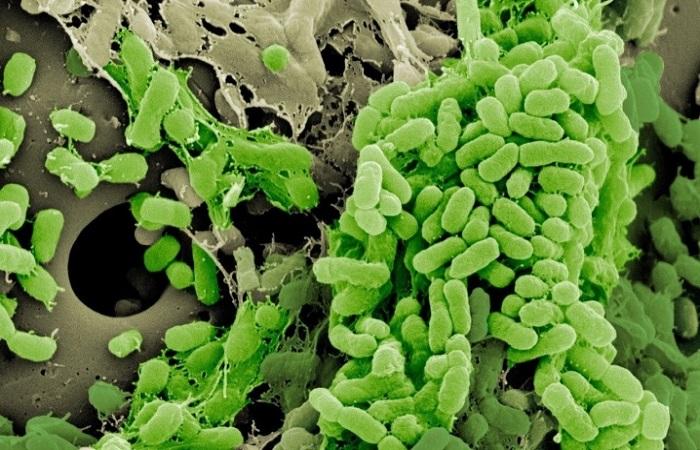
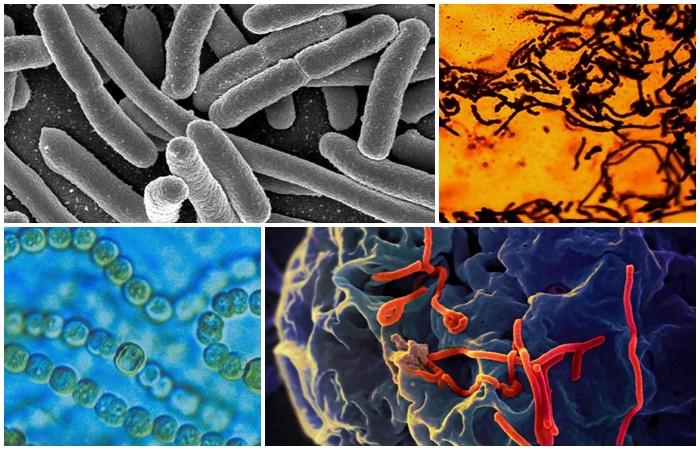
The role of soil bacteria cannot be overestimated. They are necessary to process organic residues into minerals, which is their main purpose. Let's consider the features of the habitat of microorganisms, their varieties and classification according to various criteria, how and what they feed on. How do soil bacteria differ from decay bacteria?
general information
Soil bacteria and fungi contribute to the decomposition of organic residues into mineral elements; without this process, the existence of biocenoses would be impossible. Their main significance is that they process particles of plant and animal tissues into nutritious humus, which is then used by new plants for nutrition, growth and development. The positive effect of bacteria is also noted in the fact that the humus resulting from their activity forms soil, makes the top layer fertile, and improves the structure of the soil.
The benefits and harms of soil microorganisms are determined by their composition, varieties and quantity. Beneficial microorganisms do not always predominate in the soil; if for some reason harmful ones, such as mold, multiply, the substrate becomes unsuitable for use. The negative impact of mold manifests itself in the suppression of plants, which leads to their death. The soil may also contain carriers of dangerous infectious diseases - tetanus, anthrax, intestinal infections and others.
Habitat
Different types of microorganisms in the soil feed on different organic residues and live in different layers. They are mainly located in the area where plant roots are located. Microorganisms consume both fresh plant residues and substances that are located near the root system of plants.
For successful growth of crops, it is necessary that, first of all, photosynthetic bacteria live in the soil. Microorganisms of this type fix nitrogen and carbon from the air, produce organic matter and bind many other nutrients that nourish plants and participate in the cycling of compounds.
Types of soil bacteria
The entire bacterial flora of the soil is divided into groups depending on their structure, oxygen consumption, functions, nutrition and other characteristics.
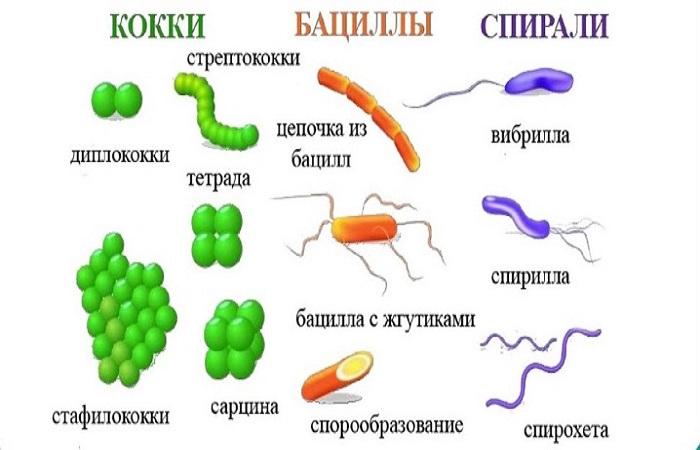
According to the shape of the cell walls
The difference in the structure of the cell walls of soil microorganisms was revealed as a result of research. Based on this feature, unicellular organisms are divided into 3 main groups:
- bacilli, in which the cell has a cylindrical shape;
- cocci with spherical cells;
- spirilla having a spiral shape.
There are bacteria with complex shapes, for example, actinomycetes, which have a branched shape.
In relation to oxygen
All soil bacteria are divided into groups, one of which consumes oxygen, the other can do without it. These are aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms. The attitude towards oxygen also determines what reactions will take place with the help of these microorganisms. Anaerobic bacteria are responsible for fermentation processes; less energy is produced with this method than with the aerobic method, which is more effective in this regard.
According to the ability to stain using the Gram method
The method is based on the fact that some types of soil microorganisms have an outer protective shell that does not allow substances to enter. Such bacteria are considered gram-positive, those that stain with dyes are gram-negative. These include: pseudomonads, azotobacteria, nodule unicellular organisms, enterobacteria, cytophages, myxobacteria, nitrifying bacteria. Gram-positive microorganisms: bacilli, anaerobic, coryne-like and spore-forming bacteria.
By food type
Microorganisms are divided into autotrophic and heterotrophic.Autotrophic organisms create organic compounds from inorganic ones in the process of life activity; heterotrophic organisms use organic matter for nutrition.
By function
Nitrifying microorganisms are used to increase the nutritional value of the soil. Nodule microorganisms fix nitrogen from the air and transfer it to the soil, while nitrifying microorganisms convert nitrogen from ammonium to nitrate form, thereby increasing its availability to plants.
Based on their functional characteristics, there are the following groups of microorganisms:
- Decomposers, which consume fresh organic matter, decompose and mineralize it.
- Mutualists are able to exist with plants on mutually beneficial terms. An example is nodule bacteria.
- Chemoautotrophs process inorganic matter that does not contain carbon.
- Pathogens that cause diseases in plants and animals.
How do bacteria feed?
To obtain food and energy, soil bacteria use different methods. Some feed on organic, others on inorganic substances. By decomposing organic matter, they build their own cells and use inorganic substances for nutrition.
What is the difference between rotting bacteria and soil bacteria?
The processes of decay are caused by saprophytes. They are located in the upper layer of soil, their goal is the decomposition of dead tissue at high speed. Saprophytes are demanding of organic matter; their life activity is impossible without proteins, carbohydrates, nitrogen-containing substances, nucleotides, and vitamins.
Soil microorganisms perform functions in the soil related to the circulation of nutrients, water and the inhibition of pathogenic bacteria. Some produce substances that bind soil particles into aggregates, making it more structural and increasing its water-holding capacity. Many beneficial microorganisms compete with pathogens in above-ground surfaces and root systems.