Rhinopneumonia is considered a dangerous disease. Pathology of this type provokes severe complications, including a sharp weakening of the immune system and loss of the ability to bear offspring. The basis for preventing the development of equine rhinopneumonia is a vaccine, the instructions for use of which contain the rules for use and storage, as well as possible complications that arise after administration of the medicine.
Release form and composition of the vaccine against rhinopneumonia
The vaccine against rhinopneumonia is produced in the form of a dry porous mass of pale yellow color, packaged in a transparent container. The basis of this remedy is the avirulent strain of the virus that causes this disease. The pathogen was previously reproduced in a culture of cells taken from a piglet and subjected to freeze-drying.
This type of vaccine is used to prevent the spread of rhinopneumonia in horse breeding farms. The product is mainly used on disadvantaged farms with a high risk of spreading the virus.
In addition to the cultured pathogen, the vaccine contains edible gelatin. The initial mass is not introduced into the animal’s body. Before vaccination, the product is first diluted in a 0.9% isotonic sodium chloride solution or distilled water. The initial mass should completely dissolve, leaving no sediment or flakes behind.
Principle of operation
The principle of action of the vaccine is based on the ability of the animal’s body to repel the attack of viruses. This product contains a weakened pathogen. After the latter is introduced into the horse’s body, the animal’s immune system begins to produce antibodies that fight the virus. Thanks to this, stable immunity to the effects of a specific pathogen is developed.
The effectiveness of vaccination depends on how accurately the rules of the procedure are followed. Animals develop immunity to rhinopneumonia after 10-14 days. However, a one-time procedure gives a temporary effect. That is, in order to develop stable immunity to rhinopneumonia, the horse will need to be revaccinated.
Despite the fact that a strain of the virus is introduced into the animal’s body, the resulting meat or milk from mares can be eaten after 10 days.Such products are not dangerous to humans.
Advantages and disadvantages
The usefulness of vaccinating horses is due to the fact that this procedure:
- reduces the risk of developing rhinopneumonia;
- reduces the likelihood of complications, including the need for induced abortion;
- prevents the development of an epidemic among horses within the same farm;
- minimizes the risk of developing paralysis and paresis;
- allows you not to restrict animals in movement.
It should be understood that a vaccine is not a drug that cures a horse of rhinopneumonia. If the disease develops, other means will be required. The vaccine is used only to prevent the occurrence of rhinopneumonia. Moreover, this remedy does not exclude the possibility of developing the disease in animals.
The second pronounced drawback of the vaccine is that complications are possible after administration. This is due to the body’s reaction to the incoming pathogen. In such cases, a temporary increase in temperature and other symptoms characteristic of rhinopneumonia cannot be ruled out.
Indications for use
Indications for the use of the vaccine against rhinopneumonia are:
- unsuitable conditions of detention;
- young age;
- purebred.
Rhinopneumonia develops in horses of any type and age. However, the younger the animal, the higher the likelihood of contracting a viral disease. More often, this pathology is diagnosed in young animals under one year of age. The disease is also typical for purebred horse breeds. Rhinopneumonia does not develop in large and small cattle, humans and pigs.
Vaccination against this disease will be required for horses that are not fed properly. The development of pathology is facilitated by insufficient immunity and closely related breeding.In addition, improper use of the animal in some cases provokes the spread of the virus among the livestock.
Instructions for using the vaccine
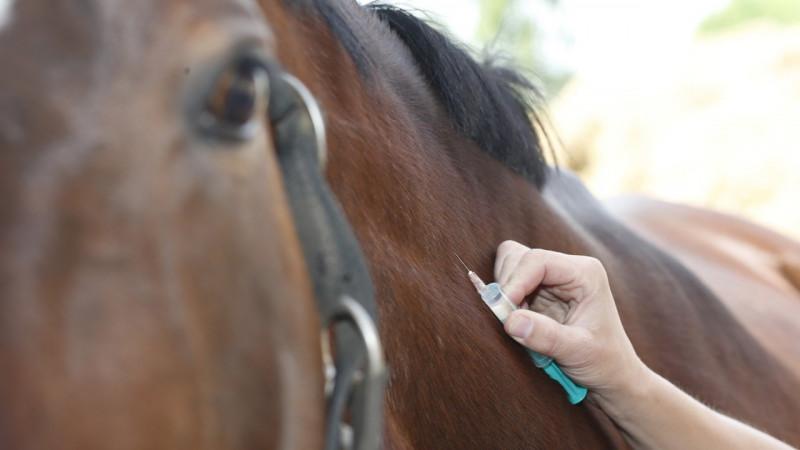
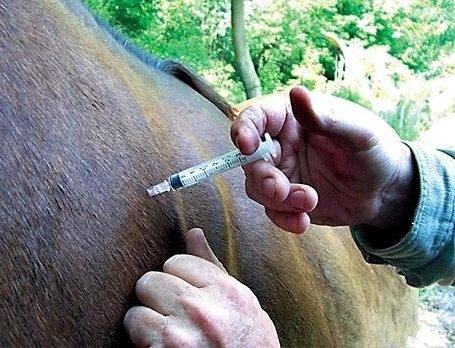
Before administration, the vaccine must be diluted in distilled water or sterile saline solution heated to a temperature of 18-25 degrees. When carrying out this procedure, it is necessary to follow the rules of antiseptics: perform manipulations with gloves. You should also boil syringes and needles, and treat the injection site with alcohol or iodine.
The vaccine against rhinopneumonia is injected intramuscularly into the neck area. Each time you can use no more than 2 milliliters of the drug. The frequency of vaccine administration depends on the type of animal. For pregnant mares, this procedure is carried out:
- at 1-3 months of pregnancy;
- 3-4 months after the first vaccination (no later than 7 months of pregnancy).
Adult horses are also vaccinated twice every 3-4 months. For young animals, different tactics are used to prevent rhinopneumonia. Stallions up to one year old are vaccinated for the first time at the age of 3 months, and again 3-4 weeks before the end of breastfeeding.
An important condition for the success of the prevention of rhinopneumonia is annual revaccination. Each subsequent procedure is carried out according to the given algorithm. If the horse is used in sports competitions, then vaccination/re-vaccination is carried out no later than 2 weeks before departure from the farm.
After each procedure, the animal requires supervision for a week.
Are there any side effects and contraindications?
Due to the fact that the animal’s body reacts to the administered vaccine, after 2-3 days the temperature may rise to 39.5 degrees. This reaction is not considered dangerous.Body temperature is usually restored without outside intervention.
Vaccination/re-vaccination is prohibited if the horse has been diagnosed with diseases of the respiratory system. The procedure is also contraindicated in animals with elevated body temperature.
Storage conditions
The vaccine remains effective if the storage conditions of the drug are met. The latter must be kept in a tightly closed container. The drug should be stored indoors away from direct sunlight at a temperature of 6-8 degrees. If these conditions are met, the vaccine has a shelf life of 12 months. Unused drugs must be disposed of. Expired vaccines should not be administered to animals.