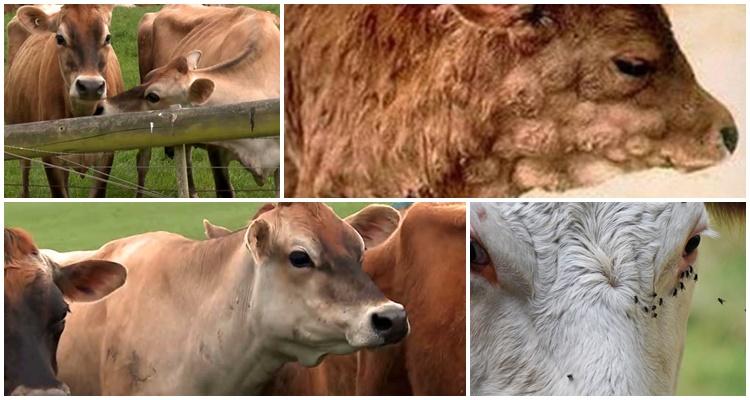
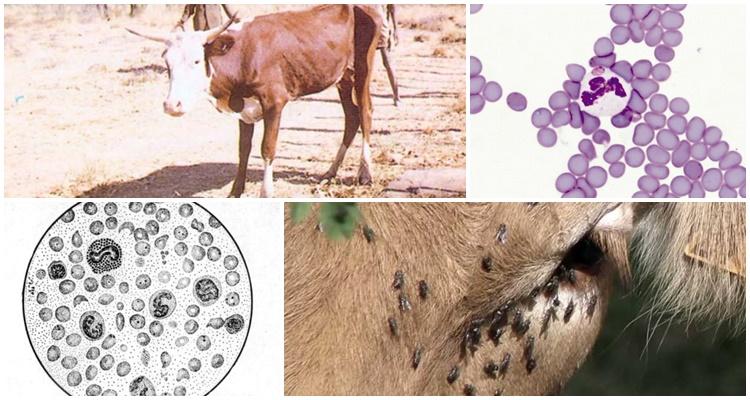
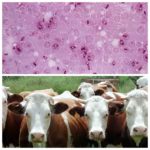
The development of bovine anaplasmosis is quite common and can cause serious harm to the health of animals. The disease rarely causes death, but is characterized by a severe course. It can be quite difficult to deal with it. Therefore, it is recommended to combine the fight against the disease with preventive measures that are aimed at preventing re-infection.
What is anaplasmosis: pathogens and vectors
This term refers to the pathology carried by small microorganisms. Their sizes are 0.2-2.2 microns. They enter red blood cells and multiply there. Anaplasmas cause metabolic disorders and impair the distribution of oxygen in the body. This causes the development of anemia in animals.
Zones and conditions of infection spread
This pathology is widespread everywhere. Its causative agents are considered to be intracellular bacteria. Parasites form colonies and reproduce by fission or budding. Bacterial carriers can be mosquitoes, ixodid ticks, and horseflies. They are also spread by biting beetles, midges, and burner flies. Sometimes infection occurs through infected instruments. The peak incidence occurs in spring and summer – it is during this period that carriers of pathology wake up and become active.
Features of the development of the parasite
Anaplasmas are two-host parasites. They absorb nutrients from the blood of cattle. However, they spread from one individual to another with the help of various insects. When a pathology carrier attaches itself to an animal, dangerous bacteria enter its blood.
Some time after infection, anaplasma begins to actively develop in blood cells - most often in red blood cells. Although sometimes they also penetrate platelets and leukocytes. As a result, within a few days entire colonies are formed in the blood of animals. Bacteria reproduce by budding or fission.
Bacterial microorganisms enter the body of ticks or other insects while sucking the blood of infected individuals. In the body of insects, pests mainly reproduce in the intestines and Malpighian vessels. From there they can be passed on to offspring.
Signs and symptoms of infection
Key manifestations of pathology are associated with blood clotting disorders. At the same time, the following characteristics predominate in cattle:
- a sharp increase in body temperature;
- change in the shade of the mucous membranes - an excess amount of bilirubin in the blood of infected animals causes yellowing of the membranes;
- increased heart rate;
- heavy intermittent breathing due to oxygen deprivation;
- loss of appetite;
- cough;
- problems in the functioning of the digestive organs;
- physical exhaustion, rapid weight loss;
- general weakness and apathy;
- decrease in milk yield;
- swelling in the extremities and in the chest area - observed in advanced cases;
- general weakness;
- anemia;
- convulsions;
- fever;
- miscarriages in pregnant individuals;
- sterility in males.
As an additional sign, a change in the eating habits of sick individuals can be identified. Due to metabolic disorders, animals may try to eat inedible objects. When the disease is chronic, intermittent fever occurs. In animals, body weight decreases and hypotension of the digestive tract is observed. The mucous membranes remain pale.
