Coccidiosis is an infectious disease caused by protozoan microorganisms - coccidia. The body of domestic rodents can be affected by 10 types of parasites localized in different organs. There are two forms of coccidiosis in rabbits, differing in symptoms - intestinal and hepatic. To save the livestock, treatment must be started immediately; medications and folk recipes can be used as therapeutic agents.
What is coccidiosis in rabbits?
Coccidiosis is caused by a single-celled parasite of the order Coccidia of the genus Eimeria. Therefore, the second name of the pathology is eimeriosis. These parasites are specific, settle only in the body of rodents, and are harmless to other farm animals. In the rabbit body they capture certain organs:
- coccidia living in the small intestine - Eimeria intestinalis, media, magma, calcicole;
- settling in the liver – Eimeria stiedae.
Outside the host’s body, coccidia are in the form of cysts, that is, they have a shell that protects them from temperature fluctuations and other negative environmental factors. Having penetrated the rabbit’s body, the parasite loses its protective shell, begins moving through the digestive tract, and settles in a suitable organ.
How does infection occur?
Transmission of infection occurs from an infected rabbit to a healthy one. The feces excreted by sick animals contain coccidia cysts. The infection spreads from feces to food and drinking water. A few days are enough for all individuals living in one cell to become infected.
Infection with coccidiosis is inevitable if:
- put a healthy individual in a cage with a sick one;
- the pet eats food contaminated with cysts or drinks contaminated water;
- a farm worker will bring infection on clothes or equipment after contact with sick individuals;
- a sick mother rabbit will feed her babies milk with parasites.
Coccidiosis is most often detected in young individuals. This is due to the fact that up to 4 months of age, baby rabbits switch from mother’s milk to adult food, while their immune system is still weak.
