Pododermatitis, or hind paw disease in rabbits, is a common infectious skin disease. Bacterial infection affects the forelimbs less frequently. The main cause of the disease is incorrect content. True, the occurrence of pododermatitis is influenced by a number of unfavorable factors. The disease is treated with wound-healing ointments, antiseptics and antibiotics.
Causes of pododermatitis in rabbits
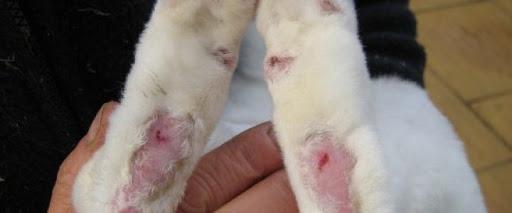
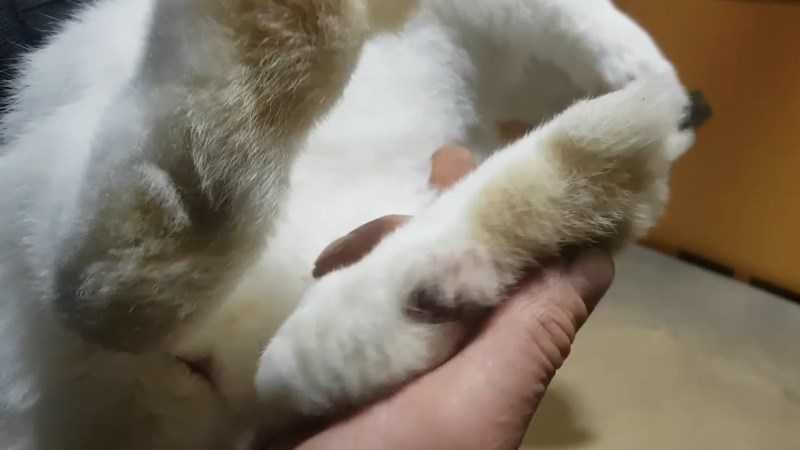
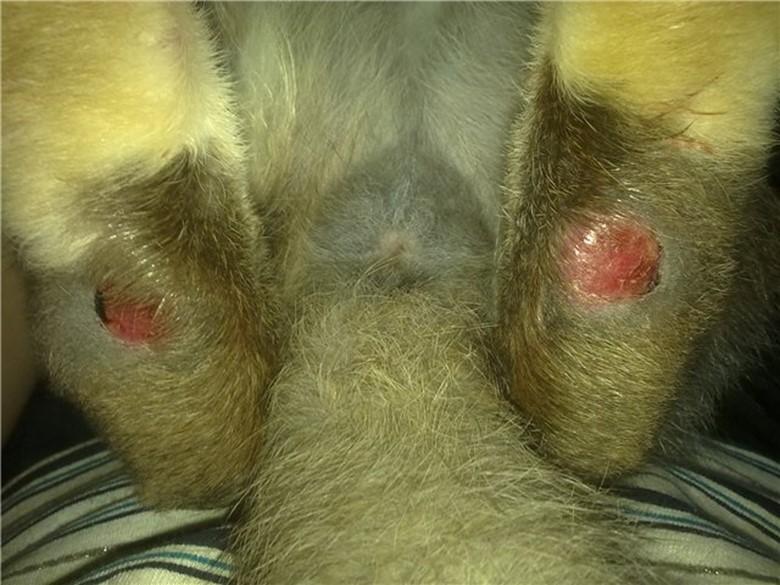
Pododermatitis - peeling, corns, crusts, calluses, abscesses, wounds, ulcers on the hind legs, less often on the front legs of a rabbit. This is a superficial skin disease, which is often accompanied by a bacterial infection, resulting in the formation of pustules. Ulcers can reach soft tissue and even bone and tendons, causing rotting, blood poisoning and death.
