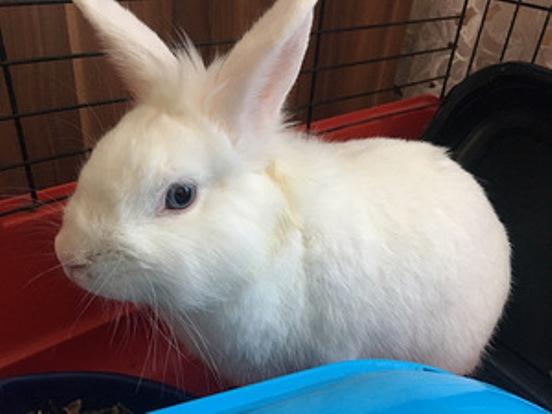
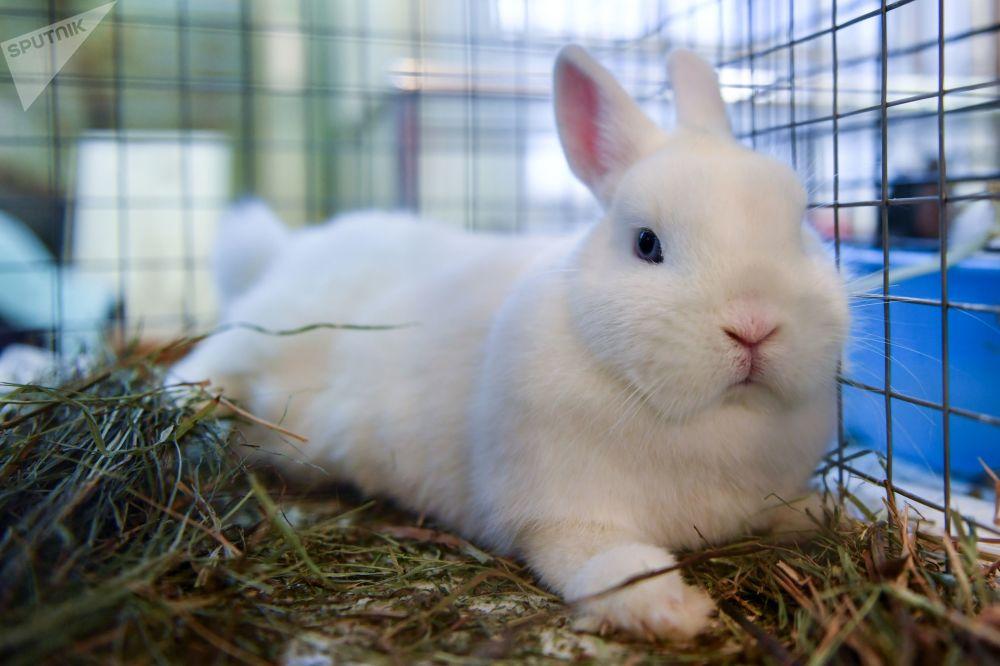
Hermelin is a miniature breed of rabbit, most often used as pets. This is due to their attractive appearance, beautiful coloring, unpretentiousness and dimensions, allowing you to keep a pet even in the smallest apartment. These cute rabbits have a good-natured, easy-going character and no aggression. They easily get used to home conditions and behave almost the same as other pets - cats, indoor dogs, ferrets.
Origin
Hermelins are often called Polish rabbits, but some mistake has clearly crept into this name. There is no single name for the breed in different countries. Although the animals are called Polish, such a breed does not exist in Poland itself, at least at the state level. The same applies to other countries.
In Great Britain, Hermelins are called Polish rabbits, although experts believe that it was in this country that breeding work with animals was carried out. In the USA, Hermelin rabbits are called Britannia petite.
Most likely, the breed was developed in Germany at the beginning of the twentieth century. The Hermelins are periodically confused with Dutch dwarf rabbits, but there is no particular external resemblance or genetic similarity. The Dutch are true dwarfs, and the Hermelins are specially selected miniature representatives of the breed. In addition, Netherland rabbits have a rounded head, smaller dimensions and short pointed ears. All the similarities lie in the same white body color of both Dutch dwarf rabbits and Hermelins, as well as the red tint of the eyes.
Description of hermelin
Although the animal is miniature in size, it is not a dwarf rabbit in genetic terms. The dwarfism gene is absent in Hermelin. The animal is used as a show animal and as an unpretentious and beautiful pet.
The Polish rabbit has a compact body, short, straight ears close to each other, a small head with lush cheeks (“whiskers”). Eye color depends on the variety:
- Hermelins, true albinos, have red eyes.
- Blue-eyed rabbits are not albino; their unique iris shade is associated with the presence of white Viennese genes in the genotype.
The color standard for Hermelins was originally considered pure white.But the American Rabbit Breeders Association recognized black as the appropriate color in 1957, later chocolate, and in 1982 blue became legal. The last variant to be recognized was “broken” (spotted) - in 1998.