There is a possibility of infection of rabbits if meadow grass is used as feed.It may contain traces of wild mouse feces containing coccidia cysts.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of hepatic and intestinal forms of pathology differ. However, in rabbits both organs are often affected simultaneously.
Intestinal form
The period between infection and the appearance of the first signs of coccidiosis is about 5 days. Symptoms of intestinal coccidiosis:
- decreased appetite, refusal to eat;
- dehydration;
- dullness and ruffled coat;
- blanching of the mucous membranes;
- green diarrhea, later streaked with blood.
Before death, convulsions are observed, then the rabbit is paralyzed.
Liver form
Signs of hepatic coccidiosis:
- decreased appetite;
- unquenchable thirst;
- apathetic, lethargic, drowsy state;
- the desire to hide in the far corner of the cage;
- swollen belly;
- stooping, tension due to unbearable pain.
Hepatic coccidiosis can be acute or chronic. In the first case, approximately 10 days after infection The rabbit begins to have intense diarrhea. The animal falls into a coma and dies.
Diagnostic methods
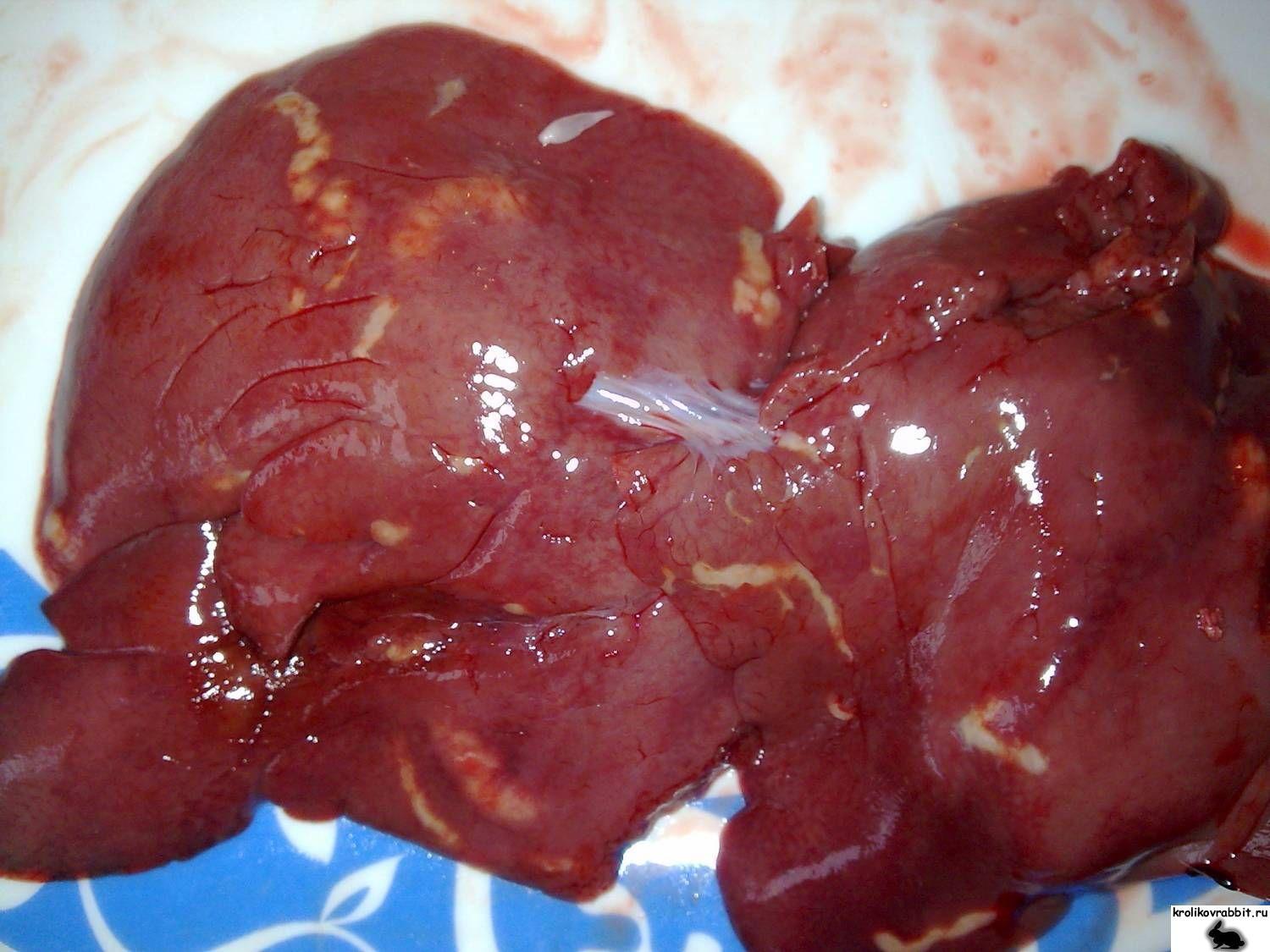
To make a diagnosis, the observed symptoms are analyzed, a microscopic examination of feces is carried out, and the internal organs of dead animals are also examined. The pathologist discovers white nodular formations in the tissues of the liver and intestines in the dead rabbit, ranging in diameter from poppy seeds to cereal grains - these are accumulations of parasites. The material taken during the autopsy is sent for microscopic examination. Coccidia cysts detected under a microscope allow an accurate diagnosis to be made.
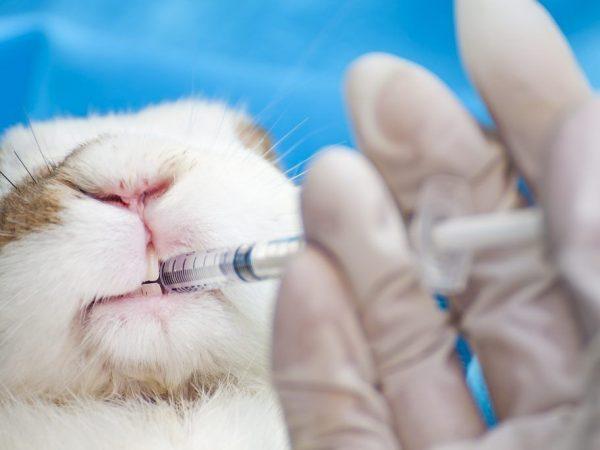
How to treat coccidiosis in rabbits at home
If symptoms of coccidiosis are detected, treatment cannot be delayed, otherwise the livestock will die.
The same drugs cannot be used to treat each new outbreak of infection, as coccidia gradually become resistant to the drug.
Every 2 years you should take a new medicine.
