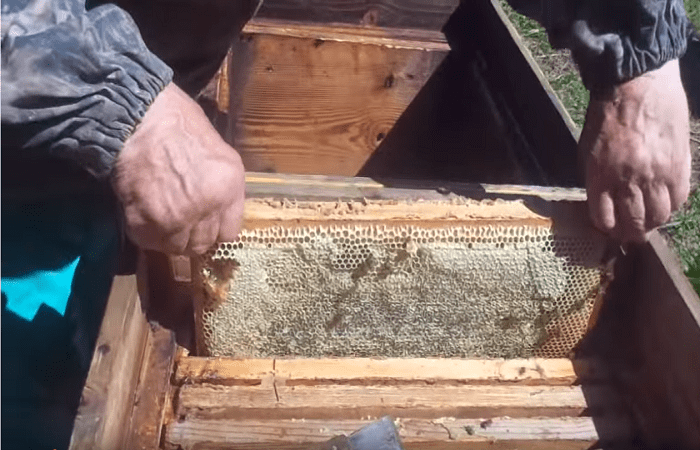
The American foulbrood of bees refers to an infectious pathology that is associated with infection with the Larve bacillus. It affects worker bees, queens, adult larvae and rapidly spreads throughout the apiary. If measures are not taken in time, there is a high probability of death of bee colonies. Therefore, at the first symptoms of pathology, it is necessary to send samples of honeycombs and bees to the laboratory.
Description of the disease
American foulbrood is a complex infectious pathology of closed brood bees.Infected families are difficult to treat and die. The pathogens are characterized by a high degree of resistance. They are preserved for a long time in beehives, honey, soil, beebread, and on tools. Even after treatment, outbreaks of infection are possible. Therefore, American foulbrood is classified as a malignant disease.
Causes and symptoms of foulbrood in bees
Bacterial spores can enter the hive in a variety of ways. This leads to the following:
- bee theft;
- use of old honeycombs, tools, beehives;
- purchasing bee packages that contain infected bees;
- spread of spores by moths, wasps, ants, earwigs;
- feeding with infected honey;
- the use of foundation that has not undergone proper heat treatment;
- the presence of bacteria in other apiaries within the summer of bees;
- spread of spores on hands, chisels and other devices.
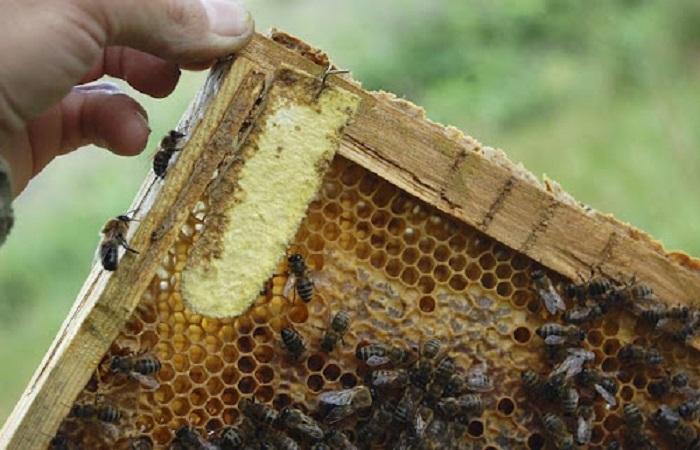
After drying, the corpse of the larva is fixed at the bottom of the cell. The bees cannot clean it out, and therefore the source of the disease remains in the honeycombs.
Bacterial spores develop well at a temperature of +37 degrees. Therefore, infection most often occurs in July. At first, diseased larvae cannot be distinguished from healthy ones, since they are concentrated in sealed cells. Their changes will be noticeable later. Characteristic signs will appear when the disease affects part of the brood.
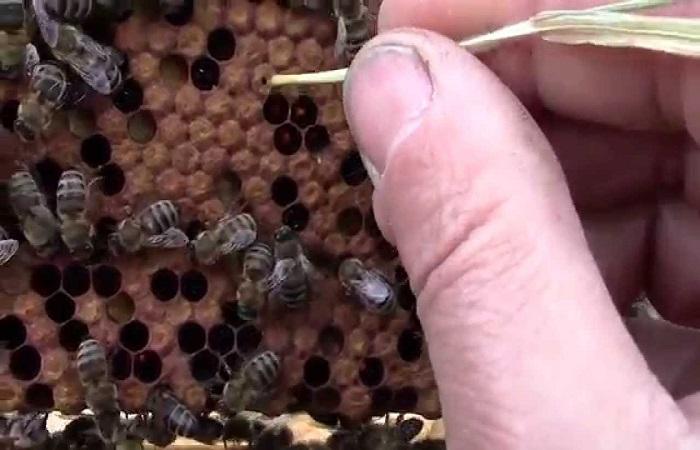
The incubation period is 2-7 days. For the first 3 days, the larvae are protected by the bactericidal properties of the milk. Then active spread of spores occurs. The death of the larvae occurs at the prepupa stage - after the cell is sealed. It turns brown and smells like wood glue. In addition, the head of the larva pulls the cell lid down, which leads to the formation of a hole. Honeycombs with affected brood become variegated.
