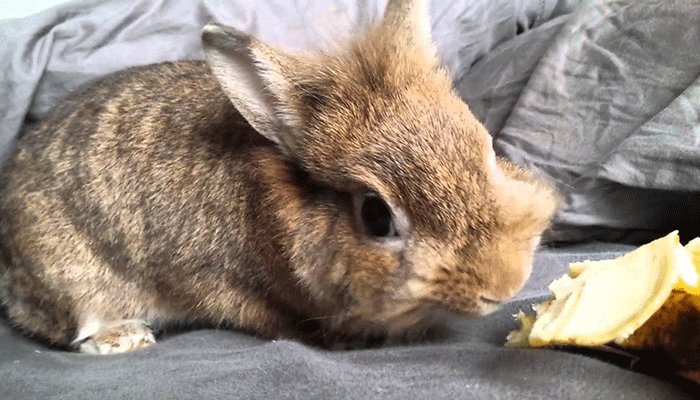
In the autumn-winter period, the diet of herbivores does not contain enough vitamins and microelements, which they received from greens. Rabbit breeders introduce vegetables as complementary foods to the main diet. The question remains controversial: can rabbits be given raw or boiled potatoes? The consequences of feeding tubers depend on the form and volume in which the animals eat them.
Is it possible to give rabbits potatoes?
Potatoes are a valuable vegetable crop.The tubers include:
- carbohydrates;
- vitamins;
- macro- and microelements;
- cellulose;
- amino acids.
The raw tuber contains vitamins B, C, H, PP, and folic acid. Of the extensive list of minerals, potatoes are richest in potassium, magnesium, and iron.
The source of carbohydrates is starch, the content of which in potatoes is from 10 to 25%, depending on the variety and ripening period. In 100 grams of starch, carbohydrates make up 80%, fats account for 0%, proteins – 0.1%. The calorie content of potatoes is determined by the starch content: 327 kilocalories/100 grams.
Raw
Under natural conditions, rabbits do not eat raw potatoes. The reason is starch, which is poorly digestible without heat treatment. But because of the vitamin component, it makes sense to accustom the animals to eating raw potatoes in small quantities.
Tubers can be given:
- peeled;
- in peel (clean);
- entirely;
- cut into pieces;
- separately;
- as part of a mash with other vegetables and herbs.
Potatoes must be healthy, ripe, without damage, rot, green spots, sprouts or eyes.
Boiled
Boiled potatoes can be used to feed animals, as they are easily digestible and provide good weight gain. During heat treatment, most of the vitamins are destroyed, but starch and fiber are preserved. The boiled product will be useful for rabbits from 1 month. Meat rabbits can be given boiled potatoes daily, increasing its volume to 50% of the weight of the fed food.
Boiled potatoes can be given:
- mixed with feed;
- as part of moistened mash;
- separately.
Based on boiled potatoes, you can prepare briquettes from acorns with the addition of bran and water.Acorns are an astringent and help in treating animals with intestinal upset.
Dried and crushed acorns are mixed with boiled potatoes, a small amount of bran and water to a dough-like state.
The resulting mass is laid out in molds and dried in the oven or in the sun until it becomes dry and light, like cookies. Briquettes are not only a therapeutic and preventive product, but also satisfy the natural need of rabbits to chew. Adding briquettes to the diet protects the cell from destruction.
Potato tops
You can feed potato tops to rabbits if there are no traces of pesticides from the Colorado potato beetle on them. In dry summers, potato tops are harvested as a supplement to hay and twig feed. In summer, the tops are dried before being given to rabbits. Stems and leaves should be clean, without signs of disease.
Potato peeling
Potato peelings are added to food in small quantities after boiling or drying. The peel should be clean, without eyes or green spots. Boiled and dried peelings are crushed and mixed with the main feed, as a vitamin-carbohydrate supplement.
Rules for introducing into the diet
Potatoes are not a natural food source for rabbits, which requires knowledge about their introduction into complementary foods.
For young animals
Raw potatoes are offered to rabbits after 3 months, when their digestive system is able to absorb starch without heat treatment. The initial portion is 10-20 grams, in the form of finely chopped pieces. The maximum amount is 50-70 grams per day mixed with grain and mixed feed. Boiled vegetables are given starting from 1 month. Potatoes are introduced into the diet of young rabbits in the autumn-winter period to increase the calorie content of the feed.The amount of boiled tubers in the feed mixture should not exceed 10%.
For adults
Rabbits, starting from 4 months of age, are given potatoes raw and boiled. To quickly gain weight, meat breeds can be given up to 200 grams of boiled potatoes (or up to 50% of the total weight of the feed) per day. Raw tubers yield no more than 70 grams in crushed or whole form. The boiled product should be given to ornamental animals with caution so as not to cause obesity. When kept in cages, the daily norm should not exceed 50 grams; when kept free-range – 70 grams.
When is it better not to give potatoes?
Tubers, neither raw nor cooked, are not given to female rabbits after birth and during lactation. Starch will cause blockage of the mammary glands and the death of the rabbits. The vegetable is contraindicated for breeding animals (males and females) a week before mating. High-calorie food leads to obesity, which affects the reproductive abilities of animals. Males and females who have gained excess weight refuse to mate. For animals that are weakened after illness or have digestive problems (liquid feces), raw potatoes are not introduced into the diet.
Useful tips
To introduce raw potatoes into complementary foods, you should choose varieties with a low starch content. Such a vegetable is easier to digest by the animals’ digestive system and will not cause obesity. Potatoes do not contain protein. The predominance of this vegetable crop in the feed will cause muscle atrophy, the degeneration of muscle tissue into fatty tissue.
Green or sprouted potatoes are harmful to animals, both raw and cooked, due to solanine, a toxic substance. The content of plant glycoside (alkaloid) in healthy tubers used for food is 0.01%.During germination and in the light, its percentage in the vegetable crop increases sharply. The organic compound has a bitter taste. Ingestion by both humans and animals can cause poisoning. For rabbits, the lethal dose is 0.06-0.12 grams per kilogram of live weight.
In potato tops, flowers contain the most solanine (0.73%). Feeding tops in large quantities before and during flowering can lead to the death of animals.
In the stems and leaves, the alkaloid content changes during the growing season:
- before flowering – from 0.085 to 0.114%
- during flowering – 0.055%;
- after flowering – 0.037%;
- in dried tops – 0.01%.
Solanine irritates the intestinal mucosa and affects the nervous system. In mild forms of poisoning, rabbits experience diarrhea; in severe cases, they experience loss of coordination of movement, wobbly rear, and decreased response to external stimuli.
Before boiling potatoes, the eyes and sprouts of the tubers should be removed. Water after boiling the tubers cannot be used in the diet of animals.