Fusarium is a disease that affects many plants, including potatoes. It also received another name - fusarium wilt or dry rot. Fusarium blight in potatoes is caused by the action of spore fungi of the species Fusarium oxysporum. According to experts, this disease is especially common in the Far East, as well as in the south and southeast of the Russian Federation. The disease is very dangerous; it can destroy huge areas of potatoes and tomatoes in a short time.
Reasons for the development of fusarium blight in potatoes
As already noted, the causative agent of the disease is a certain type of fungus. It can be preserved for a long time in various conditions: in plant residues, in planting soil or seeds. In these cases, the fungus penetrates into the plant environment through their root system. The fungus begins to develop, which leads to the formation of fusarium. In most cases, the plant channels through which nutrients move are simply clogged.
Fungi enter the root system through roots damaged by insects (mole crickets or wireworms) when cultivating the soil around the rhizome.
In addition, infection and development of fusarium can occur for the following reasons:
- the use of seed previously infected with the disease;
- before planting, the soil was poorly prepared, no treatment was carried out against fusarium;
- potato storage conditions were not maintained;
- Crop rotation was not maintained; potatoes were planted in the same bed for several years;
- influence of weather conditions;
- pest invasion;
- lack of mineral and organic fertilizers.
Main symptoms
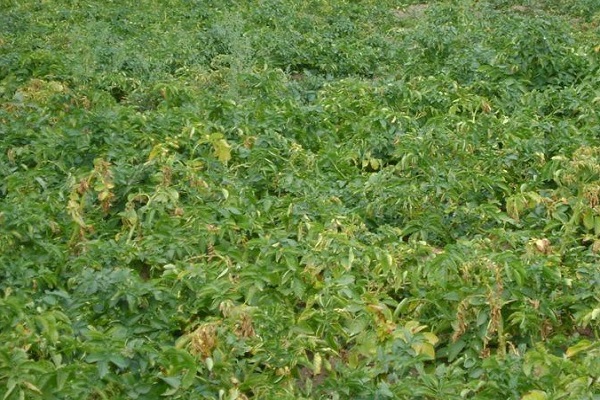
The most dangerous period for infection with fusarium is considered to be the period of setting and development of tubers. The plant begins to wilt only a month after infection.
The main signs of the disease include:
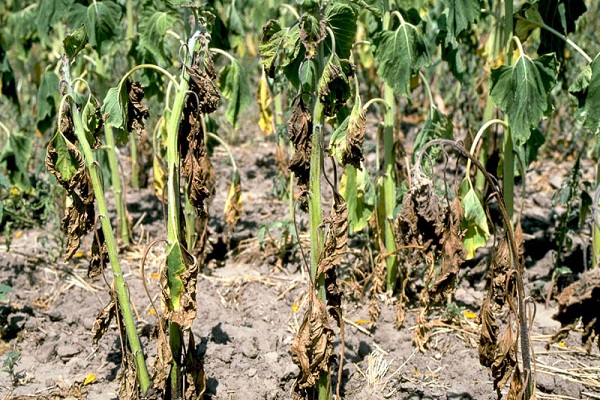
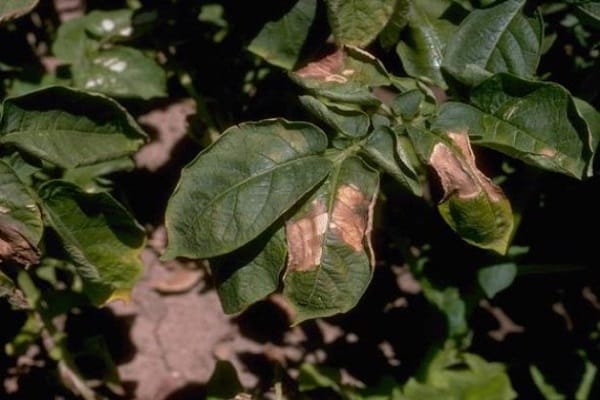
- curling of leaves at the top of the bush - this begins at the earliest stage of the disease;
- appearance yellow color on potato leaves, which first wilt and then simply fall off, appears when large areas of the beds are infected;
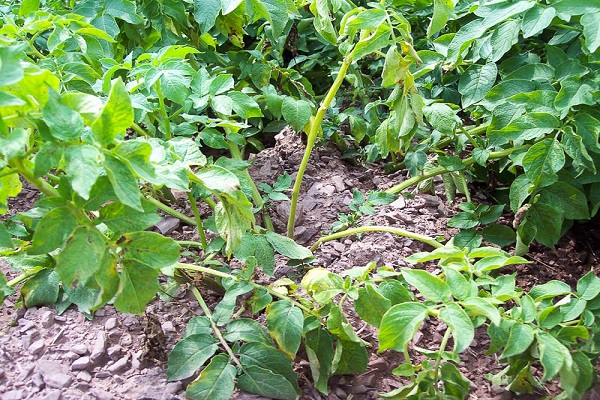
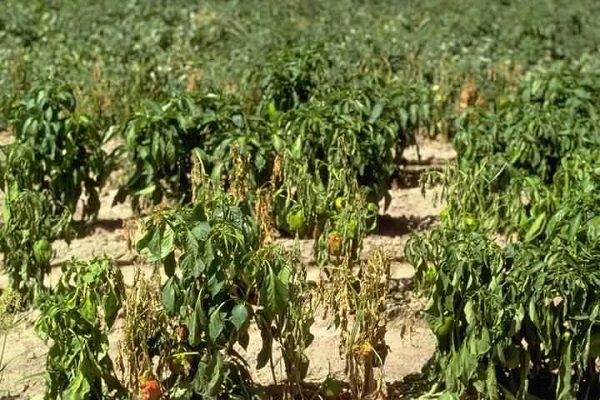
- the appearance of brown stems, especially in the upper part of the bush;
- stems begin to rot at high humidity;
- stems are pulled out of the soil without any effort;
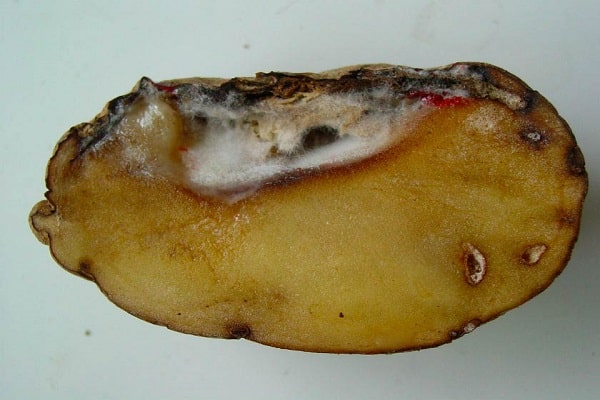
- the appearance of a brown core on the inside of the cut stem;
- the presence of dry rot on tubers during potato storage;
- the appearance of gray-brown spots on potato tubers;
- the core of the tubers becomes dry and porous, the peel wrinkles, and voids appear in the core;