Medication
To destroy the infection in the body of rabbits, the following medications are used to choose from:
- "Eimeterm." Sold in the form of 2.5 and 5% suspension. The active ingredient is toltrazuril (25 and 50 mg per 1 ml). The daily dose is 15 mg of toltrazuril per 1 kg of animal weight.
- "Bycox." Treatment is carried out according to the same scheme as Eimeterm, since the active substance is similar. For 1 liter of water take 5 ml of a 5% suspension (2.5% per 0.5 liter). The solution is given to the rabbit, the daily dose is 300 ml. Medicines based on toltrazuril are given to the animal for 2 days, a 5-day break is taken, and then the dose is repeated.
- "Sulfadimethoxine". The drug is added to the food of rabbits. The dose for the first day is 0.2 g per 1 kg of the pet’s weight, for the next 4 days – 0.1 g per 1 kg. The course of treatment lasts 2 days, followed by a 5-day break.
- "Furazolidone". The drug does not kill coccidia, but it is added to the course to strengthen the physical condition of rabbits. The daily amount of the drug is 30 mg per 1 kg of weight. The appointment lasts a week.
- "Fthalazol" + "Norsulfazol". The daily dose of the first drug is 0.1 g per 1 kg of weight, the second - 0.3 g per 1 kg. Reception lasts 5 days, after a 5-day break the course is resumed.
Sick rabbits are given retinol (vitamin A) and B vitamins to quickly restore damaged organs and strengthen the immune system.
Folk remedies
Iodine is used as a folk remedy.In the rabbit’s body, it oxidizes protein breakdown products, normalizes the functioning of the thyroid gland, which has a positive effect on well-being. Both adults and young animals are given iodine solution. A 0.01% solution of the substance is used for both therapeutic and prophylactic purposes. To prepare it, dissolve 1 ml of 10% iodine concentrate (or 2 ml of 5% iodine) in 1 liter of water.
To prepare the solution, do not use metal containers, but only glass or plastic ones, since iodine can react with metal to form undesirable substances.
In the first 10 days, young rabbits are given a 0.01% solution, the daily dose is 50 ml. Then they take a 5-day break. After this, the concentration of the drug is increased: 70 ml of a 0.02% solution per day for a week. In the third week, 0.02% liquid is given in a volume of 100 ml per day. For adults, the dosage is different: in the first 10 days, 100 ml of a 0.01% solution per day. After a 5-day break for 2 weeks, rabbits are given 200 ml of 0.02% liquid per day.
How dangerous is the disease?
The spread of infection is rapid. It is enough for one rabbit to become infected for the entire population to become ill with coccidiosis within a few days. The most dangerous for livestock are those with a chronic form of the disease, which occurs during low-intensity invasion or re-infection. The number of parasites in the body is not enough to cause severe symptoms, but the sick animal remains a carrier of the infection, releases it into the environment, and infects its cage neighbors.
In the acute form of coccidiosis, the rabbit dies within 2 weeks. Signs of imminent death are convulsions and nervous syndrome, manifested by throwing back the head.
But even if the rabbit survives, it remains a carrier of coccidia, dangerous to the livestock.Therefore, individuals who have suffered coccidiosis must be immediately slaughtered.
Prevention measures
To prevent the spread of coccidiosis, the following recommendations must be followed:
- When soiled, clean and disinfect cells;
- do not allow rabbits to be kept crowded, especially those of different ages;
- feed animals with high-quality food and provide a balanced diet;
- change feed gradually;
- avoid high humidity, sudden temperature fluctuations and drafts;
- keep purchased rabbits in a month-long quarantine.
Disinfection of cells and equipment must be thorough, since coccidia cysts are resistant to ordinary cleaning agents. Many farmers use a blowtorch to burn cells. Of the strong disinfectants, a 2% solution of “Brovadez-plus” is suitable.
Is it possible to eat rabbit meat that has coccidiosis?
Rabbit coccidiosis is not dangerous to humans. You can eat meat without fear, you just need to dispose of the affected internal organs. Temperatures above 100 °C are lethal for coccidia, so after heat treatment the meat becomes completely harmless. However, many people, having seen enough of sick rabbits, disdain to eat meat and throw it away.
The skins of sick rabbits will have to be thrown away. An infected animal's fur becomes dull and crumpled; it is useless to use in furriery.