Diagnosis of the problem
Identifying pathology can be quite difficult. Its manifestations largely coincide with other diseases, which creates difficulties in diagnosis. In such a situation, there is a risk of choosing the wrong treatment regimen.
Most often, the pathology is confused with the following disorders:
- piroplasmosis;
- babesiosis;
- leptospirosis;
- anthrax;
- theileriosis.
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is recommended to conduct laboratory tests on a blood smear of an infected animal.
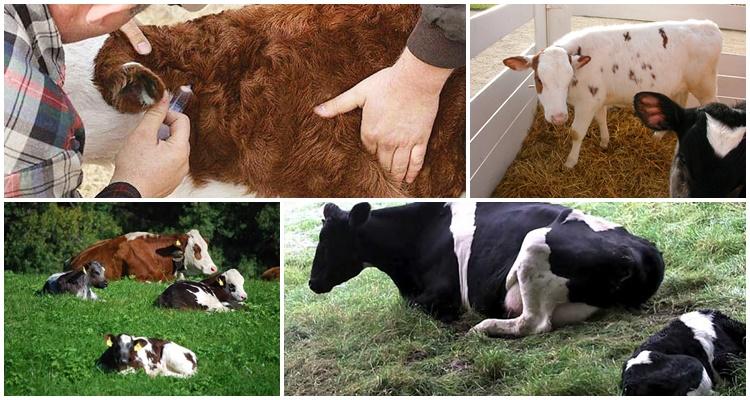
How to treat anaplasmosis in cattle
At the first symptoms of anaplasmosis in cattle, it is recommended to isolate the infected animal from the rest of the livestock. It is important to confirm the diagnosis and select treatment. To cope with the disease, a whole range of medications are used. The most commonly prescribed drugs are:
- “Terramycin”, “Tetracycline”, “Morphicycline” - they are recommended to be mixed with a solution of novocaine at a concentration of 2% and administered intramuscularly. It is recommended to administer 5-10 thousand units of the product per 1 kilogram of body weight. The drug should be used for 4-6 days.
- "Oxytetracycline-200" is a drug that has a long-term effect. It must be administered once a day with an interval of 4 days.
- “Sulfapyridazine-Sodium” – it is recommended to mix this product with distilled water in a ratio of 1:10. For 1 kilogram of weight you need to use 0.05 grams of the product. It is recommended to use it for 3 days.
- “Biomycin” – it is recommended to use 10 milligrams of the product per 1 kilogram of body weight. This must be done for 7 days.
- “Ethacridine lactate” - 200 milligrams of the product are recommended to be mixed with 60 milliliters of medical alcohol and 120 milliliters of distilled water. The composition must be administered once a day.
For symptomatic treatment, it is recommended to use antipyretics and analgesics. Animals with this diagnosis suffer from metabolic disorders in the body. Therefore, they definitely need to be provided with a dietary ration. The basis of the menu should be juicy greens. Drinking plenty of fluids is important.
In the cold season, the development of anaplasmosis is caused by a lack of vitamins and minerals in animal feed. In this case, the disease itself provokes metabolic disorders. This is why it is so important to give your pets vitamin and mineral supplements. The following substances must be used:
- phosphorus, calcium, vitamin D - a deficiency of these substances provokes a deterioration in appetite, makes animals timid and causes developmental delays;
- copper – should be an essential part of any balanced diet;
- manganese, vitamin A, cobalt - a lack of these substances causes digestive problems and leads to exhaustion;
- zinc, iodine - a lack of these elements provokes a decrease in milk yield;
- vitamin E - deficiency of this element often provokes anemia and even dystrophy.
Possible danger
With the development of anaplasmosis, a pronounced anemia syndrome often occurs. Its appearance is caused by a significant decrease in the volume of red blood cells in the body. In this case, the parameters are restored extremely slowly. The painful process has a long course.
Despite the complex course of the pathology, it rarely causes death. This is due to the biological characteristics of parasites - primarily, their virulent properties.
How to prevent the occurrence of the disease
To minimize the risk of developing pathology, it is recommended to engage in prevention.
In this case, the following rules should be observed:
- Monitor the condition of pastures for grazing animals.
- New individuals should be quarantined. It should last 1 month. During this period, diagnostic examinations should be performed to help ensure the absence of parasites.
- Periodically treat animal fur with acaricides. It is recommended to perform the procedure weekly.
- Promptly isolate sick individuals from the rest of the population.
- When purchasing animals, be sure to check the veterinary certificate.
- Systematically disinfect the premises where pets live.
There are also special vaccines that help develop immunity to anaplasmosis pathogens. This allows you to protect animals from the development of the disease for 10-11 months.
Anaplasmosis is considered a dangerous disease that often occurs in cattle. It is provoked by microscopic parasites that lead to the development of anemia. This causes various problems in animals. Therefore, at the first symptoms of a disorder, it is recommended to consult a veterinarian.