Diseases of cattle can be different, some are pronounced, the cows immediately signal them to the owner, others, which also bring considerable losses to the farm, are almost invisible at first glance. Such diseases include the development of ovarian hypofunction in cows, because the animal loses productivity and requires immediate treatment.
Causes
Hypofunction of the ovaries in cows is a hormonal disorder in which the maturation of the follicle stops, after synchronization there is no estrus or the animals do not come into heat. There are several reasons for its development:
- violation of the diet and maintenance of animals;
- hormonal disorders after calving;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- age of animals;
- infectious diseases of livestock;
- helminthic infestations.
It is necessary to restore ovarian function, since milk production is significantly reduced and milk yield is reduced.
Symptoms of the disease
Cows with ovarian hypofunction do not come into heat and are obese or underweight. The disorders develop gradually, at the initial stage the sexual cycle is disrupted, followed by anaphrodisia (cessation of estrus, lack of sexual arousal). With hypofunction, insemination does not produce results, the egg is not fertilized.
If, after synchronizing the animals on the farm, the animals do not come into heat, stimulation of ovarian function is required.
Hypofunction is often observed when kept in stalls in the autumn-winter period. With normalization of nutrition and daily walks in spring and summer, ovarian function is restored partially or completely.
How to diagnose the disease
If cow is in heat absent, she does not come into heat for a long time, a rectal veterinary examination is necessary. It allows you to judge the condition and size of the ovaries, uterus, and mucous membranes of the genital organs. Upon examination, the presence of hypofunction is indicated by a reduced size of the internal genital organs. The ovaries are dense, smooth, without traces of follicles and corpus luteum. Rectal massage of the uterus causes very weak contractions of the organ. The mucous membrane of the cervix and vagina is pale and insufficiently moisturized.
The highest quality diagnostics are carried out using an ultrasound diagnostic device (ultrasound).
If the cause of hypofunction is errors in nutrition and maintenance, it can be quickly eliminated, then the production of hormones returns to normal, without harm to the cow’s body. This is especially true for young animals.
Treatment regimen for ovarian hypofunction in cows
First, the animals’ nutrition is adjusted, vitamins and essential mineral supplements (salt, chalk) are introduced into the diet. Provide animals with daily walks for 1-2 hours. Most cases of hypofunction occur in February-April; in March and April, cows can be outside without fear of catching a cold.
The barn should have windows; natural light prevents the development of ovarian hypofunction. High humidity, infrequent manure removal, and dirt in stalls can provoke metabolic disorders and, as a result, suppression of ovarian function.
The easiest way to normalize the hormonal function of the ovaries is a rectal massage of the uterus and ovaries and subsequent irrigation of the uterus with a hot solution of table salt 1% or baking soda - 2%. Solutions must be heated to +45 °C. It is better to use ready-made sterile saline solution. The massage is carried out once a day for 5-7 minutes, repeated every other day.
To actively stimulate the hormonal function of the ovaries, Gonadotropin serum is used. It is administered to the animal with “Proserin” 0.5% or “Carbohaline” 0.1%. SFA (pregnant mares serum) and CCFA (pregnant mares blood) are used to stimulate ovarian function. Fresh colostrum is injected under the skin no later than 12 hours after milking.
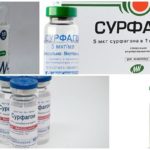
The use of a more modern drug, Surfagon, can increase the amount of the hormone in the body by 50 times. The product can restore ovarian function; in addition, it increases fertility, accelerates and normalizes the reproductive cycle, gets rid of follicular cysts, and prevents embryo death in the early stages of pregnancy. The drug is most active 2-3 hours after administration and remains in the body for 5-6 hours, after which it disintegrates. Intramuscular administration of the drug is required.
Danger of pathology
Hormonal imbalance in cows, if left untreated, leads in severe cases to infertility. Then the productivity of the animal and the quality of the milk are significantly reduced. It is not profitable to keep such a cow.
If hormonal imbalances are quickly corrected, the cow is young and strong, receives a balanced diet and is kept in good conditions, there will be no consequences for the animal. An aged or weakened animal may not recover from such a hormonal imbalance, and the cow will have to be culled.
Disease prevention
To prevent ovarian hypofunction in cows, they should be provided with a balanced diet. In summer, be sure to take animals out to pasture. Provide cows with daily walks of 2-3 kilometers. Provide veterinarian supervision for animals, mandatory inspection of livestock after calving, and periodic obstetric and gynecological examinations. Provide cows with vitamins before and after calving to prevent decreased immunity.
Animals need to be given anti-worm medications at least 3 times a year, treated for infectious diseases, and vaccinated. Replace older livestock with young animals. Systematically check animals for mastitis.
The disease is not fatal and not dangerous for animals. It can be treated well if timely measures are taken, and it is possible to maintain the level of lactation, the quality and fat content of the product.