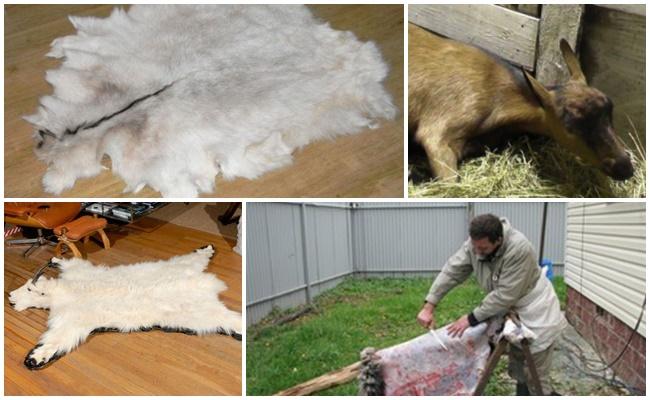
Raising animals with fur on their own plots poses a problem for the owners: what to do with the skin after slaughter? How to tan goat skin at home? The process of processing leather and fur raw materials requires time and patience. But, having the desire and theoretical knowledge on this issue, even a beginner can cope with this difficult task.
Characteristic features of hide products
Fur products made from goat skins are light, warm, and beautiful. The difference between goatskin and sheepskin lies in the structural features of the dermis. Mammalian skin consists of 3 layers:
- epidermis;
- dermis;
- subcutaneous fat tissue.
The dermis is formed by collagen fibers and connective tissue and consists of 2 layers: papillary and reticular. The strength and elasticity of the skin depends on the condition of the dermis. In goat skin, unlike sheep skin, the papillary layer is denser and the reticular layer is thicker. Collagen fibers at the papillary level form a dense network, which gives the dermis strength. The collagen bundles of the mesh layer are intertwined crosswise, which affects the elasticity of the skin.
Classification of goat skins
The weight of the freshly removed skin is about 6% of the weight of the animal. Based on thickness, paired skins are divided into IV subgroups (in millimeters):
- from 1.8 to 2.5 – adult goat;
- from 2.2 to 3.5 – adult goat;
- from 0.9 to 1.4 – kids at 2-3 months of age;
- from 1.3 to 2.2 – kids aged 5 to 6 months.
The quality of raw materials depends on the period of slaughter, on the basis of which they are classified:
- Winter goat (November-January). Purpose – fur coats, fur products, shoes and haberdashery goods.
- Spring (February-June). Not used in leather and fur production due to numerous defects in the dermis and the molting period.
- Summer (June-July). Purpose – production of chevro and linings for outerwear.
- Autumn (August-October). Purpose – production of high-quality chevro and leather linings.
Depending on the breeds, goats are distinguished:
- grain (for example, Russian breed);
- steppe (Orenburg);
- fur (donskaya).
Goat skins up to 1800 square centimeters are divided into:
- moire-klyam (at least 300 square centimeters) - from premature animals and miscarriages;
- from 400 square centimeters with a pile length of up to 4/more than 4 centimeters.
The skin is classified according to the size and age of the animals:
- fur goat (up to 1.5 months);
- very small (up to 3 months);
- small and medium (3-6 and 6-10 months);
- large and especially large (young and adult animals).
Based on the quality of hair, there are 4 varieties.
How to skin
The carcass is hung by the hind legs and 3 cuts are made:
- transverse from one hind hoof to the other through the anus;
- transverse from the metacarpal joint of one front hoof to the other through the sternum;
- longitudinal from the throat along the sternum and belly to the tail.
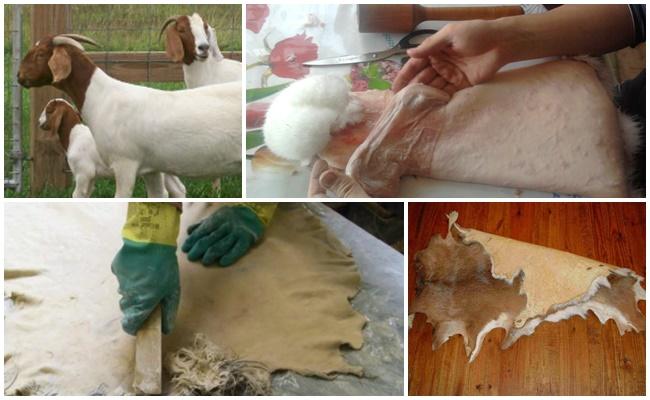
The skin is removed in one layer, from top to bottom. The tight fit of the skin to the carcass is trimmed with a knife. Lard and fat are cut off, leaving on the meat.
Required Tools
Crafting tools:
- skinning knives;
- metal scraper;
- spoon for skimming fat;
- clamps;
- hammers (wooden and metal);
- metal comb;
- brushes.
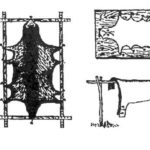
In addition, you will need devices for stretching and cleaning the goatskin (blanks, hangers, frames).
Dressing rules
At home, subject to technological requirements, a high-quality semi-finished fur product is obtained, suitable for further use.
