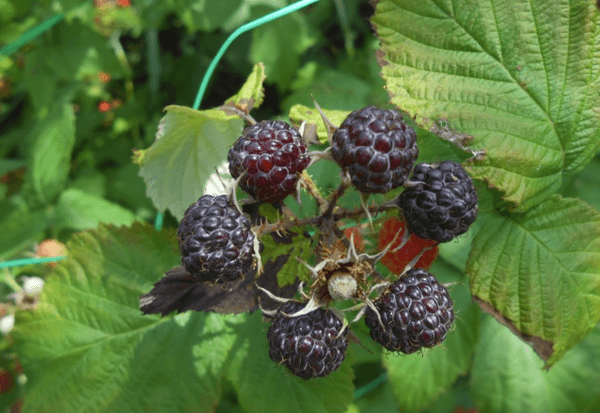
Raspberry fruits have many beneficial substances that have a beneficial effect on human health, and black raspberries contain even more antioxidants. Growing black raspberries has become very popular among gardeners; they are unpretentious, as they require almost no care.
- Black raspberry and its features
- Description and characteristics of culture
- Diseases and pests of black raspberries
- How to plant a black raspberry bush on a plot
- Optimal timing
- Preparation of planting hole and seedlings
- Technology and seating charts
- Nuances of crop care
- Frequency of irrigation of bushes
- Loosening the soil
- Principle of cutting and shaping
- How and what to feed black raspberries
- Preventative treatments
- Black raspberry propagation
- By layering
- Root suckers
- Green and woody cuttings
- Seeds
- Popular varieties of black raspberries
Black raspberry and its features
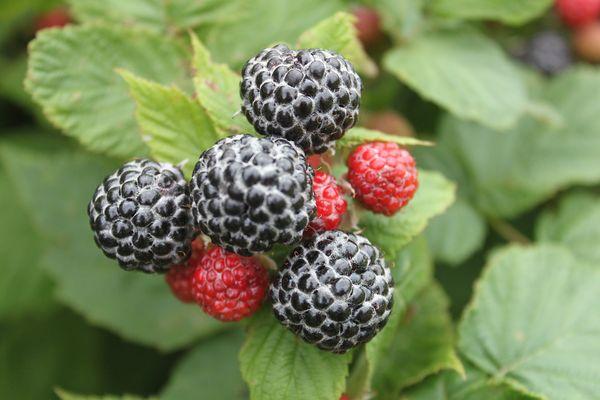
Black and red raspberries differ in the composition of nutrients, the size of the berries, and taste. The peculiarity of black raspberries is their sweet taste with a honey, tart aftertaste and slight sourness. All this is due to the amount of vitamins and minerals, digestible carbohydrates and acids.
Black raspberries contain more sucrose and fructose, but less vitamin C and 2 times more calories per 100 g. Typically, the fruit size is smaller than that of red and yellow varieties. Chokeberries are sometimes confused with blackberries. The main difference is that the berries are easily removed from the receptacle, the shoots are strewn with fruits collected in large clusters.
An unusual property of black raspberry shoots is that they do not reproduce by shoots, but, thanks to the tips of the branches bending towards the soil, they take root and germinate. After which it should be trimmed into 3-5 buds.
Description and characteristics of culture
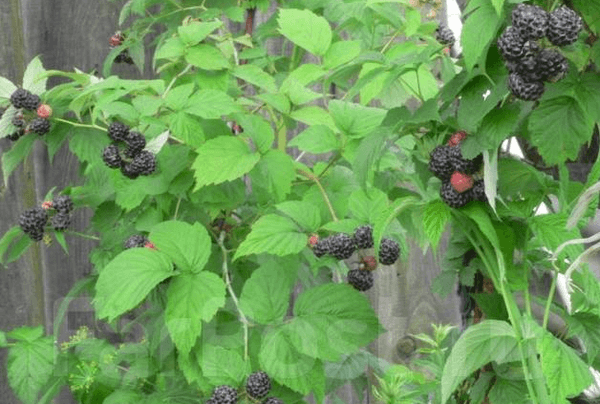
Black raspberry is a perennial plant of the genus Rubus, family Rosaceae. The bush grows up to 2 m, the shoots bend towards the soil in the form of an arc, in the first year of life the length increases, in the second year flowers and berries are formed. The shoots are flexible, young green with small thorns, the branches of the second year are brown-burgundy with a bluish bloom.
The leaves are alternate of 5 lobes, oval in shape, with small teeth along the edge. The leaf is more pubescent on top than on the bottom; the lower part has white hair. They resemble red raspberry leaves, but are smaller in size.
Flowers are collected in brushes in large quantities. They consist of 5 white, oval-pointed petals with 5 light green sepals.
