Bovine babesiosis is a common pathology that is invasive in nature. It is found in various regions and can lead to serious damage and death of large numbers of livestock. That is why it is so important to prevent the disease in a timely manner. If symptoms appear, it is recommended to immediately isolate the sick animal and take measures to treat it.
Description of the disease
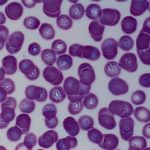
Babesiosis is a dangerous invasive disease that is associated with damage to animal tissues and organs by protozoa.Parasitic Babesia are considered very dangerous. These microorganisms have spread throughout almost the entire planet. The only exception is Antarctica. The disease is characterized by vague symptoms. It is often identified with piroplasmosis.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
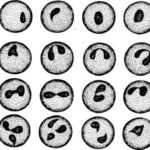
The causative agents of the pathology are considered to be fairly large parasites. They can come in different forms. However, the most common type is paired pyriform. Parasites usually enter blood cells. As a result, potent toxic substances accumulate in the body, which poison it.
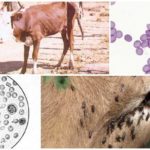
The main carrier of the disease is considered to be parasitic ticks of the genus Ixodes. Therefore, it is usually seasonal in nature and is associated with a period of mass development of ticks. Peak insect activity occurs in June-July. Almost all members of the genus spread a specific pathogen.
First of all, the disease manifests itself in the form of complex lesions of the nervous system and dysfunction of organs and systems. The pathogen is quite contagious. Therefore, it is impossible to prevent babesiosis without annual prophylaxis. In cattle, the pathology causes the following symptoms:
- decreased milk production and loss of appetite;
- increase in body temperature to 40-42 degrees, feverish state;
- blanching of the mucous membranes - they quickly acquire a yellow tint;
- pink color of urine - towards the end of the disease it becomes dark red;
- cessation of milking for 4-6 days;
- watery composition of blood.
Diagnosing the problem
To make a diagnosis, a comprehensive approach is used. To do this, it is worth taking into account the clinical picture and the results of microscopic examination of smears. Serological diagnostic methods are considered informative.
How to treat babesiosis in cattle
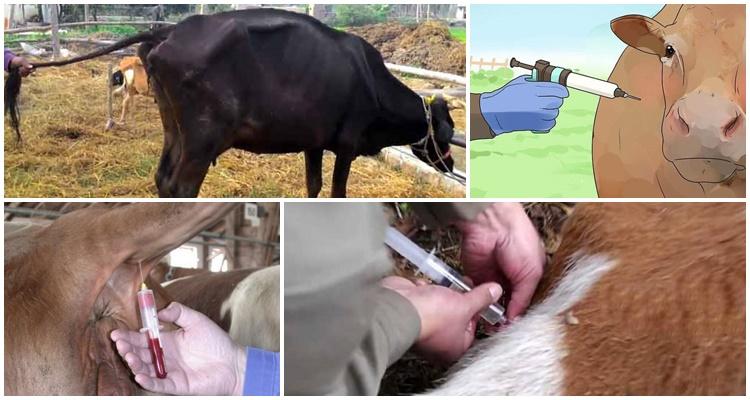
When Babesia is detected in the body, it is important to take immediate action. The parasite provokes rapid damage and causes negative changes in organs and systems. In this case, affected animals often die. Therefore, at the first symptoms of pathology, the animal needs peace and comfort. It is recommended to feed him properly and give him antiparasitic drugs.
First of all, the pet should be provided with complete rest and isolated from other animals. Increased activity and prolonged physical activity negatively affect the general condition of the animal. This negatively affects the state of the immune system. As a consequence, there is an increase in invasive lesions. To isolate affected animals, move them to a bright room. In this case, the temperature should be at least +15 degrees. Relative humidity cannot exceed 85%. The main treatments for babesiosis include:
- "Azidin-vet" - the drug is administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously. It must be entered 1 time. If the condition does not improve, a second injection is given after 24-30 hours.
- "Akaprin" - the composition is used for intramuscular or subcutaneous injections. The product should be administered in the form of an aqueous solution with a concentration of 1%.
- "Hemosporidin" - the drug is suitable for subcutaneous or intramuscular administration. In this case, a 1-2% aqueous solution is used. It is recommended to administer the substance 2-3 times at intervals of a day.
- "Imidocarb" - administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously.The product is used 1 time. If the condition does not improve, the administration should be repeated after 1-2 days.
Additional drugs that are used to treat livestock include the following:
- "Albargin" is a strong antiparasitic agent that has a complex effect. The drug is administered 1 time via intravenous injection.
- Vitamin B12 – used to stimulate hematopoietic functions. The composition is suitable for injection. 1-2 milligrams of the substance are required per animal. It is recommended to use the drug for several days until the blood structure improves.
- Glauber's salt - improves the condition of the body with the development of ventricular atony. The drug is used in the form of a solution with a concentration of 1%. The substance is washed into the rumen using a gastric tube.
- Caffeine - used to normalize the functions of the heart and blood vessels. The substance is suitable for subcutaneous injection. To do this, it is worth using 5-10 milliliters per 1 individual per day. It is recommended to administer the solution once. If necessary, the procedure should be repeated.
- Sodium chloride is used to combat persistent atony of the proventriculus. The product is suitable for intravenous administration. In this case, it is recommended to use aqueous solutions with a concentration of 10%. For 1 individual you need to use 200-300 milliliters. The duration of therapy depends on the degree of complexity of the disease. It usually takes several days.
For treatment to be effective, it is important to provide cattle with a proper and healthy diet.
At this time, the animal’s body needs vitamins, minerals and other beneficial elements that activate the immune system.
To do this, it is recommended to use chopped meadow grass hay, green grass, and fresh root vegetables. To improve the condition of animals, fresh milk or skimmed milk is suitable. This type of feeding is recommended to be used 3 times a day. 1 animal will require 1.5-2 liters.
Prevention measures
To avoid the development of pathology, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- graze livestock on proven pastures that are protected from ticks;
- keep cattle in a stall;
- monitor the appearance and keep animals clean;
- during the mass development of ticks, treat the outer covers every 10 days with acaricides - these include “Permethrin”, “Butox”;
- in regions with unfavorable conditions, at the beginning of the mass development of ticks, administer “Azidin-vet” or “Hemosporidin” once.
Is it dangerous for humans?
In humans, this pathology usually develops against the background of a weakened immune system. However, such cases are extremely rare. With normal immunity, the disease is asymptomatic.
Babesiosis is one of the most complex parasitic infestations commonly found in cattle. Every year the pathology spreads over large areas. That's why sick animals are found everywhere. To cope with the disease and prevent the death of livestock, it is important to take timely measures.