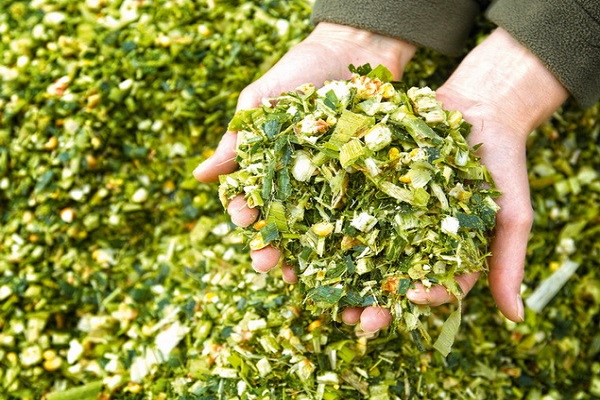
Corn for silage is grown using a special technology. To grow a quality product, you need to follow all agricultural techniques and use modern technology for making silage. This is a valuable plant food for domestic herbivores. Silage can be combined (it is made from cobs) and regular (the entire green part of the plant is used).
Corn for silage growing features
To obtain the most productive mass, corn silage is made by following certain technological techniques.But before you start making it, you need to get acquainted with the rules of growing the crop.
Cultivation of corn for silage differs from grain technology. The similarity is that the same grain varieties of corn are selected for silage and the same sowing dates are observed.
Before growing corn for silage, you need to know its biological characteristics. Corn is an annual heat-loving cereal crop with a well-developed stem, leaves and roots. At first, the roots grow in the upper, heated layers of the soil, gradually deepening by 1–2 meters.
The stem is 7 cm thick; one plant can have up to 25 leaves. The stem is divided into nodes, the number of which does not increase with plant growth. It can grow up to 5 meters in height by lengthening the space between the nodes. On the upper part there is a male inflorescence - a panicle. Stepchildren are formed on the lower nodes. If corn is grown for grain, they should be removed.
Corn seeds begin to germinate at a temperature of +10 degrees. The warmer it gets outside, the more actively the crop grows. At a temperature of +15 degrees, the first shoots appear after 8 days. The culture can withstand frosts down to -3 degrees, lack of moisture and heat, but only during the germination period. If such unfavorable factors appear during flowering, the yield may be significantly reduced.
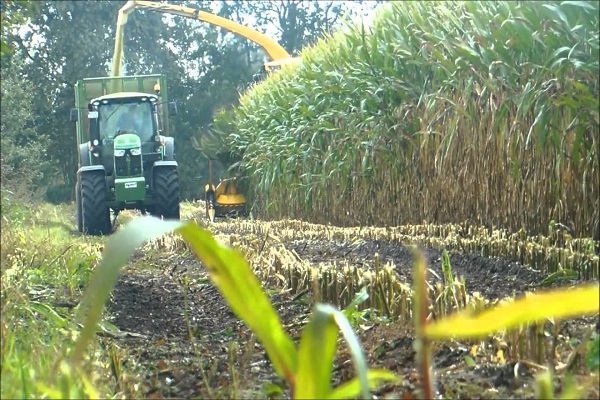
It is very important to determine the correct timing of harvesting corn silage, maintaining the dry matter ratio and stage of maturation. Dry matter content is a reliable criterion for determining the quality of corn silage. Harvesting is best started when the dry matter content is 28–30%.
Crop rotation
With good care, the yield of corn silage per 1 hectare can be 50–60 tons. If corn is grown for feed, then for the rapid development of green mass, you need to water the crop as often as possible. When using special irrigation systems, the yield can be increased to 80–100 tons per hectare.
Silage corn is used as feed for cattle, rabbits, and poultry due to its high feed value. The beneficial properties of the product include:
- the functioning of the digestive organs in animals is normalized;
- muscle mass increases;
- animal blood parameters improve;
- the amount of milk production in cows increases;
- contains many vitamins, amino acids, organic fats.
To obtain a high-quality and rich harvest, you also need to observe crop rotation. It is advisable to plant after cereals or legumes, perennial grasses. The best predecessors are vegetables such as potatoes, cucumbers, tomatoes, and beans. Every 3–4 years it is recommended to change the planting location of the crop.
The soil
For sowing corn for silage, chernozem, loamy, sandy loam and sandy soil with normal acidity is best suited. To cultivate corn, you need to carefully prepare the soil.
If the soil is prone to waterlogging and high acidity, then cultivating the crop will not work. It is recommended to lime acidic soils 1–2 years before sowing.
Corn needs good aeration, especially during the germination stage. The embryos absorb a lot of oxygen, and a good harvest will only occur if there is about 20% oxygen in the soil air.
In the fall, the area is dug up to a depth of 25–30 cm. When weeds appear or after rains, harrowing is carried out. At the same time, you can add organic fertilizers, such as manure.In the spring, harrowing is carried out to a depth of 5 cm, after which the soil is cultivated to a depth of 8 cm.
The best precursors for corn For silage, winter and spring grain crops, buckwheat, potatoes, and legumes are considered. It is not recommended to plant after beets, millet and sunflower, as these crops lead to a deficiency of microelements in the soil and a lack of moisture.