The growing season of the plant begins 1-2 weeks earlier than that of red raspberries.
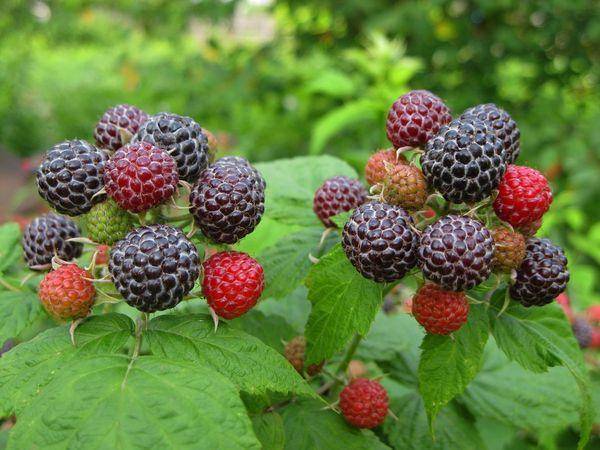
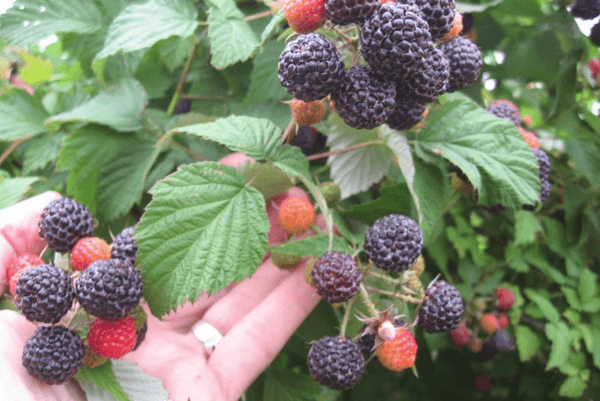
It blooms in late May - mid-June, lasting 1.5-3 weeks. After this, fruits are formed that change color as they grow and ripen, ranging from green, green-white, pink-red, bright red, purple-black. The berries are pubescent, can be like blackberries with a slight bluish bloom.
Fresh berries can be stored longer than red ones, since they have a denser structure and almost do not wrinkle during transportation.
Black raspberries have adopted their ability to reproduce from blackberries; the branches of the second year of life, if not tied up, come into contact with the soil and form not berries at the end (penetrating crown), but a thickening from which white roots sprout. Therefore, they can be cut and planted as a seedling.
Diseases and pests of black raspberries
Black raspberry bushes have good immunity against most diseases inherent in the Rubus genus and are resistant to drought and pests. Even if it grows next to other raspberry varieties, and they turn out to be sick, the black berry bushes may not become infected. But preventive measures with insecticides and fungicides need to be carried out every spring and autumn.
The main pests of black raspberries:
- spider mite;
- aphid;
- bud or prodoxide moth;
- weevil;
- gall midge;
- stem fly;
- glass butterfly;
- harmful centipede;
- nematodes;
- raspberry beetle or mite.
Diseases characteristic of black raspberries:
- powdery mildew;
- gray rot;
- anthracnose;
- mosaic;
- rust;
- root and stem cancer;
- white, ring, purple spotting;
- curliness.
To prevent plants from becoming infected with diseases and attracting pests, they and other crops on the site are treated with drugs and potential pathogens are eliminated: fallen leaves, diseased plants, weeds.Preparations: “HOM”, “Aktellik”, Bordeaux mixture, “Karbofos”, “Fitoverm”, “Fitosporin”.
How to plant a black raspberry bush on a plot
Black raspberry seedlings can be purchased at trusted nurseries or specialized stores, and if you already have several of your own bushes on the site, then propagate them.
Optimal timing
Black raspberries are planted in spring, summer, and autumn, but the climate zone should be taken into account. The most favorable period for rapid adaptation of seedlings for which the growing season begins early is spring, in March in the south of the country, in April-May in the middle zone, the Urals, Siberia. It is also possible to plant in the summer if the penetrating crown suddenly sprouted and was accidentally cut off, but such a plant will take longer and be more difficult to adapt.
The optimal time for planting in the fall in the southern regions is until the end of October, in the middle zone until the end of September. In colder regions with sudden climate changes, it is better to avoid planting in the fall, but if seedlings were purchased, they should be thoroughly mulched after planting.
It is important to remember that black raspberries are less resistant to sudden temperature changes and severe frosts.
Preparation of planting hole and seedlings
For better growth and adaptation to new conditions, the seedling should be planted in a place where nightshades have not grown before; ideally, the soil should rest for a year. You can plant it next to other varieties of raspberries, but it should be taken into account that in 2-3 years the usual variety will quickly overwhelm the chokeberry plantings.