The disease occurs in animals that sit in cramped cages and lead an inactive lifestyle. The development of the inflammatory process in the hind limbs is stimulated by a traumatic floor surface, for example, a metal mesh, as well as unsanitary conditions.
Most often, pododermatitis affects overweight rabbits, since obesity increases the load on the paws. In an animal sitting motionless in a narrow cage, the process of grinding its claws is disrupted; they grow too long, so the animal rests not on the metatarsus, but on the talus and calcaneus. The skin of the hind paws is constantly in contact with damp bedding or metal mesh, resulting in the formation of calluses, cracks, wounds, and purulent ulcers. The older the animal, the higher the likelihood of pododermatitis occurring under improper conditions.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Pododermatitis is diagnosed based on clinical signs. Examine the hind and front legs of rabbits. At the very beginning of the development of the disease, the skin on the hind legs begins to peel and flake off. Then corns and calluses form, and abscesses and bleeding wounds appear along the entire length of the paws.
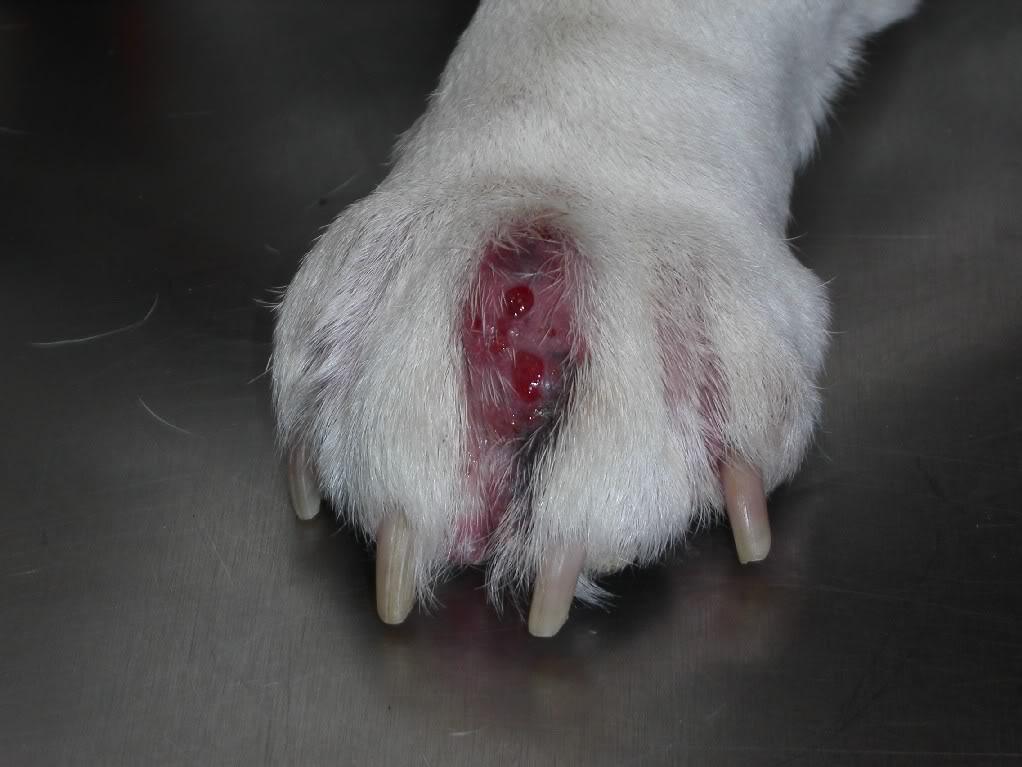
Due to unsanitary conditions, bacteria become infected and purulent ulcers form. A bacterial infection penetrates the skin and internal tissues, they become inflamed, rot, and the damage reaches the bones. The hair on the limbs falls out.The animal lies motionless most of the time, with its legs stretched out. There is a lack of appetite. The body is exhausted, blood poisoning occurs, and the animal dies.
