Brucellosis is a disease of infectious etiology in cattle, which also poses a danger to humans. In many animals, the consequences of pathology are spontaneous abortions, defective discharge of the placenta, inability to reproduce, stillbirth of young animals or early mortality. Brucellosis is a socially dangerous disease, which is why when it is detected on farms, a quarantine regime must be introduced.
What is bovine brucellosis
Brucellosis is an infectious disease transmitted from cattle to humans and manifested by multiple lesions of internal organs and systems. The pathology was discovered by the scientist D. Bruce in 1886, the pathogens were called Brucella, and the disease itself was called brucellosis.
The causative agent is a group of pathogenic microorganisms that are small in size and non-motile. They do not form spores, but can form capsules. Brucella remains viable in conditions favorable to them (warm soil, manure, feed) for up to several months. Under the influence of direct ultraviolet rays they die after 1.5 days.
The danger of the disease is the high risk of human infection through consumption of meat, milk and products prepared from it (cheese, cottage cheese, butter) obtained from cows with brucellosis. A person can become infected through contact with cattle excretions, for example, when fertilizing a summer cottage with manure from sick animals.
Transmission routes
The infectious disease is transmitted through injured skin, mucous tissue of the respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract, as well as through punctures of the skin made by mice and blood-sucking insects.
A cow can become infected from an already sick animal. Often the pathogen is taken from contaminated amniotic fluid at the birth of a calf and spreads from a dead fetus during an abortion. The sources of the disease are affected fluids - urine, semen, discharge from the genital tract, milk, and feces.
How to recognize the disease
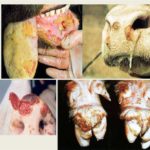
The incubation period of brucellosis lasts from one to three weeks; before that, a blood test does not detect antibodies to the pathogen. In most cases, the disease is asymptomatic and chronic. Often, farmers can suspect pathology only after several abortions in adult cows, occurring in the second half of gestation. Common complications of childbirth with brucellosis are retention of the placenta with further infection of the uterus, the development of mastitis, and prolonged fever.
Acute form
Acute disease has the following symptoms:
- temperature rise to 38 OWITH;
- increased sweating;
- lethargy, weakness;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- eye damage;
- inflammatory process of the heart, joints, bronchi and lungs.
There are severe pain in the ligaments, muscles, loss of appetite and weight loss.
Subacute animals
Signs of the subacute form boil down to the appearance of joint inflammation (arthritis) in cows. Knee, carnal and other joints are painful and swollen. The subcutaneous tissue of the extremities and vaginal mucosa are affected, and the udder becomes inflamed. Bunions and abscesses may form on the hind legs. Sometimes the temperature rises to 37-37.5 O, but decreases on its own. The subacute form of the disease can last up to three to six months.
Chronic
In the chronic form of brucellosis, the cow is sick for six months or longer. Symptoms of the disease are erased. The pathology manifests itself as low-grade fever, chronic inflammation of the joints, and damage to the spine. Involvement of the nervous system in the process causes the development of neuritis and polyneuritis.
Diagnostic methods
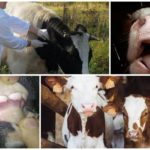
Since the signs inherent in brucellosis can also appear in other diseases, the main diagnostic method is taking blood to detect antibodies to the pathogen. In parallel, pathogenic microbes are searched for in milk and amniotic fluid. Pieces of tissue from a stillborn calf are examined. An allergy test is required.
The diagnosis of brucellosis is sometimes made posthumously, when the pathogen is identified during a biopsy of lymph nodes, joints, and examination of the testes in bulls.
Treatment regimen for the disease
It is recommended to treat brucellosis with antibacterial agents, but this group of drugs is effective in the acute form of the disease. Antibiotics stop the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and help destroy their colonies.
Antibacterial drugs are combined with each other, medications are changed to avoid loss of sensitivity of the pathogen to the active substance. Combine two or three drugs from the following:
- "Tetracycline";
- "Doxycycline";
- "Streptomycin";
- "Gentamicin";
- "Netilmicin".
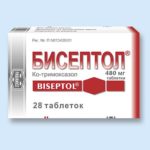
The listed drugs have a better effect on the pathogen with the simultaneous use of drugs that can penetrate into the affected tissues - Biseptol, Ofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin and Fleroxacin (this medication is considered the most effective).
To relieve pain and reduce the level of inflammation, drugs from the group of anti-inflammatory nonsteroids are used - Brufen, Indomethacin. Reducing the intoxication of the body of cows is achieved by prescribing “Methionine” and “Adenosine triphosphate”.
In case of mass death of the pathogen in animals, a pronounced allergic reaction may occur, which is reduced by antihistamines. At the recovery stage, B vitamins and immunomodulators (Dibazol, Timalin) are necessarily introduced into therapy.
Vaccine and general prevention
Immediately after identifying an infected animal, it is isolated from the general stall. To avoid further spread of the disease, disinfection is carried out with bleach or caustic soda (a solution of 3% concentration). General prevention involves preventing infection of cows in healthy farms and includes:
- regular disinfection and disinsection;
- maintaining proper herd recruitment;
- compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards when feeding, watering, keeping, and mating animals;
- conducting routine serological examinations of cattle for brucellosis.
Workers caring for animals are required to clean their hands with a 0.5% concentration of chloramine solution or soda ash. Washbasins with warm water, hygiene products and clean towels should be installed in the barn.
The most cost-effective means of preventing brucellosis is routine vaccination. Generally recognized and effective vaccines against bovine disease:
- Brucella abortus: CZV B-19 and RB-51 CZV;
- Brucella melitensis CZV Rev-1 and
Vaccines provide powerful and long-lasting immunity against brucellosis.
Is it possible to eat meat and drink milk from patients?
When brucellosis is detected on a farm, it is declared unfavorable. Animals with diagnosed pathology and showing symptoms of brucellosis are sent for slaughter. It is prohibited to slaughter livestock on farms where cattle are bred; for this purpose, cows are sent to meat processing plants and sanitary slaughterhouses.
It is not recommended to eat the meat of sick animals, despite the fact that the causative agent of brucellosis quickly dies when boiled.
Milk and cream obtained from cows from disadvantaged herds should be pasteurized at 70 OC for half an hour or boil for 15-20 minutes. Milk taken from cows reacting to brucellosis tests is used only in animal feeding, after boiling for half an hour.
To prevent the spread of brucellosis in a healthy farm, it is important to carry out frequent hygienic treatment of stalls. The causative agent of the disease is easily destroyed by a solution of carbolic acid in 2% concentration, solutions of chloramine and bleach (concentration 0.2-1%), solutions of creolin and Lysol in 3% concentration.
To prevent the disease in humans, it is important to eat cow meat purchased at points with certificates confirming the absence of brucellosis in cattle. For prevention, it is recommended to pasteurize milk from domestic cows for 20-30 minutes.