The area for cultivation is dug up in the fall, adding organic fertilizers, green manure, rotted manure, and droppings.
In the spring, they dig a hole 40-50 cm deep and up to 50 cm in diameter. If the area is often flooded or the soil is heavy and wet, then a layer of drainage and sand is laid on the bottom.The rest of the soil is mixed with organic fertilizers, ash, peat, and rotted sawdust. The third part of the mixture is applied on top of the sand. The seedling is planted from the root collar 4-6 cm in the center of the hole and sprinkled with soil mixture, lightly pressing down and watering from above.
If the soil is heavy, then it is better to water in half: part in the hole, part after planting.
The place should be sunny on the east or south side of the plot, without drafts. The seedling is placed in a bucket of warm water a day before planting; growth or root formation stimulants can be added. Before planting, 30-40 minutes for disinfection in a manganese solution, if the seedling was not soaked in stimulants.
Technology and seating charts
The technology and planting schemes for black raspberries are the same as for other species and varieties of the Rubus genus.
The correctly chosen method guarantees the gardener a high yield.
| Scheme | Description |
| Single row | Suitable for planting around the perimeter of the territory or for farms. Dig a long ditch up to 40 cm deep and plant black raspberry bushes at a distance of 80-100 cm |
| Double row | Similar to the single-row pattern, only between the first and second ditch the distance is about 50-70 cm, the row spacing is 1.5-2 m |
| Trench | The same as single-row, but the depth of the planting ditch is more than 60 cm, since layers of organic matter are laid on the bottom for future nutrition of the bushes |
| Yamochnaya | Often used in individual gardens when the number of seedlings is small |
| Nesting | It involves planting bushes in a small circle, like a nest. Circle diameter 100-120 cm, distance between bushes 50-80 cm |
| Kurtinnaya | Applicable for regions with unfavorable climatic conditions.Plants are planted close to each other, creating natural thickets that are more likely to survive the cold winter |
For planting on a regular garden plot of 6 acres, it is optimal to use a hole pattern. For example: plant seedlings along the fence at a distance of 50-80 cm between the bushes, without picking up the shoots, but leaving them bent towards the ground. Only giving the direction of all shoots in one direction: left or right. After a year, the shoots will begin to sprout; they are cut off and planted between old bushes, and their branches are directed in the opposite direction. This way the bushes will gradually move around the garden.
Nuances of crop care
Black raspberries are easy to care for, can go without watering for a long time and produce a solid harvest; they are suitable for growing by summer residents who visit their plot on weekends. Compliance with agricultural care techniques will extend the life of the bushes and obtain a bountiful harvest.
Frequency of irrigation of bushes
The first watering is carried out in the spring. If there was little precipitation, then as soon as the soil warms up to +15 and no frost is expected, moisten each bush with 10-12 liters of warm water, you can add fertilizer, weed infusion, manure or nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium. Watering frequency 1-2 times a week. During the flowering period, the number of times is increased to 3-4, especially if the weather is hot and without precipitation.
Reduce the frequency of irrigation during berry ripening. After harvesting, the frequency is 1-2 times every 2 weeks. Before sheltering for the winter, 2-3 weeks before the expected frost, watering is completed. Irrigating bushes too frequently can harm crops and cause disease.
Loosening the soil
Loosening the soil is carried out once every 1-2 weeks, usually when weeding, in dry weather or 1-2 days after rain or watering, this allows you to make the soil breathable.
Principle of cutting and shaping
The first pruning occurs when young shoots grow more than 2 m, they are shortened to 1.6-1.8 m, this gives impetus to the growth of side shoots, pruned in the fall, leaving 20-30 cm. Old shoots that have bear fruit are removed in the fall in late September - early November.
How and what to feed black raspberries
During the growing season, black raspberries require more nitrogen, phosphorus, and calcium, so you can feed them with complex purchased fertilizers, urea, or add rotted manure, ash, peat, and topsoil from the forest to the soil.
In the summer, along with watering, nitrophoska and chicken manure are added to ensure abundant fruiting at the flowering stage. In the fall, mulch the soil with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers, adding chlorine, fluff, and green manure.
Preventative treatments
To prevent infection of plants by diseases or pests, the soil around the bushes is spilled with a weak solution of manganese, lime, copper sulfate, TMTD, boiling water, Fitosporin, and sprayed with Bordeaux mixture.
