The attractiveness of a long-eared animal depends almost entirely on the spectacular beauty of the pet's fluffy coat. For farmers and lovers of ornamental breeds, there is no sadder sight than a bald, sick rabbit. Only an experienced veterinarian can determine the cause of the problem. Don't despair, in most cases the animal can be helped.
- How does shedding occur in rabbits?
- Possible diseases that cause baldness and methods of their treatment
- Lichen
- Presence of fleas
- Ticks
- Spirochetosis, or rabbit syphilis
- Hormonal disorder
- Ringworm in rabbits
- Other causes of hair loss
- Eating fur from other rabbits
- The rabbit chews its own fur
- Prevention of baldness
How does shedding occur in rabbits?
In the wild, rabbits change their coats only in spring and autumn. The frequency of molting is affected by temperature changes and changing seasons. To the chagrin of owners, pets shed almost continuously. This misunderstanding has a simple explanation: heated houses always maintain a comfortable temperature.
The first coat change occurs when the rabbit reaches 1.5 months. At this moment, the young creature changes its infant downy coat to a full-fledged fur coat of an adult animal. Shedding itself is safe for the rabbit, but the process requires the attention of the owner. The pet carefully licks its skin, removing dead hairs. As a result, the gastrointestinal tract of the eared cat becomes clogged with scraps of fur. Animals are not able to regurgitate hair, as cats or dogs do, and if he is not helped in time, the pet risks dying.
When changing fur, the rabbit is thoroughly combed. If an admixture of fur is clearly visible in the animal’s feces, and the amount of excrement becomes smaller, it’s time to take urgent measures. It is not difficult to help the trouble, you need to give your pet 10 ml of Vaseline oil and increase the daily portion of hay. It is dry grass that prevents intestinal blockage.
Shedding happens:
- Seasonal. Rabbits change their fur only in autumn and spring.
- Year-round. The animals are constantly molting.
- Compensatory. In this case, the hair grows back to replace the hair lost as a result of injuries (burns, wounds).
Possible diseases that cause baldness and methods of their treatment
The causes of pet baldness can be various diseases.Prescriptions from a veterinarian and the caring care of the owner will help restore your long-eared pet to its former beauty and health.
Lichen
Ringworm is a dangerous disease for all livestock. The fungus easily affects weakened animals that have recently suffered from illness. There are known cases where animals fell ill with ringworm after hypothermia. The disease is accompanied by inflammation of the skin and hair loss. Bald patches appear on the coat of an infected rabbit.
An aggressive infection is easily transmitted to humans, so all medical and hygienic procedures must be performed with gloves. There are a lot of drugs on the market to combat this unpleasant disease. Miconazole and Ketoconazole are popular among animal lovers. Before treatment, the hair growing around the resulting bald spot is cut off.
To treat a pet, you cannot use a product intended for humans. The medicine is toxic to animals, because the rabbit will definitely lick its fur. In this case, the drug will most likely enter the animal’s body, and the pet risks poisoning.
Simple preventive measures will help you avoid troubles in the future. Help keep your animals healthy:
- Timely vaccinations.
- Mandatory isolation of newly acquired rabbits. New pets are quarantined in a separate home.
- Thorough cleaning of pets' apartments. The cell is treated with chlorine-containing agents.
- Maintaining a comfortable air temperature. The room should be warm and dry.
Presence of fleas
Fleas serve as carriers of a dangerous disease called myxomatosis. The disease is accompanied by conjunctivitis, which causes pets a lot of suffering. As the disease progresses, subcutaneous bumps appear in the rabbit's eye area.An insidious infection can wipe out the entire livestock. In the event of an outbreak of myxomatosis, a quarantine is declared on the affected farm.
Painful flea bites often cause an allergic reaction in animals. Due to the fault of insects, pets scratch their bites until they bleed. As a result, the affected areas are partially exposed. Special flea remedies will help you cope with the problem. For eared pets, a preparation for treating kittens’ fur is suitable. The product is applied to the animal’s withers. However, the product is not suitable for decorative rabbits; there are special sprays for exotic beauties. The drug is applied to the rabbit's back area, evenly distributing the product along the spine.