Stages and stages of disease development
Pododermatitis has two stages: initial and final. At the very beginning, peeling is visible on the rabbit’s paws, and calluses form. At this stage, the disease is quickly treated. If the disease is started, cracks appear on the corns, bacteria penetrate into them, infection occurs, fistulas and purulent formations develop. The disease is entering its final stage. If the animal is not treated, it may die.
There are aseptic and purulent pododermatitis. These are two types of the same disease, which differ from each other in the degree of damage and severity.
Aseptic
This is a superficial skin lesion. Initial and mild stage of pododermatitis. Peeling occurs on the paws, corns, calluses, and even hematomas appear. Sometimes the wounds bleed.
Purulent
When the infection penetrates the skin and soft tissues, the development of purulent pododermatitis begins. In advanced cases, bacteria affect bones and tendons. The wounds become inflamed, blood and pus flow from them. The rabbit's body temperature rises. The animal refuses to eat and soon dies.
How to treat pododermatitis in rabbits?
The sooner treatment begins, the greater the chance of saving a sick animal. First of all, it is necessary to change the conditions under which the rabbit is kept. It is recommended that the sick animal be moved to a spacious cage where there is no wire floor, but rather soft, clean bedding or at least a rubber mat on top of a metal mesh. It is advisable to wash the floor on which the animal will lie with a “Whiteness” solution.
Drug treatment
At the very beginning, calluses on the paws are treated with an antiseptic and lubricated with zinc ointment. The skin can be washed with hydrogen peroxide or a solution of potassium permanganate. If wounds appear, they can be covered with iodine. To disinfect purulent calluses, you can use “Chlorhexidine”, “Dioxidine”. Wound treatment is carried out 2-3 times a day.
The inflammatory process is relieved with Tetracycline or Levomekol ointments. The affected areas are first treated with an antiseptic, then lubricated with an antibacterial agent and a bandage is applied. It is necessary to constantly monitor the well-being of a sick animal.
If a rabbit has a high fever, does not eat anything, and has many wounds on its paws from which pus and blood flow, then antibiotics should be used. Animals can be given injections of Baytril 2.5% or Bicillin 3. The course of antibiotic treatment is 3-5 days. However, before giving injections, it is advisable to consult a veterinarian.