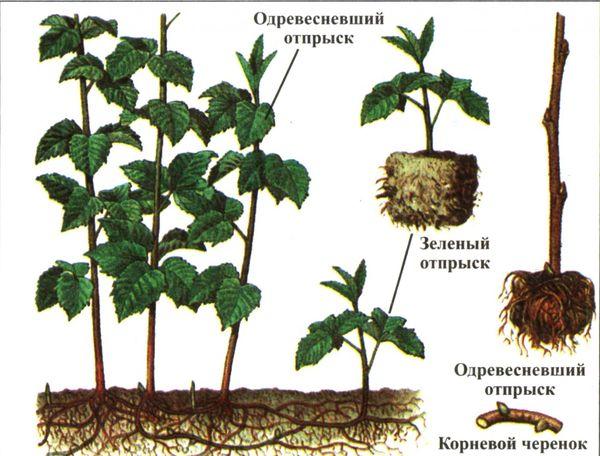
Black raspberry propagation
Black raspberries are propagated in several ways: cuttings, branching, dividing the bush, offspring - these methods retain the properties of the parent bush, but the seed method may not convey these qualities. Cuttings allow you to quickly grow raspberries in the country.
By layering
Propagation of black raspberries by layering - the simplest method, two-year-old shoots after fruiting are bent to the ground with a drooping crown and sprinkled with 2-3 cm of fertile soil. Shoots begin to sprout after 2-4 weeks; in October they are cut off from the main bush or in early spring.
Root suckers
Black raspberries reproduce poorly by root suckers, since they take longer to develop than red raspberries. It is better to take an offspring located at a distance of at least 20-30 cm. Cut it from the parent bush with sharp pruners and plant it in a new place.
Green and woody cuttings
Green cuttings are prepared from young shoots in late spring, early summer, the crown is removed, cut into 15-20 cm long, treated with a root formation stimulator and planted in separate containers with a nutrient substrate or in a greenhouse. In spring, rooted plants are planted in open ground.
Lignified shoots are cut according to the same principle, but in the fall. Wrap it in plastic and put it in a cool place until spring. In March-April, viable ones are selected and planted in open ground under a glass jar or separate containers, which must be covered with polyethylene to maintain high humidity. In the fall or next year in the spring, planting is carried out in open ground.
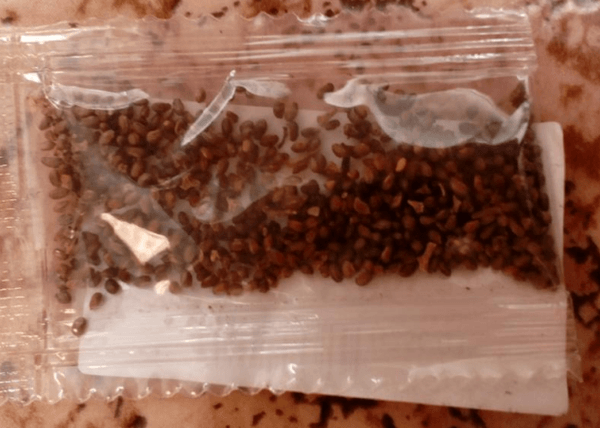
Seeds
The seed method is the longest. In the fall, dried berries are collected from the bush and placed in the refrigerator to stratify the seeds for 1 month. Then they are sown in containers with soil mixture and covered with glass, creating high humidity and heat. When 2-3 leaves appear on the seedlings, gradually open the lid, adapting them. As the seedlings grow, they are transplanted into separate large pots. Ready plants can be transplanted into open ground a year later, in the spring.
Popular varieties of black raspberries
Breeders have developed many varieties that can grow in different climatic zones and produce large harvests. One of the best varieties described by gardeners - raspberries Cumberland, which comes with yellow and black fruits:
- Cumberland is the most popular and unpretentious mid-early variety. Berries are collected in 10-12 pieces. in the brush. Polydrupe up to 2 g, small, yield up to 10 kg per bush. Resistant to drought, frosts down to -30. The leaves are larger than those of other similar varieties, with a glossy surface.
- New Logan is an early variety, high-yielding, up to 10 kg per berry season. Requires shelter at winter temperatures above -24. Medium sized berries up to 3 g.
- Bristol is one of the varieties resistant to drought, frosts down to -30 and diseases. Harvest up to 5 kg per bush. The fruits are black with a bluish coating, medium ripening.
- Coal is resistant to diseases, pests and long periods of rainless weather. Tolerates frosts down to -30. Productivity up to 8 kg, medium berries, 2-3 g.
- Boysenberries are medium-sized elongated berries with a raspberry-blackberry sweet taste without sourness. High-yielding variety of medium ripening period. Withstands frosts down to -25.
- Litach is a young Polish variety, mid-season, high-yielding, but requires shelter, since the permissible temperature is -23.
- Black Jewelo - the branches of the bush in the first year are green with a white milky coating. Early ripening variety, late June - early July, high-yielding, fruits up to 2.5 g. The bush is very spreading, 8-10 shoots per season.