- on infected tubers in the spring, the eyes sprout very slowly, their processes are weak and resemble a thin cobweb.
Preventive procedures
To prevent the disease in order to reduce the risk of infection with fusarium, it is necessary:
- use only healthy planting material;
- choose varieties of planting material only those that can resist fusarium;
- choose planting material that has been treated by the manufacturer against fungal wilt; such seeds have a distinctive color;
- before storing, as well as before planting, treat potato tubers with a fungicide;
- strictly follow the rules of crop rotation;
- mercilessly remove infected plants, together with root soil;
- burn infected plant remains;
- carefully handle garden tools that were used to work with infected plants;
- thoroughly clean shoes from contaminated soil;
- treating with bleach all containers that were used to prepare planting material;
- thoroughly disinfect the soil, especially greenhouse soil;
- Fertilize the planting soil with potassium oxide or lime.
Preparations for fusarium wilt
Control measures against fusarium wilt of potatoes are divided into two main groups: biological and chemical.
Biological agents
Biological agents are used to protect against diseases during preparation for planting.For this purpose, drugs such as Baktofit, Integral, Fitosporin-M have been used.
Baktofit
Biktofit is a microbiological preparation developed to combat fungal diseases of various plants, including potato fusarium. It acts directly to suppress the development of Fusarium fungi. This drug is not recommended to be mixed with other products intended to stimulate plant growth, as well as with some fertilizers.
The drug is available in the form of a powder or suspension. For use in small garden plots, one package contains from 10 to 12 g of the drug.
The consumption of the drug is determined by the manufacturer's instructions. Usually it is 1 g of the drug per 1 liter of water.
Integral
The drug Integral was created relatively recently. It contains live bacteria and has a fungicidal effect. It can perform many functions, from plant protection to accelerating germination by 1-2 days. It is also used to disinfect seeds and accelerate growth.
Fitosporin-M
The drug can be used for various purposes, but in most cases it is used for processing vegetables.
Before planting, potato tubers are treated in the following proportion: 3 tablespoons of the drug per 1 glass (250 g) of water.
In order to prevent or treat diseased potato bushes, it is recommended to spray them once every 10–14 days. The concentration of the drug should be: 10 g per 5 liters of water. The leafy mass of potatoes is sprayed.
