Dermatological diseases often cause a decrease in the productivity of cows and the development of severe systemic pathologies. Psoroptosis manifests itself in cattle with local skin symptoms at the initial stage, but quickly progresses, depleting the cattle. The contagious disease is easily transmitted to other animals, so it is necessary to promptly respond to signs of invasion and take therapeutic and preventive measures.
Reasons for appearance
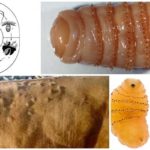
The causative agent of the disease is an acarimorphic mite of the genus Psoroptes bovis, which parasitizes the surface of the skin of cattle.In most cases, the source of infection is a sick animal, and the cause is direct contact and shared objects (drinkers, feeders, brushes). A person who has been in contact with a sick animal can also bring a tick to a cow.
Favorable conditions for the reproduction of the parasite are high humidity, thick hair and weak immunity of the carrier.
The following factors contribute to the development of psoroptosis in cattle:
- unfavorable living conditions for animals (overcrowding, untimely change of bedding, treatment of feeders and drinkers);
- improper care;
- unbalanced diet;
- the animal has chronic diseases;
- hypovitaminosis.
Ticks primarily attack weakened cows and fragile calves. Often the reason for the spread of invasion is the joint walking of the herd with animals from disadvantaged farms, violation of the requirements for mandatory isolation of infected cattle.
Cows are vulnerable and susceptible to illness during cold periods. The peak incidence occurs in late autumn and early spring. In the summer, when the herd spends most of its time in the fresh air, eating fresh grass, psoroptosis usually occurs hidden.
Signs of psoroptosis in cattle
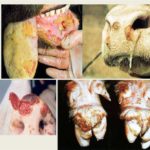
Symptoms of psoroptosis are observed in cattle at the end of the incubation period, during which the mite reproduces. From the moment of infection until the first signs of the disease appear, it takes from 1 to 6 weeks, which depends on the level of local and general immunity of the carrier. Psoroptosis in cows is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- skin itching;
- the formation of bald patches in the primary foci of localization of the parasite (the area of the base of the horns, the base of the tail, the sacral area);
- dryness, roughening of the skin;
- formation of keratinized folds on the skin;
- agglomeration of lesions.
The acute onset of psoroptosis is accompanied by severe itching until the end of the incubation period. In subacute cases, there may be no itching. The tick, sucking its proboscis to the epidermis, releases a toxin and starts the inflammatory process. The resulting papules burst. Dried exudate in the form of pale yellow crusts becomes noticeable on the animal's fur.
The cow tries to relieve the condition by scratching the itchy areas on nearby objects and licking the lesions. Saliva creates a favorable environment for parasites.
As the disease progresses, rough skin folds form (mainly in the neck area), there are more lesions, and they merge. The lower parts of the extremities, the groin and scrotum area, the lower part of the peritoneum, and the front side of the head remain intact. Without treatment, the cow weakens and becomes vulnerable to other infections, which can cause the death of the animal. It is important to diagnose the disease in time and begin treatment.
Diagnostic measures
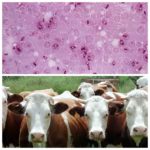
Diagnostics includes a visual examination of the animal and laboratory tests. It is necessary to exclude psoroptosis with similar manifestations of skin inflammation of a different nature (dermatitis, eczema, lichen, sarcoptic mange, trichodectosis).
To confirm the diagnosis, a scraping is taken from the skin and sent to the laboratory for acarological examination.
Treatment of the disease
The sick cow is isolated and treatment with local antiparasitic agents is started. The keratinized layers of skin and crust must be softened 3 days before treatment of the animal using oil, fish oil or soap solution, and then carefully removed.
For local treatment of psoroptosis in cattle the following is used:
- dust (300 grams per 1 animal);
- 2% oil solution of colloidal sulfur (irrigate the surface of the skin at the rate of 2 liters per 1 animal);
- "Tiovit" (ready-made preparation of colloidal sulfur);
- "Isofen";
- "Baitikol";
- "Psoroptol";
- "Acrodex";
- "Dermatosol".
Bathing preparations are also used for cattle: “Tactic”, “Bipin”, “Kenaz”. Severe inflammation and the addition of a microbial infection require the administration of antibiotics.
Prevention
To prevent infection of cattle with psoroptic mange and stop the spread of the disease, it is necessary to provide the animals with comfortable conditions, proper care and regular veterinary control.
The set of preventive measures includes:
- compliance with sanitary rules for keeping livestock;
- providing adequate care;
- regular and balanced nutrition;
- timely treatment of diseases;
- eliminating contact of the herd with sick and disadvantaged animals;
- isolation of cows with signs of disease.
If cattle with symptoms of psoroptosis are detected in a herd, it is recommended to carry out preventive treatment of the entire livestock.