Breeding birds is a labor-intensive task. Birds often succumb to various infections and viruses. One of the serious pathologies is Newcastle disease in domestic chickens.
- What is Newcastle disease?
- Forms of the disease
- Scourge Form
- Doyle form
- Beaudette form
- Hitchner form
- Is Newcastle disease dangerous for people?
- Causes
- Signs and symptoms of Newcastle disease
- Diagnosis of the disease
- How to treat pathology
- Possible consequences
- Prevention of occurrence
- Purity
- Disinfection
- Quarantine
- Chicken vaccination
To prevent the development of the disease and save the livestock, you should familiarize yourself with its features.
What is Newcastle disease?
Newcastle disease is an acute, highly contagious disease of birds caused by viruses and hemorrhagic diathesis. The digestive tract, respiratory tract and central nervous system are affected. Waterfowl are not susceptible to pathology.
Death occurs in 80% of cases. The virus may spread to nearby farms and people.
Forms of the disease
Newcastle disease is acute, the clinical picture is easily recognized. There are 4 forms of the pathological process, differing in the intensity of symptoms and the scale of damage. Young chickens are at greater risk.
Scourge Form
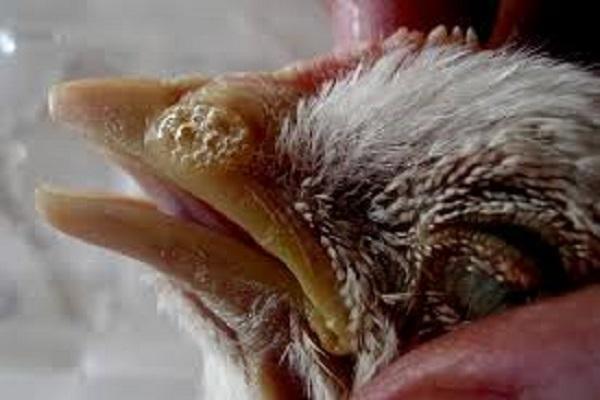
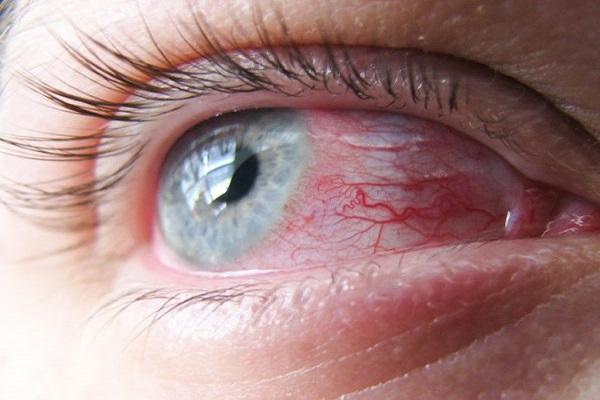
An acute form of infection of viral etiology, entails the death of almost all chickens. Symptoms include cough and breathing problems. The conjunctiva of the eyes becomes inflamed.
Doyle form
The form of Newcastle Doyle's disease is experienced most severely by birds, they lose their appetite, muscle spasms, weakness, and accumulation of mucus in the nasal passages appear. Chickens often go blind and paralysis of the limbs occurs.
Beaudette form
Compared to previous forms, this one is lighter. With successful treatment, 2/3 of the population is saved. Young chickens suffer the disease more severely than adults and often die after serious damage to the central nervous system. The mold is used to make a live vaccine.
Hitchner form
The mildest form is Hitchner's, birds lose their appetite, become weak, and overall performance decreases. Due to its low virulence, the variety is used to create most vaccines. Death is rare.
Is Newcastle disease dangerous for people?
Newcastle pathology does not threaten adults, but infection is possible through interaction with a sick bird, since the virus is transmitted by airborne droplets.You can also become infected by rubbing your eyes with dirty hands. The incubation phase for humans lasts 1 week. The symptoms are similar to the first manifestations of the flu. Hyperthermia, runny nose, and general weakness in the body begin. In more rare cases, diarrhea and conjunctivitis occur.
Prevention includes thorough hand washing after working in the chicken coop, avoiding eating raw eggs, and wearing a mask when getting vaccinated.
The virus poses a danger to children, but such cases are rare. In its severe form, Newcastle disease causes brain damage.
Causes
The sources of Newcastle disease pathogens include infections. 2 days after infection and one day before the onset of symptoms, the virus is released during breathing and coughing, with discharge from the oral cavity, feces, and eggs.
Possible causes of Newcastle disease include the following:
- poor sanitation in the chicken coop;
- lack of vaccination of birds;
- contact of domestic animals with wild birds, lack of demarcation in the form of a poultry house.
Passive-immune chickens infected from birth and adults with low protective properties can be carriers of pathogenic agents.
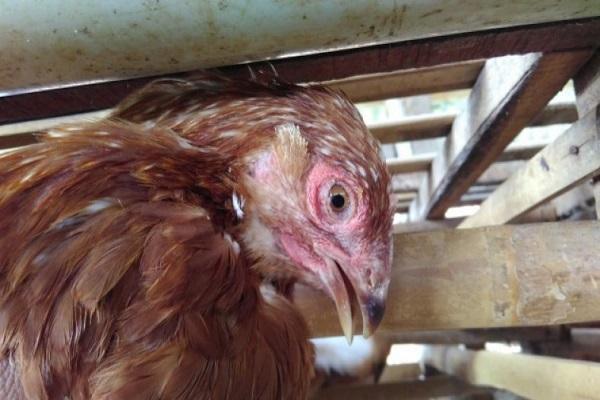
Signs and symptoms of Newcastle disease
In chickens, the incubation period lasts 3-6 days, the symptoms are varied and depend on the form of the pathology and the stage of its development.