ethnoscience
If you don’t have an antiseptic on hand, you can wash the wounds with herbal tea. A good disinfectant is an infusion of chamomile, St. John's wort, and calendula. To get rid of and wash pustules at home, you can use vodka, diluting it with water. The paws must be covered with a bandage made of clean cloth. During illness, animals should be given more dried fresh nettle, plantain, and shepherd's purse.
Rules for applying a bandage
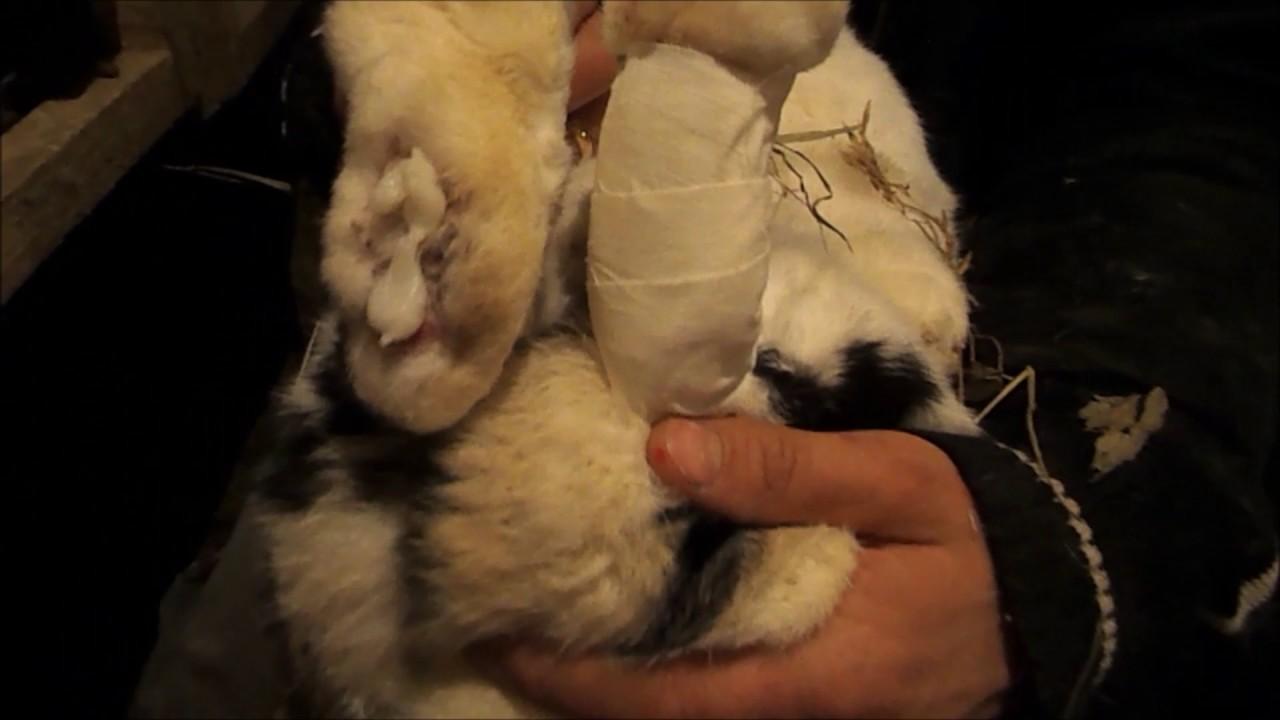
If there are bleeding wounds and pustules on the paws, they must be treated with an antiseptic and lubricated with antibacterial ointment. True, the benefit from such treatment will be small, because the affected areas will remain unprotected and will constantly be in contact with the floor or bedding. It is recommended to apply a cotton-gauze bandage to the affected areas. Instead of cotton wool, it is better to buy a cotton pad for a plaster bandage at the pharmacy.
While the bandage is being applied, the animal is taken out of the cage, turned over on its back and placed on its lap.
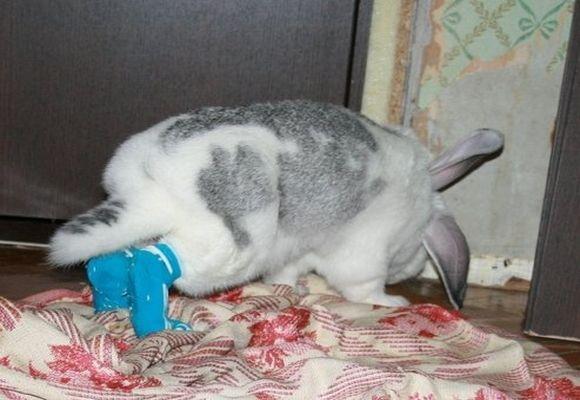
First, the wound is lubricated with ointment, then a cotton swab is applied to the skin, and a bandage is tightly wrapped on top. You can wear a narrow baby sock over the headband. True, the animal often tears off the bandages from its paws. It is better to hold it in your hands for 30 minutes during the procedure. It is recommended to change the bandage 1-2 times a day for 15-30 days.
Possible complications
Timely treatment always gives a positive result. If the disease is started, the infection will penetrate the skin, then into the soft tissues and reach the bones. Blood poisoning will begin. You can save the animal if you give it antibiotic injections and give it boiled, cooled water with Gamavit daily (1 drop per 1 liter).
Prevention and hygiene rules
Rabbits will not get sick with pododermatitis if they are kept in clean and spacious cages. It is advisable to use dry and fresh straw as bedding material. Rabbits of large breeds and heavy weights are not recommended to be kept on a metal mesh floor. It is better to place animals in wooden boxes. If there is no other cage, you can lay a rubber mat on the mesh floor.