Varieties
Foulbrood is considered a dangerous pathology, which can have several varieties. Each of them has certain characteristics.
American
This is the most dangerous form of foulbrood. It is called malignant. This type of pathology leads to a loss of productivity of 80%. Complete extinction of a family takes 2 years.
The peak activity of infectious agents occurs in late spring and summer. In this case, the infected larvae die in closed cells. Bacterial spores are resistant to adverse factors. On the corpses of the larvae, they can remain viable for 30 years.
European
The difference between this type of disease is that it affects larvae of open brood 3-4 days old. With the rapid development of infection, there is a risk of damage and sealed brood.
Infected individuals lose segmentation and acquire a straw-yellow color. Then a sour smell occurs. Dead individuals first become stringy and then dry out. Moreover, it is easier to remove them than with an American infection. European foulbrood can infect queen larvae and drone larvae.
The peak of infection is observed in spring and summer. During the honey harvest period, the incidence drops slightly. At this time, the bees are more active in cleaning their cells.
Paragnilets
This is a less dangerous form of pathology. Pararotworm provokes damage to older larvae. Most often it develops in highlands with a cool climate. Dead larvae are odorless, dry quickly and are easily removed.
Usually the brood dies in the sealed cell. This happens much less often in the open. The main signs of pathology include the following:
- increased motor activity of sick pupae;
- unnatural position of affected individuals;
- dark color of sealed lids;
- a cone-shaped depression in the center of the convexity;
- absence of the hole characteristic of the American foulbrood;
- ease of removing dried pupae from the cells.
Diagnosis of the problem
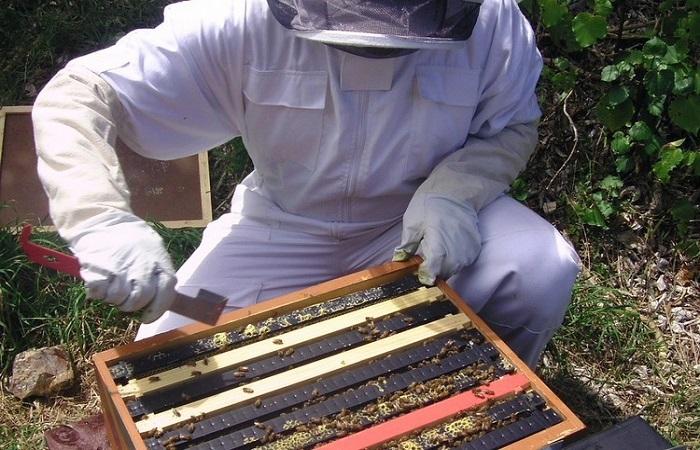
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct an epizootological examination of the apiary, study the clinical picture of the disease and perform laboratory tests. In this case, you need to do analyzes of cut honeycombs measuring 10x15 centimeters. Most often, diagnosis is carried out using the PCR method.
Treatment of disease in bees
To cope with pathology, it is important to begin treatment as early as possible. In this case, it is worth using special drugs.
Pharmacy products
The best time to treat bee colonies for foulbrood is in June. In this case, the affected insects can take part in the main bribe. If a bee colony is severely damaged, it has to be disposed of. Formaldehyde is used to kill insects. The fallen specimens must be burned.
Treatment of foulbrood in bees requires the use of antibiotics and sulfonamides. Most often, sulfantrol or norsulfazole sodium are used for this purpose. Medicines must be mixed with sugar syrup. To calculate the dosage, it is worth taking into account the number of families that need help.
Traditional methods
It is impossible to cope with foulbrood using folk remedies. However, some beekeepers use celandine for this purpose.After completing the last pumping of honey, it is necessary to carry out preventive treatment of the hives with a herbal infusion.
To make it, you need to take 100 grams of fresh grass per 2 liters of boiling water. The components need to be mixed and left to infuse for half an hour. Then the composition needs to be poured into a sprayer and used to treat bees and working surfaces of hives.
Driving
To combat foulbrood, families must be resettled. The distillation has 2 varieties:
- With fasting. In this case, you need to shake off all the bees in the hive, cover the entrances with a grill and place them in a dark room. Fasting is aimed at complete consumption of honey in the crops of insects, since spores may be present in it. During this period the bees hang under the cover. When the insects begin to die, they are moved to a clean hive.
- No fasting. In this case, the hive needs to be removed and the bees shaken off onto paper. In this case, the queen must be removed from the family. If there is a sufficient amount of healthy brood, it is placed in a new family. In this case, the entrances need to be closed and food provided to the bees. A week later, the queen cells are broken out. When the brood appears, the colony must be moved to a disinfected hive.
Disease prevention
To avoid the development of pathology, it is recommended to follow these rules:
- detect the disease in time;
- do not give bees honey of unknown origin;
- protect healthy apiaries from infected ones;
- collect and burn dead bees;
- keep bees in clean hives.
American foulbrood is a serious pathology that can lead to dangerous consequences and the complete death of bees. To cope with the disease, it is important to take timely measures.