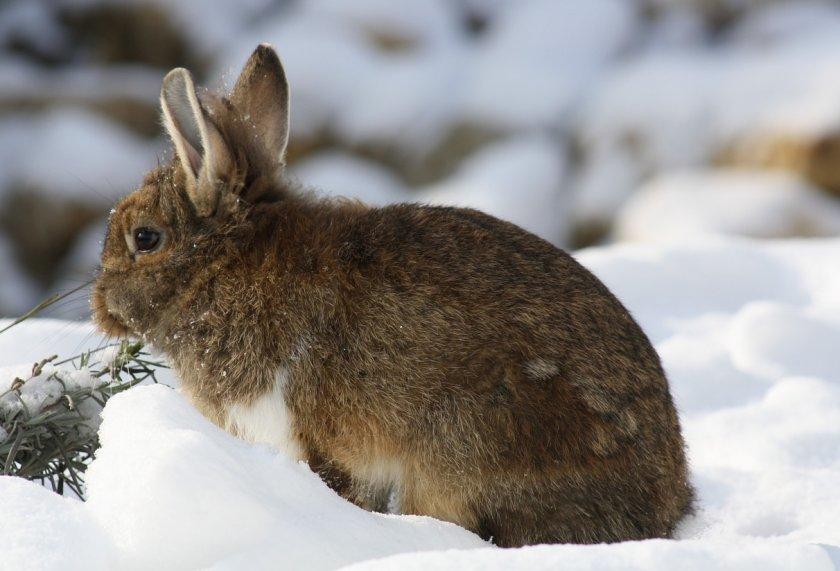
The rabbit's body is adapted to winter conditions, but still, to successfully keep rabbits in winter, it is necessary to prepare the rabbitry and follow the recommendations for care and feeding. During the cold months, animals should not be kept in damp, drafty environments with sudden temperature fluctuations. Failure to comply with the conditions leads to weight loss and the appearance of colds in rabbits.
Is it possible to keep rabbits outside in winter?
It is possible to keep pets outside indoors in winter.This will even benefit the animals, but subject to proper conditions and quality feeding.
Advantages
Keeping rabbits outside has the following advantages:
- Frosty weather helps strengthen your pet's immune system.
- Less money is spent on insulating cages than on building a buried rabbitry.
- During the frosty period, many pathogenic microorganisms die, thereby reducing the likelihood of the livestock being affected by infectious pathologies.
- Animals breathe fresh air around the clock.
Flaws
There are also disadvantages to keeping rabbits outside in winter, but they are minor; with proper cage arrangement and quality nutrition, they do not interfere with the pets’ ability to live a full life:
- In high frosts, reaching -30 °C, the immunity of rabbits suffers.
- To produce offspring in winter, it is necessary to install artificial lighting sources to extend daylight hours, which makes the cost of electricity more difficult.
- Water for drinking must be constantly heated so that pets do not catch a cold while drinking it.
What temperature can rabbits withstand?
Rabbits look tender and weak, and inexperienced farmers naturally wonder whether their pets are afraid of frost. They are afraid, but only of the strong.
Thanks to its fluffy coat with dense undercoat, the rabbit’s body can easily withstand temperatures down to -12 °C. Within 2-3 days, a rabbit can withstand temperatures dropping to -18 °C. If the cages are well insulated, the animals will tolerate a short-term drop in temperature to -25 °C. However, prolonged exposure of animals to extreme temperature conditions is unacceptable. If prolonged frosts are predicted, it is better to move your pets indoors.
The optimal temperature for the rabbit’s body is from +10 to +18 °C, and humidity is 60%. Unfavorable microclimatic conditions cause deterioration in well-being.