Primary conservation
The removed skin is cooled by placing it, flesh side up, for 30 minutes. Preparing for preservation begins with removing any remaining meat and fat.Then the goat is covered with salt (1.5-2 kilograms), folded in an envelope and left in a cool room for 3 days so that the salt absorbs moisture from the flesh. After this, the salt is scraped off and the skin is stretched onto a frame to dry. Thin skins of kids are dried without the use of salt (fresh-dry method). Dry the skins in a dry, warm, ventilated area for 2 weeks.
Soak
Hard and dry skins must be softened for dressing, which requires soaking. 1 skin requires at least 10 liters of water. To speed up soaking, prevent rotting and excess moisture in the flesh, you need:
- water temperature 25-30 degrees;
- washing powder (2 grams per 1 liter);
- antiseptic (1 gram per 1 liter);
- table salt (30/50 grams per 1 liter);
- mixing.
For overdried skins, vinegar essence is added to the solution at the rate of 2 grams per 1 liter. The duration of soaking ranges from 20 to 48 hours, depending on the condition of the goat after drying.
Soaked goats should be degreased before proceeding to the next operation. To do this, dissolve washing powder, salt, and gasoline (if the skin is very greasy) in water at a temperature of 40 degrees.
Quantitative composition for 10 liters of water at a temperature of 40 degrees:
- washing powder – 200 grams;
- salt – 300 grams;
- gasoline - 1 gram.
The skins are kept in the solution for 24 hours at a constant temperature and stirring. Then the goats are washed in clean water for 30 minutes, hung to drain and proceed to the next stage of dressing.
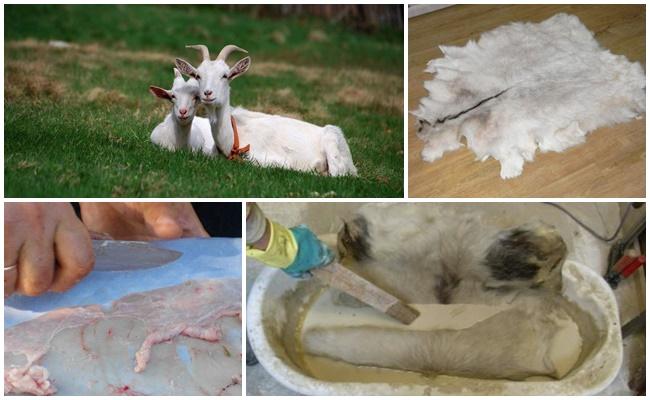
Flesh
The soaked and fat-free flesh is cleaned of films. The goat is laid out on a block/bracket and the remaining fat and tendons are carefully scraped off so as not to break the skin.The flesh is leveled in thickness by cutting off the thickenings with a sharp knife. Hatched goats are washed in soapy water (2 grams of detergent per 1 liter) at a temperature of 35 degrees. Then rinse for half an hour in warm water.
Pickling
At the pickling stage, collagen fibers are subject to processing. The acid-salt effect dissolves the proteins that bind them, increasing the porosity of the dermis. The composition of pickel includes (per 10 liters of water):
- salt – 500 grams;
- acetic acid 70% - 250 milliliters;
- 100 milliliters of liquid soap;
- 300 milliliters of gasoline.
The temperature of the aqueous solution is 40 degrees. The skins placed in the pickel are periodically stirred and kept for 2 to 3 days. The end of pickling is checked by drying or pinching. In the first case, in the groin area, the skin is folded into a cross and drawn along the fold with a fingernail. A white mark remains on the straightened dermis, disappearing after a while. A pinch is a test of the strength of the pile.
If it is easily separated from the flesh, then the skin can be removed from the pickel.
Layover
The pressed goats are placed in a container with the fur facing out, covered with burlap, and pressure is applied. In this state, the ripening process occurs in the flesh within 2 days. The temperature in the room at which storage occurs is not lower than 18 degrees.
Tanning
After pickling, the flesh becomes soft and elastic, but susceptible to moisture and temperature. Tanning treatment creates a protective film on collagen fibers.
For tanning goats, chemical or natural tanning agents are used:
- chrompic (potassium dichromate) + sulfuric acid;
- chromium sulfate with basicity 42;
- willow/oak bark;
- horse sorrel.
Half of the prepared chrome tanning agent is dissolved in 10 liters of water at a temperature of 40 degrees (90 grams of chromium sulfate is poured with 900 milliliters of boiling water, stirred and divided into 2 parts). Place the skin in the tanning agent, stirring once an hour for 10 minutes. After 5-6 hours, add the 2nd part of the tanning agent.
The entire tanning process lasts from 20 to 24 hours. Finally, neutralization is carried out. To do this, dissolve 250 grams of baking soda in hot water and divide into 2 portions. The first is poured in 4 hours, the second - 2 hours before the end of tanning. The tanned skins are squeezed out and laid to rest for 12 hours.
Fatliquoring
To prevent the tanning agent from being washed out of the flesh, the skins are covered with a layer of fat emulsion. At home, it can be prepared from equal parts of yolk and glycerin. The skins are stretched on a frame, coated with a brush and left to dry in a place protected from the sun. As the goats dry, they are kneaded and stretched so that they retain their softness and elasticity.
Stripping
The last stage of dressing is cleaning the core with sandpaper. It is then treated with chalk/tooth powder. The fur is combed with brushes and a comb.