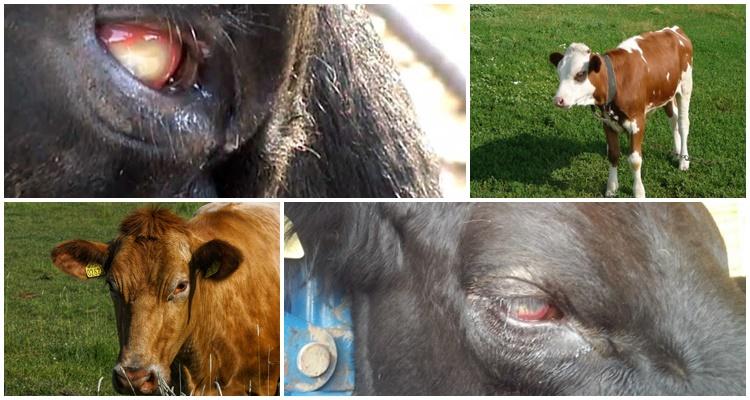
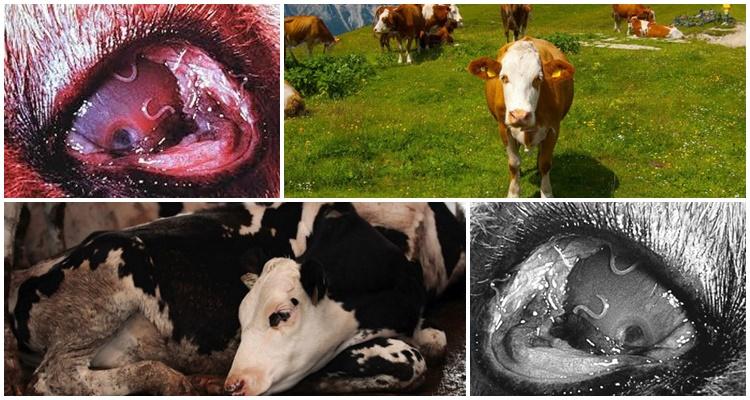
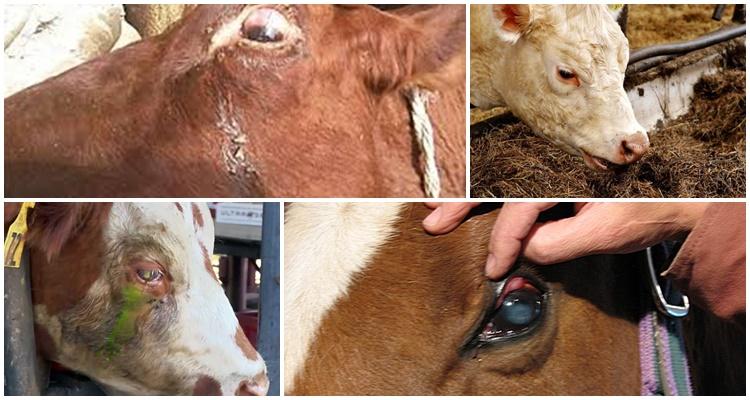
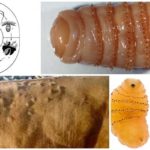
Bovine thelaziosis is a dangerous pathology that can cause blindness in the animal. The causes of the disease are parasites. They affect the eyes of an infected individual, which provokes the development of purulent conjunctivitis. In addition to visual impairment, the infestation causes a general decrease in productivity and impaired milk quality. The disease is transmitted by cowflies, so preventing its development can be quite problematic.
Causes of thelaziosis in cattle
To understand the principle of cattle infection, you need to familiarize yourself with the biology of parasite development. Before entering the animal’s body, the larva goes through a number of stages:
- Initially, the Thelasia female produces a certain number of larvae, which are considered non-invasive. They are not dangerous to animals.
- The larvae are then consumed by cowflies, where their development begins. Due to short modifications, which take about a month, the larva becomes invasive. At this stage, it can develop in the host’s body.
- Cow flies fly up to individual animals and land on an area that is as close to the eyes as possible. After this, they distribute the larvae along the eyelids and near the palpebral fissure. Many young thelyas can be identified already in early July.
- After infection, the so-called incubation period begins. At this time, the larvae gain strength to take part in reproduction.
Thelyasia that have reached sexual maturity live for a maximum of 1 year and then die. They are able to remain vitally active in winter. However, during this period the parasites do not produce offspring. This is due to the absence of disease outbreaks during the cold season.
Symptoms of the problem
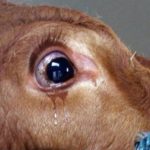
Treatment of thelaziosis in cattle is characterized by specific development. Moreover, each stage has certain stages. At the initial stage, the pathology is rarely noticeable. At the first stage, the following signs appear:
- increased lacrimation, shine in the eyes of infected animals;
- inflammation of the conjunctiva, appearance of a red tint.
The second stage of the disease is more obvious than the first. Many pastoralists identify pathology at this stage. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- swelling and increase in the size of the inflamed conjunctiva;
- discharge of a whitish fluid from the eyes - this includes mucus and pus that seeps from the tear duct.
At the second stage, thelaziosis is easily confused with conjunctivitis. Drug treatment provides results only in the first two stages.
Sometimes it is possible to cure the animal when moving to the next stage. However, the longer the parasites remain in the cow's eyes, the worse the prognosis.
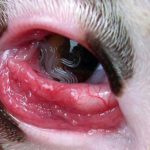
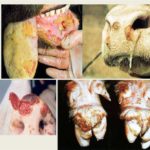
At the third stage, irreversible changes begin in the animal’s body, which can cause final blindness. The following manifestations indicate that the process is neglected:
- clouding of the cornea - it may bulge or perforate;
- general oppression of the animal;
- temperature increase.
