeds on the tops of the plant. If you do not get rid of the Colorado potato beetle in a timely manner, the bushes will die from wilting.
Potato parasites
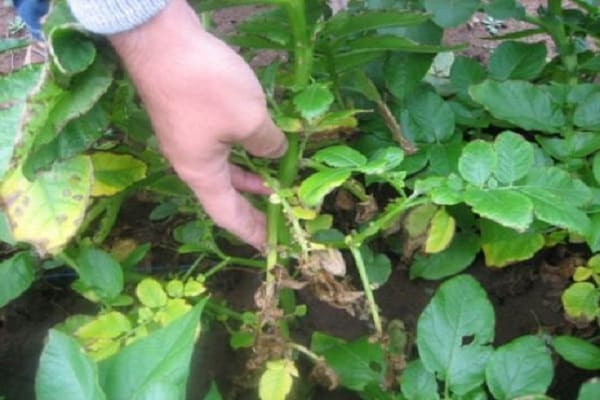
Potato parasites are very dangerous for this vegetable, as they can reduce yields by two and a half times.The most common parasite is the golden nematode, which penetrates the roots of bushes. Because of this, the potato tops gradually fade and turn yellow. It is quite difficult to detect a nematode, since with a weak infection, visible signs on the plants do not appear immediately. In the first 2-3 weeks the bushes seem absolutely healthy.
There is also a stem nematode that attacks plants through their stems. After infection, potato fruits darken and cracks appear on them.
Harmful insects
The causes of yellowing of vegetable leaves are harmful insects that often attack plants.
If there is insufficient moisture in the ground, wireworms appear and attack the root system with tubers. Root crops affected by wireworms have reduced immunity and because of this, plants are susceptible to bacterial diseases, which are accompanied by yellowing of the leaves.
Plants are also attacked by potato moth, which penetrates the leaves. The main difference between this pest is that it spoils the plant even after harvesting.
Plant protection
To protect the first shoots from pests and diseases, you need to take care of their protection in advance. To do this you need:
- Plant varieties with immunity to the most common diseases and dangerous insects.
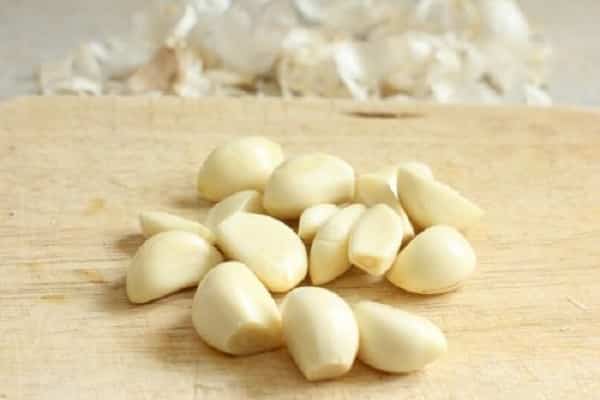
- 15 days after planting the tubers in the soil, treat the area with garlic solution to preserve the green mass. To prepare it, 350 grams of the vegetable are passed through a meat grinder and poured with a liter of heated water. The resulting solution is infused for at least a day, after which it is filtered with gauze. Before using the liquid, another 10 liters of water are added to it to make the solution less concentrated. You need to spray the bushes with garlic mixture three times a month.
- During flowering of bushes, fungicides can be used for prevention. Ditamine, copper oxychloride and Kuproxate are suitable for this.
Advice from an experienced summer resident
Not everyone knows what to do if the potatoes turn yellow and dry out. To get a high-quality harvest, you need to familiarize yourself with the basic tips for growing this vegetable:
- Plant marigolds, peas, oats, beets and cabbage near potato bushes to repel pests from potatoes.
- Before planting, fertilizers with urea are added to the soil. No more than 700–800 grams of fertilizer are consumed per hundred square meters of land.
- During planting, the holes should be treated. They add bird droppings with overripe manure mixed with soil.
- After planting, the area must be treated with liquid chicken droppings. At least ten liters of solution are consumed per square meter.
Conclusion
Every vegetable grower who grows potatoes has encountered the problem of yellow leaves. To get rid of yellowing, you need to understand the reasons for its appearance and become familiar with the methods of treating bushes.