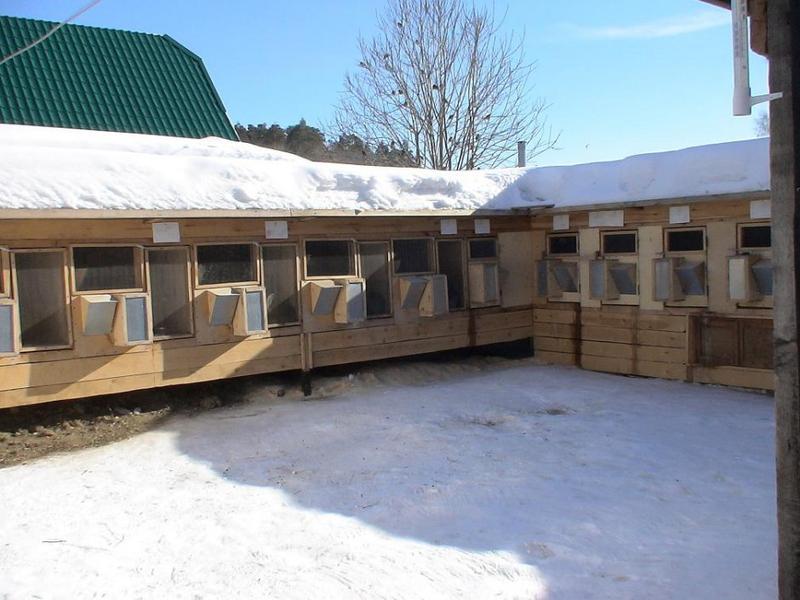
Preparing cells for cold weather
Tips for beginning farmers on how to insulate rabbit cages for winter:
- The first step is to insulate the floor in the cages. To do this, it is covered with a thick plywood sheet. Or they make a boardwalk. A thick layer of straw or sawdust is placed on top. We must not forget about regularly changing the litter during the winter.
- The cage doors are covered with a plywood sheet or polycarbonate film.
- The back and side walls are insulated with foam boards, felt or synthetic fiber. Moreover, it is better to place the insulation on the outer surface of the wall, and cover it with roofing felt or other dense film material on top.
The insulating coating is removed in the spring, as soon as warm weather returns. Otherwise, mold will begin to multiply inside the cells due to increased steaminess.
Cages in the yard in winter should be positioned so that they are covered by a building on the north side. It is advisable to make two rows with a narrow passage between them so that the cage doors face each other. With this design solution, you can even make a pitched roof, under which you can attach a lighting source. And on the north side you can put up a temporary plywood fence.
It is advisable to keep cages with young individuals at home in a barn or greenhouse. To keep rabbits in greenhouse conditions in winter, you don’t even need cages; it is enough to build a mesh enclosure inside, 0.5 m deep into the ground. But you need to take into account that in the spring, females can dig holes and breed offspring.
How to feed and water?
If you keep rabbits incorrectly in winter, then their body will not be able to maintain normal functioning in low temperatures: the immune system will weaken, followed by exhaustion and loss of body weight.
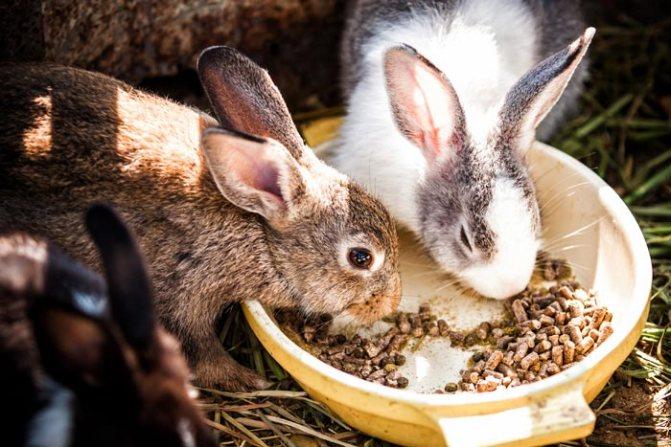
Therefore, pets should be fed well in winter; food should be high in calories and warm.
Rabbits should not be given cold water. It needs to be reheated regularly to make it a comfortable drinking temperature. Some farmers make their work easier by giving their pets snow instead of water. But this is a bad option, fraught with colds in rabbits.
The basis of the winter diet is hay. In winter, rabbits should receive succulent food (vegetables and root vegetables), branches, silage - these are sources of vitamins and minerals to strengthen the immune system. You need to make sure that the mash and juicy vegetables placed in the feeder do not freeze. The frozen food is taken away, thawed, and put back into the feeder.