At this stage, many animals develop a purulent form of conjunctivitis. In infected animals, a decrease in milk yield is observed and the quality of milk deteriorates significantly. If calves are affected by thelyasia, they lag behind in development and slowly gain body weight. There is an opinion that the younger the animal, the worse it tolerates thelaziosis, therefore treatment must begin at the first symptoms.
How to diagnose the disease
The diagnosis can be made after a veterinary history examination. Diagnostic methods depend on the stage of the disease. When primary symptoms appear, a laboratory test of the tear fluid is performed. In some individuals, the first stage is practically asymptomatic. However, it is impossible to identify the disease by external examination. In laboratory conditions, specialists study tear fluid under a microscope. In the presence of pathology, it is possible to identify sexually mature nematodes and their larvae.
A differential diagnosis is required. Thelaziosis is recommended to be distinguished from rhinotracheitis, rickettsial keratoconjunctivitis, and vitamin A deficiency. It should also be differentiated from non-contagious conjunctivitis and herpes virus infection. The pathology is characterized by the following pathological changes:
- development of keratitis and conjunctivitis;
- corneal clouding;
- formation of ulcerative defects on the cornea.
Methods of treating the disease
Taking into account the severity of thelaziosis, the veterinarian will select a treatment regimen. It should be comprehensive and include antibiotics, broad-spectrum anthelmintics, and immunomodulators. Homeopathy, medicated ointments and drops are also often prescribed to cattle.
Antibiotics
Antibacterial agents from the macrolide group help to obtain good results in the treatment of thelaziosis. They are recommended to be placed once into the cavity of the conjunctival sac. The product should be used for 5 days. The most common drug is Azithromycin. For cattle, the dosage is 0.9-1.1 grams. At the first symptoms of thelaziosis, you need to immediately contact a veterinarian, without waiting for subsequent stages to appear.
Drops, ointments
To speed up recovery, special solutions and drops should be used.
The most effective drugs include:
- Solution of iodine with potassium iodide. To prepare it, you need to mix 1 gram of crystalline iodine with 1.5 grams of potassium iodide. Dilute the resulting composition with 2 liters of purified water. Rinse the affected eye three times daily. It is recommended to do this with a syringe with a rubber tip. 1 procedure requires 75 milliliters of solution.
- Boric acid solution with a concentration of 3%. It is recommended to moisten a cotton swab and wipe the walls of the eye cavity and the inner corner of the eye. Carry out the procedures three times a day for 5-7 days.
- Antibacterial penicillin drops for 50 thousand units. They are used on prescription from a veterinarian.
- Novocaine-penicillin ointment. This remedy is used for the appearance of ulcerative defects on the eye cornea. Before use, it is recommended to keep the composition for 5-7 days at a temperature of +2-4 degrees.
- Infusions of chamomile, wild rosemary, calendula in a ratio of 1:100.
In addition, the main therapy is supplemented with retrobulbar blockade using novocaine solution. To do this, 15-30 milliliters should be injected from below and above the eye. It is recommended to do this for at least 5 days until the symptoms go away.
Antiparasitic agents
To completely eliminate the pathology and prevent the occurrence of thelaziosis in other animals, antiparasitic treatment is carried out for the entire herd. The most effective antiparasitic agents include:
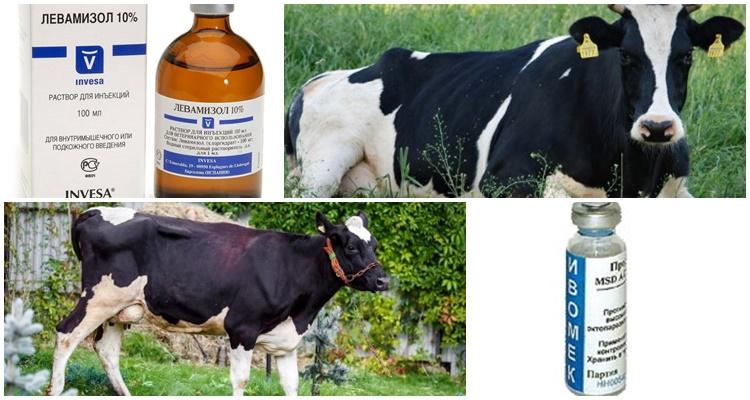
- "Ivomek" - administered once. It is recommended to use 1 milliliter of medicine per 50 kilograms of individual weight.
- "Levamisole" - administered once. For 1 kilogram of body weight, you should use 0.0075 grams of the product.
- "Rivertine" - should be administered for 2 days, 0.2 grams per 1 kilogram of weight.
- "Faskoverm" - administered once. It is recommended to use 0.005 grams per 1 kilogram of weight.
- A ditrazine citrate solution with a concentration of 25% is administered subcutaneously at intervals of 24 hours. The dosage is 0.016 grams per 1 kilogram of weight.
Prevention of cow thelaziosis
To avoid the occurrence of thelaziosis, it is recommended to perform preventive deworming and try to exterminate pasture flies.Preventive deworming is performed on animals during stabling and before being put out to pasture.
To kill flies, it is recommended to use the following:
- "Ectomin" at a concentration of 0.1%;
- “Neostomazan” at a concentration of 0.25% with an interval of 2-3 weeks;
- "Neocidol" at a concentration of 0.1%.
To combat flies indoors, it is recommended to use Ectomin at a concentration of 1-2%. You can also use Neocidol emulsion at a concentration of 0.5%. Use 50-100 milliliters of product per 1 square meter. It is recommended to bring animals into the premises no earlier than after 2 hours.
Bovine thelaziosis is a rather dangerous pathology that can cause complete blindness. It is almost impossible to cope with advanced forms of the disease. Therefore, at the first sign, you should consult a veterinarian.