Main positive and negative aspects
Polish rabbits have many advantages:
- Small dimensions, allowing you to keep animals in apartments.
- Calm, friendly and flexible character.
- Unpretentiousness.
- Economical in maintenance - dwarf rabbits eat little.
- Ability to learn to use a litter box like cats.
- Ability to walk in a harness on a leash like a dog.
- Attractive appearance, especially among blue-eyed hermelins.
The following properties can be added to negative traits:
- During the rut, males and, less often, females can show aggression towards people and their fellows. For indoor rabbits, the situation is corrected by castration.
- The room in the house where the hermelin walks freely can suffer, because the rabbit can chew furniture, baseboards, carpets, cardboard boxes, magazines and books. Wires - electrical and computer - are especially dangerous. The animal will not only damage expensive equipment, but may also receive an electric shock, be poisoned by heavy metals, or suffer from swallowed pieces of wire and plastic braiding.
If you carefully monitor your rabbit and create suitable conditions for it, it will become the cutest and most enjoyable pet.
The nuances of keeping and caring for animals
Like other breeds, Polish rabbits do not tolerate heat and direct sunlight well, but cope well with low temperatures if there are no drafts in the room and there is no high humidity.
Animals can chew on everything, so when you let them out for a walk, you need to monitor their actions. You should not allow hermelina to be fed from your table - human food, especially bread, is poison for them.
Representatives of the Hermelin breed have compact dimensions, so they should not be walked outside in severe frosts, especially in wet weather.
There is also a pronounced tendency for the fur to become tangled, become matted and clog the digestive organs with hairballs. To prevent this from happening, Hermelina is regularly combed like a cat.
Feeding rules
It is preferable to use ready-made pelleted feed. They are balanced in composition and are highly nutritious, so the rabbit is given a quarter cup of feed every other day. Additionally, it is necessary to feed the hermelin with fresh green food (hay in winter). Carrots and apples are treats, give them little by little as they contain too much sugar. Cabbage vegetables, especially white cabbage, should be excluded from the menu. You should also avoid foods high in starches and sugars. Eating corn by Polish rabbits can cause gastroenteritis.
Treats for pets include young dandelion leaves, spinach and parsley. To wear down their teeth, Hermelin rabbits need to be given hard food, such as tree branches. Animals should always have 24/7 access to clean water.
Features of breeding
Bathing rabbits is prohibited. In the absence of natural grinding, the claws are carefully trimmed once a month. The coat needs to be combed, and a special mineral stone should be given for healthy teeth and bones.
Sexual maturity in representatives of this breed occurs at 6-8 months. The female is placed with the male, but if she behaves too aggressively, they will have to be separated and tried with a different breeder. Like cats, these rabbits can be selective in choosing a partner. The male and female are left for mating for about five days.
The duration of pregnancy is standard for all rabbits - about a month. If you chase fashionable trends in breeding and breed ultra-small hermelins with a body weight of up to 750 grams, then reproductive function may suffer. Males may be infertile, and females, even if they become pregnant, bring no more than 2 rabbits.
To obtain full-fledged, healthy offspring, it is necessary to select sires with a body weight within the breed standard - 1.5 kilograms. This is a normal weight for a healthy rabbit. The maximum weight of a male is up to 2.5 kilograms. Excess body weight also negatively affects the general health of the Polish rabbit and its ability to have offspring.
Diseases and breed defects
The defects of the Hermelin breed include non-standard fur color, for example, the presence of a yellowish or grayish tint, dullness of the coat. Deviations from the standard in the shape, size, length or thickness of the ears are also considered defects.
Diseases characteristic of Polish rabbits:
- Ear mites.
- Felting of fur.
- Dental problems.
- Respiratory diseases.
- Infectious diseases.
- Urolithiasis with the formation of stones in the bladder.
- Gastrointestinal disorders.
- Spinal injuries.
- Nutritional allergies.
At the slightest suspicion that your pet has fallen ill, you must seek professional medical help from a veterinarian.Rabbits die very quickly without treatment, especially when it comes to infections and severe injuries.
How to choose?
When choosing a rabbit to keep at home, it is important to find a good breeder, and not a fancier from whom you can purchase an animal with congenital defects and hidden health problems. This may not appear outwardly, but it will affect itself over time and can cause the premature death of the pet.
This is even more important if Hermelin is purchased for breeding. Breeding rabbits must be unrelated, have sufficient fatness, but not obese. This is checked along the spine. If it is round, with protruding vertebrae, the rabbit is malnourished. If the bones cannot be felt, it is overfed.
A healthy Polish rabbit is clean, fluffy, with clear eyes and clean ears. There are no mats on the body, no discharge. The animal is cheerful, cheerful, not too timid, regularly goes to the toilet and does not refuse food. Weight is within normal limits. The average lifespan of hermelin is 5-6 years. Castration and sterilization can extend it to 8-10 years.