Corn varieties and hybrids
For growing corn There is no need to wait for the grain to fully ripen for silage. Therefore, it is better to choose late-ripening varieties, which accumulate many nutrients upon reaching milky-waxy ripeness. To increase the size of the crop, you can sow early and mid-ripening varieties mixed together with late-ripening varieties.
The most popular varieties of corn grown for silage include: Sterling, Partizanka, Osetinskaya, Dnepropetrovsky, Adavey, Dubrava, Kalina. All these varieties have increased digestibility by animals, develop quickly and produce a rich harvest.
In order for the seeds of the selected variety to germinate well and the plant to have good immunity, they must be disinfected. For this purpose, seeds are treated with manganese.
Corn stover (stalks and leaves after decobs) of any variety are best ensiled at about 45% moisture content. In this state they soften, after which they are crushed into small pieces (1 cm). The straw can be dried in special drying units or spread out in a thin layer on level areas. Dry straw is used in granulated or briquetted form.
Sowing dates
The fields begin to be sown only after the soil has warmed up to +12 degrees to a depth of 8 cm. If the soil is heavy and clayey, then the seeding depth should be about 4 cm.The dates fall approximately at the beginning of May.
After sowing, it is necessary to carry out harrowing. The second harrowing is carried out after 4–5 pairs of leaves have unfolded on the plant. More details on the technology of cultivating corn for silage can be found in the table.
| Types of jobs | Dates | Requirements |
| Autumn plowing | From late August to early October | Layers of earth are turned over, plant debris is removed from the site |
| First harrowing | First days of April | Loosening depth 4 cm |
| Second harrowing and cultivation | April | Cultivation depth 15 cm, weed removal, cultivation is carried out to a depth of 5 cm |
| Sowing | From May 5–10 | Seed preparation |
| Harrowing before emergence | A week after sowing | Loosening the top layer of soil |
| Harrowing by seedlings | On the 20th of May | Loosening and killing weeds |
| Treatment of beds from weeds and treatment with herbicides | As it grows | The treatment is carried out with drugs that are diluted according to the instructions. |
| Harvest | Mid August | Cutting and chopping the plant |
To get a large harvest of cobs and prevent problems from developing, you need to follow the basic rules of cultivating the crop. What is important is the density of sowing, compliance with crop rotation, soil composition and proper preparation, timing of sowing and harvesting, methods of controlling weeds, pests and diseases.
Density of sowing corn for silage
The density of corn depends on the ripeness group, variety and soil moisture. The norm for sowing corn for silage is a planting density of 55–100 kg per hectare of area. The density of plants in the garden for green mass in the garden is 6–8 plants per meter of land. In these cases, the ears are almost never set; only green mass is collected for feed.Most of the plants are in the shade, more moisture is retained in the soil - these are all the conditions necessary for growing plants for food.
Early varieties of corn You can sow thicker than late-ripening ones. The higher the plant stem stretches, the fewer plants should be sown per 1 square meter. m. An increase in the standing density of corn for silage by at least 10% leads to an average yield.
When sowing seeds in the fields, maintain a distance between rows of 65–70 cm. In the garden, they are sown mainly in a square-cluster method according to a 40x40 cm pattern.
Fertilizers
To get a good harvest of corn intended to feed herbivores, you need to apply fertilizers on time. Corn responds equally well to both mineral and organic fertilizers.
When growing corn for animal silage, the emphasis is on the development of green mass, so early stages of corn development Nitrogen is of great importance. In case of its deficiency, the growth and development of the plant slows down. Calculate approximately 25 kg of nitrogen fertilizer per hectare. After 3–4 weeks, fertilization is repeated.
With a lack of potassium, the leaves become dark green, the growth of the green and root parts of the plant slows down, then the leaves begin to curl, turn yellow and dry out.
Throughout the growing season, corn needs phosphorus. The crop especially needs this microelement after germination, as well as during the flowering and grain formation phase. With its deficiency, the formation of grains in the cob slows down, the leaves become dark green with red-violet veins and gradually die off.
It is recommended to apply phosphorus and potassium fertilizers in the fall.Unlined manure is especially useful for corn silage. It is useful to apply nitrogen fertilizers between rows before sowing.
Herbicides
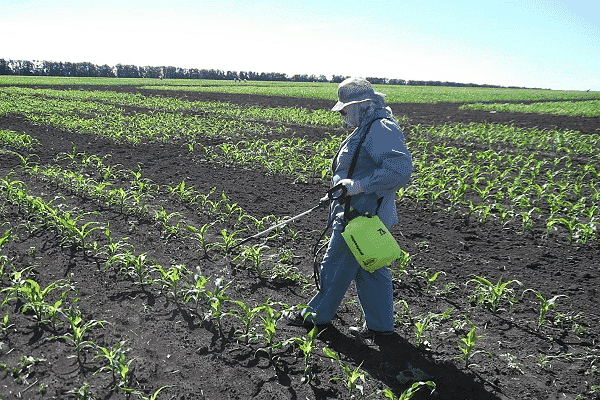
Weeds cause a decrease in yield, the spread of pests and various diseases. Therefore, in addition to observing agrotechnical practices, the cultivation of corn cannot be done without timely weed control. The use of herbicides is considered an effective method.