Chemicals
Chemical agents are used to protect potato tubers both during the growing period and during storage. For these purposes, drugs such as Titus, Maxim, Vist and Colfugo Super.
Titus
Titus is a systemic herbicide that can be used on many plants, including potatoes and tomatoes. Its main purpose is weed control. Already after a few hours after treatment, weed growth stops, and after 15–25 days the weeds die.
To process potatoes, it is necessary to prepare a solution of the drug. Yes, for processing one hundred square meters of potatoes It is necessary to dissolve 0.4–0.5 g of the drug in 2–3 liters of water.
Maksim
The drug is intended for the prevention and treatment of fungal diseases of various plants. On the other hand, it stimulates an increase in their immunity and also prevents the development of various pests. It is widely used in the process potato storage.
This drug has one significant drawback - it does not treat fungal diseases inside the tubers.
To process potatoes, you need to dissolve 4 ml of the drug in 2 liters of water and mix well. To process 1 kg of potatoes, you need to use 1 liter of water.
Whist
This drug is used mainly during potato storage. Processing is carried out by fumigation - fumigation of tubers.
The drug is placed in smoke bombs of various sizes. Fumigation should be done no later than a week after storing the potatoes for storage.
Before processing, all doors, gates and other openings in the storage facility should be closed. Then light the checkers and the closed room is ventilated for at least 3 hours. After processing, the storage facility should remain closed for at least 24 hours.
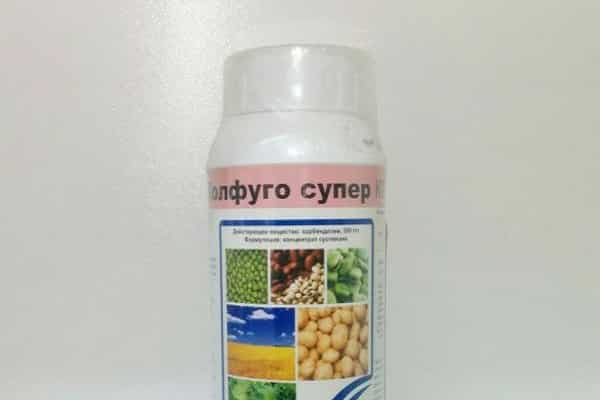
Colfugo Super
The active ingredient of the drug is carbendazim.The drug is intended for the prevention and treatment of plants from various diseases, including fusarium of vegetable crops.
To treat potatoes, you need 0.5 liters of the drug per hectare of plants.
Processing scheme
The fight against potato fusarium begins with the preparation of planting material and planting. First of all, you should remember that you can plant potatoes in the same beds only after 5 years.
To grow a good and healthy harvest, you should adhere to the following scheme:
- Inspect the seed in good light. Reject tubers suspected of having fusarium disease, as well as dents, spots or other damage to the skin.
- Germination of tubers. It should be started 25-30 days before planting. For germination, it is recommended to place the tubers in a room with a temperature of +19–21 ⁰C.
- Select the strongest tubers with clearly defined sprouts.
- Treat the tubers with any disinfectant solution.
- Potatoes should be planted in pre-prepared soil. The planting depth should be within 10 cm.
- Before the stems close, the potatoes are hilled.
- For the purpose of prevention, when the tops reach about 25–30 cm, they are sprayed with one of the systemic fungicides.
- The next spraying should be carried out before flowering begins. To do this, you can use the drugs Epin, Oksigumat or Exiol.
- Then, after 1–2 weeks, the potatoes are treated with contact fungicides. It can be any drug.
- After flowering, the potatoes are treated with Bravo, and then after 7–10 days, the same product is sprayed again.
- At the stage of potato ripening, it is sprayed with Alufit.
- 15–20 days before harvesting, it is recommended to cut off the tops and take them outside the garden bed. Removing the tops promotes rapid overgrowth of the tuber skin when it is damaged. And this will reduce the risk of disease during its storage.
- Harvesting. This procedure should only be performed in dry weather.
- Storing tubers for storage. The storage for this purpose begins to be prepared 2 months before laying. It must be thoroughly disinfected. Bleach is good for this. To prepare the disinfectant mixture, you need 2 kg of lime per 10 liters of water.
What mistakes do gardeners make?
In the process of growing potatoes, gardeners most often make the following mistakes, which contribute to the development of fusarium:
- due to small planting areas, the crop rotation order is not maintained;
- potato varieties are planted that are not immune to fusarium;
- harvesting is carried out without preliminary cutting of the tops;
- tubers are not inspected before planting, and, as a rule, diseased specimens are planted;
- The storage facility is not disinfected before storing.
If you follow the recommendations presented above, then you don’t have to worry about infecting your potatoes with fusarium.