Breeding Features
In winter you can have rabbits, but subject to certain conditions:
- Rabbits that have already given birth before are selected for mating.
- Selected females must be in good health.
- Animals are found in a warm room.
- Mating is organized on days when there is no severe frost.
- Before birth, the queen cell is disinfected.
In winter, a pregnant rabbit is moved directly in a cage with a nest to a greenhouse. The queen cell should remain clean and the room ventilated, but without drafts. While the female is bearing offspring, the room temperature should not fall below +5 °C.
In order for rabbits born in winter to remain healthy, the temperature around them should be about +30 °C.It is important to control that the female does not leave the cubs for a long time, and that she feeds them at least 2 times a day.
Possible problems
Although caring for rabbits in winter is not particularly difficult, and infectious pathologies occur rarely, but with insufficient cage insulation and a poor-quality diet, pets begin to have problems due to hypothermia and weakening of the body.
Often, when mistakes are made in winter keeping, rabbits are exposed to frostbite. The problem occurs when the air temperature drops to -25 °C. The first to freeze are the paws and ears. The injured animal is worried, licks the affected areas of the body, and sits in unnatural positions.
There are 3 stages of frostbite:
- 1st – the skin turns red, swells in certain areas, the sick animal should be taken to a warm room, and the damaged areas of the body should be lubricated with fat;
- 2nd – blisters form, the affected rabbit is kept warm, the affected area is lubricated with camphor oil;
- 3rd – the affected area becomes deformed and dries out, in this case veterinary care cannot be avoided.
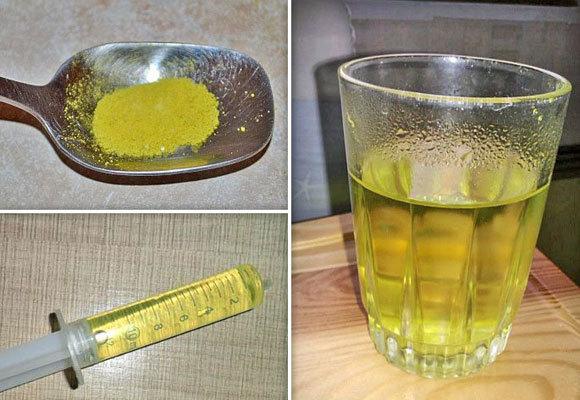
In winter, rabbits often develop rhinitis. More often it is a cold, less often it is infectious. The main symptoms are mucous nasal discharge, sneezing, lethargy, and poor appetite. If the nasal mucus is clear, then the rhinitis is a cold. If it is green or yellowish-white, then it is infectious. The sick rabbit is transferred to a warm room, fed well, given vitamins, and the nasal passages are washed with a solution of Furacilin (1:100). A veterinarian deals with the treatment of infectious rhinitis.
On frosty days, your rabbit may develop bleeding, painful calluses on the soles of their paws. The pathology is called pododermatitis.The sick animal is kept in a warm room, fed well, and wounds are treated with medications prescribed by the veterinarian.
Frost-resistant breeds of rabbits
All rabbits quickly adapt to winter conditions in temperate climates. With quality care and nutrition, animals can survive outdoors without problems. Rabbit breeds bred for fur and fluff are especially resistant to cold weather. But meat breeds are also quite adapted to unfavorable conditions, since they also have a dense undercoat.
The following breeds of rabbits are suitable for outdoor keeping in winter:
- Californian;
- Soviet chinchilla;
- white New Zealand;
- Viennese blue;
- butterfly;
- Burgundy;
- downy angora;
- downy white;
- white giant;
- black-brown;
- Russian ermine;
- silver;
- Soviet marder.
Proper maintenance, quality care and good nutrition are factors that contribute not only to maintaining the health of the rabbit population during the winter, but also to the appearance of offspring with strong immunity. By taking good care of rabbits in winter, the farmer receives healthy animals with good weight in the spring and ensures business profitability.