Ticks
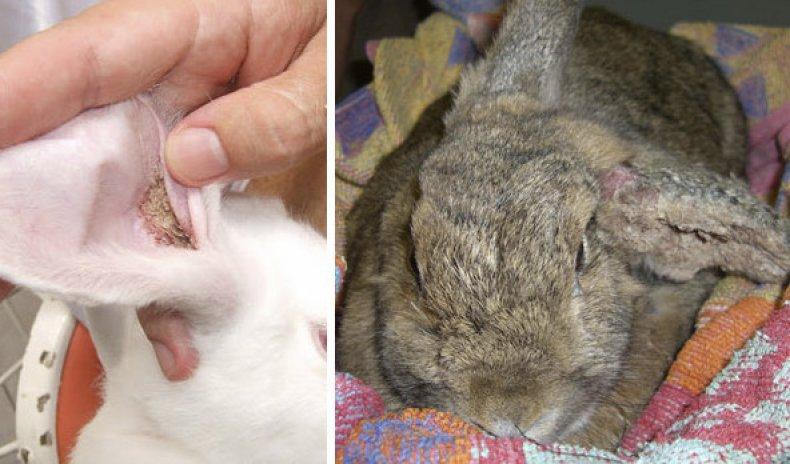
Fur mites cause a lot of trouble for animals. Insects occupy the skin on the pet's body. As a result of the activity of pests, the back and sides of the rabbit become partially bald and covered with white dandruff crumbs. The skin in the affected areas becomes inflamed and itchy. In some areas, entire strands of hair fall out. The disease is called cheyletiellosis.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, you must contact an experienced veterinarian. The specialist makes a verdict based on laboratory tests and examination of the animal.
The situation is much more complicated with the subcutaneous mite. The insect is difficult to see with the naked eye, because the pest lives under the upper layers of the skin. The presence of mites is indicated by tiny bumps that appear on the skin in places where insects accumulate. This is where pests lay their eggs. The unfortunate animal frantically scratches the itchy swellings, tearing the skin until it bleeds. Small wounds become inflamed and fester.
Subcutaneous mites can poison the lives of not only big-eared beauties.Dogs, cats and other domestic animals often become victims of pests. In some cases, the infection also affects humans. In the event of an outbreak of the disease, the home of eared pets is thoroughly disinfected. Pets in their entirety are treated with a special preparation. Injections of Selamectin or Ivermectin will help solve the problem. However, it must be remembered that medications intended for cats or dogs are dangerous for herbivorous rabbits.
Spirochetosis, or rabbit syphilis
An unpleasant disease affects the long-eared inhabitants of large, densely populated paddocks. Signs of the disease: ulcers in the head and genitals. In the affected areas, hair falls out rapidly. The infection is transmitted through sexual contact between animals. Penicillin is used for treatment.
Domestic ornamental animals are not at risk of infection with rabbit syphilis.
Hormonal disorder
As a result of hormonal changes, animals often lose entire tufts of hair. The hair on the body of rabbits clumps into separate clumps. These balls literally fall off the pet’s once attractive fur coat. Only a veterinarian can determine the cause of the unpleasant phenomenon. Conclusions are drawn based on laboratory studies.
Treating hormonal hair loss is not that difficult. Dietary nutrition and taking specially selected hormonal medications will help cope with this unpleasant phenomenon.
Ringworm in rabbits
The culprit of the trouble is a skin fungus. Ringworm affects the area of the animal's ears and nose. In a healthy rabbit, the infection may resolve without consequences. As a rule, a pet’s strong immunity allows it to survive the disease without symptoms.
A weak rabbit will lose hair between its ears.The wound becomes inflamed and festers, and then becomes covered with a crust. If left untreated, the fungus spreads throughout the pet's body. For treatment, specialists use the drugs “Surolan” or “Fenistil”.
Other causes of hair loss
In some cases, hair loss is caused by tumors of various origins or vitamin deficiency. Often, baldness is caused by the behavior of animals.
Eating fur from other rabbits
In a confined space, pets get bored and, from idleness, pluck hairs from their neighbor’s skin. In such cases, pets need to be released into an enclosure for a walk. This diversifies the life of rabbits. Damage to the fur can also occur as a result of fights between young males. Such brawlers will have to be moved to separate cells.
The rabbit chews its own fur
If your pet is constantly biting into its own skin and methodically tearing out pieces of fur from it, it means that the animal is under stress or experiencing physical pain. Rabbits are timid and vulnerable creatures. An unexpected move to a new place or a sudden change in food can undermine an animal’s nervous system. A veterinarian can determine the cause of changes in your pet's behavior.
Prevention of baldness
Following the rules for keeping animals will help avoid many problems that contribute to baldness in rabbits:
- regularly clean and disinfect enclosures and cages;
- constantly ventilate the room;
- carry out routine vaccination;
- limit access to cages to strangers;
- isolate pets from dogs, cats and birds.