The main manifestations of Newcastle disease include:
- refusal of food;
- decreased activity;
- lack of response to sounds;
- hyperthermia up to 44 degrees;
- conjunctivitis and clouding of the eye mucosa;
- increase in goiter, release of foul-smelling exudate from the beak;
- green diarrhea with mucous impurities, sometimes bloody streaks;
- breathing problems - the beak is open, the chickens are coughing, sneezing, stretching their necks, wheezing.
In acute cases, birds die within 2 days. When the nervous system is damaged, coordination is impaired, chickens walk in circles, tremors, convulsions, wing paralysis, and neck twisting are noted. Death occurs within 3-12 days.
When the bird recovers, it remains a source of infection for 2-4 months. It is necessary to isolate recovered individuals from healthy chickens for this period.
Diagnosis of the disease
To establish a diagnosis, the results of clinical and pathological studies using laboratory tests are needed. The spread of infectious agents to nearby territories is also taken into account. A veterinarian is called to the site; you cannot independently determine a verdict based on symptoms.
How to treat pathology
There is no therapeutic regimen for Newcastle disease. The poultry farmer must only stop the spread of the virus. The following complex of manipulations is carried out.
- All excrement is removed from the chicken coop and burned.
- The room is treated with caustic soda, formaldehyde solution, carbolic acid and alcohol.
- Sick individuals are killed and cremated.
After processing, the chicken coop is closed. When the quarantine is completed, the premises are chemically treated. Sometimes a veterinarian will prescribe antibacterial agents that are given to isolated, sick chickens. The success of therapy is questionable and depends on the stage and form of the pathological process.
The following events are prohibited:
- export birds and their eggs;
- sell the meat of a dead bird, its down and feathers.
It is necessary to deny access to the territory to unauthorized people.
Possible consequences
If left untreated, the livestock dies and the virus spreads to nearby birds.Children can become infected, and the well-being of adults will worsen. When new chickens are brought into the house, they also become infected with the virus because the room is not treated.
Prevention of occurrence
On poultry farms, chickens are vaccinated. Chicken coops are disinfected approximately 2 times a year. Newcastle disease virus is susceptible to 2% sodium hydroxide solution and 3% bleach solution.
Purity
The poultry house must be cleaned once a week. It is important to remove all feces and fallen feathers and burn them.
Disinfection
The poultry house should be periodically disinfected with ultraviolet rays and lamps should be installed in it. They also resort to quartz. Disinfection should be carried out once every 2 weeks.
Quarantine
The poultry farm is closed for quarantine for a period of 1 month. Notify local authorities, veterinary services, supplying farms and partners about viral infection of livestock. Poultry farms are fenced and access to third parties is prohibited. The supply of birds is suspended and trade is stopped. Diseased individuals are destroyed by strangulation; a bloodless method is required. To prevent the spread of viral agents, while killing birds, close all windows, doors, and hoods.
The corpses are burned in pits 0.7 meters deep or in ovens. The equipment and burial site are disinfected. Healthy individuals are kept in isolation and vaccinated. Before the quarantine is completed, the poultry house is disinfected. Metal equipment is not resistant to chlorine and alkali. Their treatment is carried out with formaldehyde, wet or aerosol. When mass mortality of birds occurs due to Newcastle disease, quarantine is established for 5 days. During this time, all individuals are destroyed, making complete disinfection of the territory dangerously contaminated.
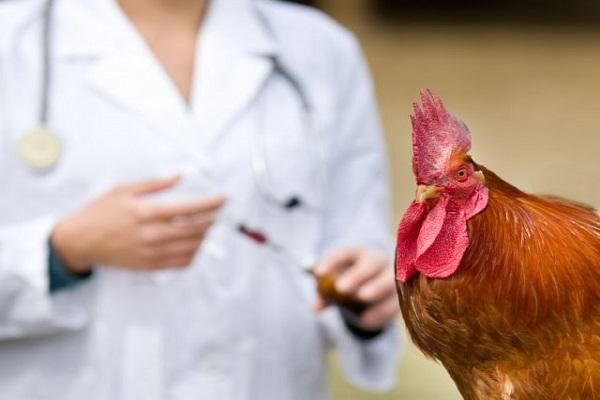
Chicken vaccination
Chickens are immunized with vaccines based on live or inactivated viral strains. The choice of drug depends on the age of the bird, the well-being of the area, and the direction of the farm.
There are such features of different types of vaccinations:
- inactivated - the manipulation is carried out when the chickens reach the age of 120 days, the duration of immunity protection is 6-12 months;
- live - weakened viral agents are used in areas disadvantaged by pathology - the North of the Caucasus, the South, drugs are prepared from the La Sota or Bor-74 strain.
After vaccination, birds develop antibodies within 3 months. Mostly young chickens are vaccinated at 15 days. Young eggs of egg breeds are vaccinated again from 2 months. The effectiveness of forming an immune response is determined by the conditions of keeping and quality of nutrition of chickens, and the method of vaccination.