Before the emergence of seedlings, herbicides such as Aurorex, Erodikan, Reglon are incorporated into the soil (consumption rate is about 8–10 l/ha). The surface of the earth can be treated with preparations such as Harnes, Roundup (consumption rate 3 l/ha).
If pre-emergence herbicides have not shown their effectiveness, use post-emergence preparations: Ballerina, Milady, Adengo, Dialen, Turbin, Desormont, Luvaram (consumption rate 2 l/ha). The preparation Cowboy 200 g/ha can be used.
Silage harvesting begins in August. When sowing 50 thousand seeds per hectare, about 55 centners of feed units per hectare and about 220 centners of green mass are obtained.
Diseases and pests
If diseases or pests are detected on plants, the problem must be dealt with in a timely manner. This will prevent the massive spread of infection, which will save most of the harvest.
Among the pests most often attacked:
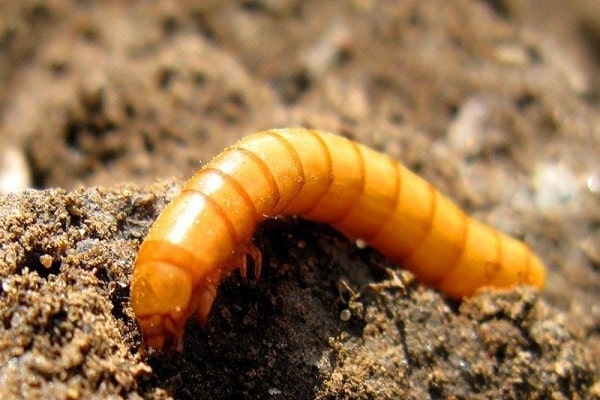
- wireworm (the larvae penetrate the stems, cobs and after a couple of weeks the grains turn black);
- meadow moth (larvae feed on young leaves of the plant);
- leaf cutworm (insects gnaw not only the entire green part of the plant, but also the grains);
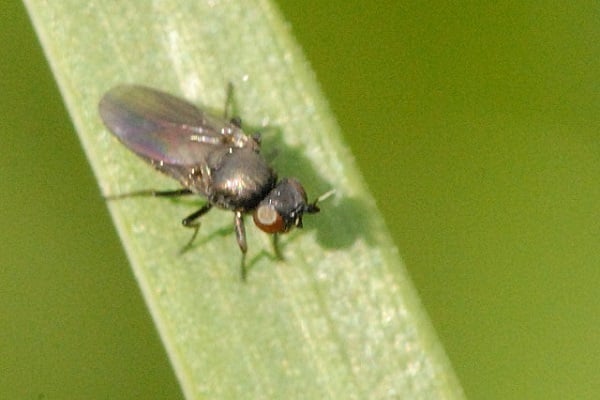
- Swedish oat fly (insects eat young shoots).
The diseases that most often affect are powdery mildew, rust, and blister smut.Corn leaves turn pale, black dots and stripes may appear, dry out, and curl.
It is very important to properly treat the seeds before planting and carry out preventive treatments with insecticides. You can use drugs such as Force, Karate, Vantex.
To reduce the risk of disease development and pest infestation, it is necessary to follow the technology of cultivating corn for silage. It is imperative to monitor crop rotation, deeply cultivate the soil in the fall, treat the seeds, sow the seeds on time, and harvest.
Harvesting corn for silage
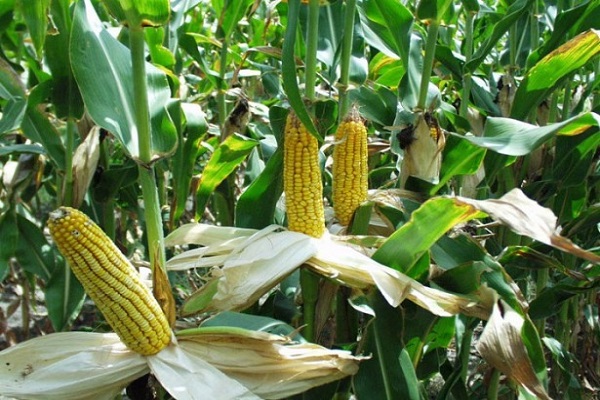
In corn, there are 4 stages of grain development: grain formation (lasts two weeks from the beginning of fertilization), milk and milk-wax (these two stages last about 10–12 days), wax (about 15 days) and full maturity.
Harvesting corn for silage begins from the moment the grain reaches milky-waxy maturity. When pressing on the grain, a light liquid and a thick mass are released. At this stage, the grains contain an average of 46% moisture, the leaves 34%, and the stems 80%. Harvesting continues until the waxy ripeness phase is reached.
Mowing is carried out with special agricultural equipment (forage harvester) to a height of 12–15 cm. By observing the timing and rules of harvesting, you can obtain healthy and high-quality food for pets.