Nitrogen is considered one of the most important chemical elements that affects the development of agricultural plants. This substance affects the process of photosynthesis and the amount of chlorophyll in crops. At the same time, nitrogen fixation is an important agricultural process. However, applying nitrogen in the form of fertilizers is not considered the only solution. The use of nitrogen-fixing bacteria is considered a very effective option.
What are bacteria
This term refers to representatives of the kingdom of living nature, which represent the category of prokaryotes. They are organisms whose cells do not contain a nucleus. However, this does not mean that such organisms are completely devoid of hereditary information. DNA molecules are freely located in the cell cytoplasm. In addition, they are surrounded by a shell.
Bacteria are microscopic in size, and therefore microbiology studies them. Researchers have determined that prokaryotes are single-celled or form colonies. They are characterized by a very primitive structure. In addition to the nucleus, bacteria lack all types of plastids, mitochondria, and lysosomes. However, in any case, their cells are capable of carrying out a variety of vital processes. They are characterized by anaerobic respiration without the use of oxygen, asexual reproduction, and cyst formation in unfavorable conditions.
Main classes
The classification is based on various characteristics, one of which is the shape of the cells. Cocci are round in shape, vibrios are comma-shaped, spirilla are spiral-shaped, and bacilli are rod-shaped.
In addition, the classification of bacteria is carried out taking into account the characteristics of the cellular structure. True varieties can form a mucous capsule around their cell. In addition, they have flagella. Cyanobacteria have the process of photosynthesis and are classified as lichens.
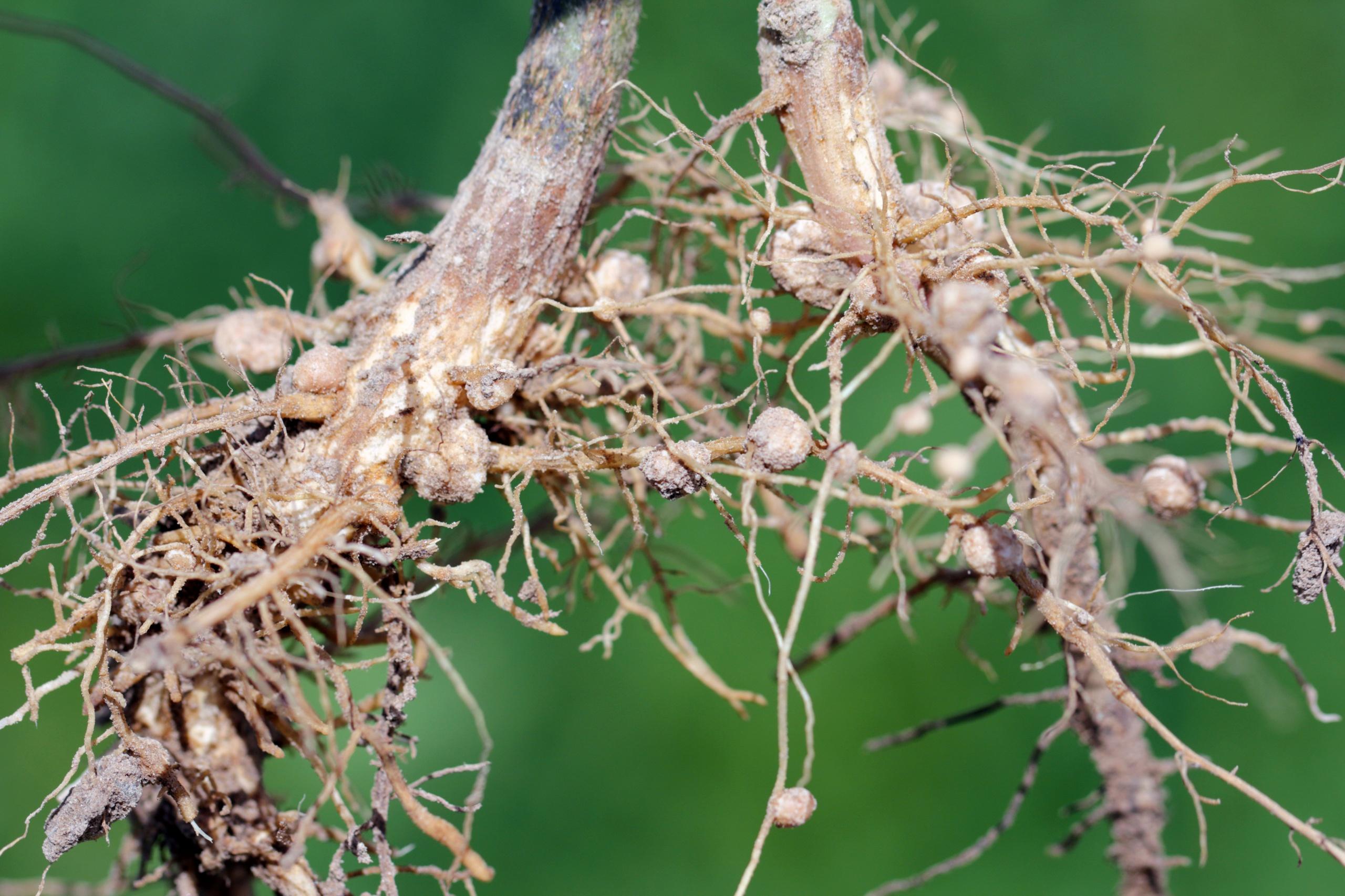
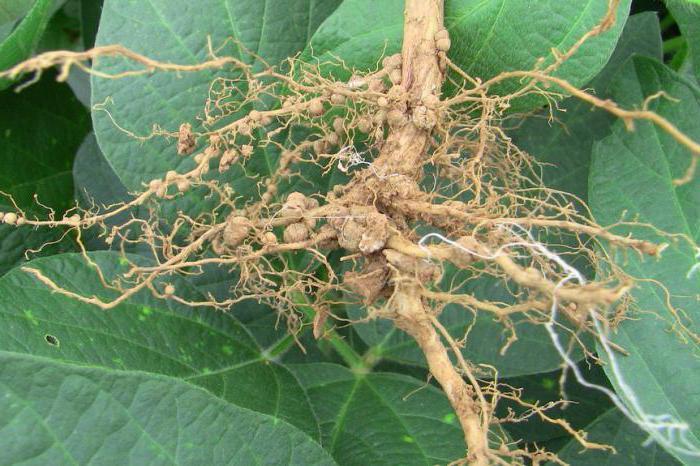
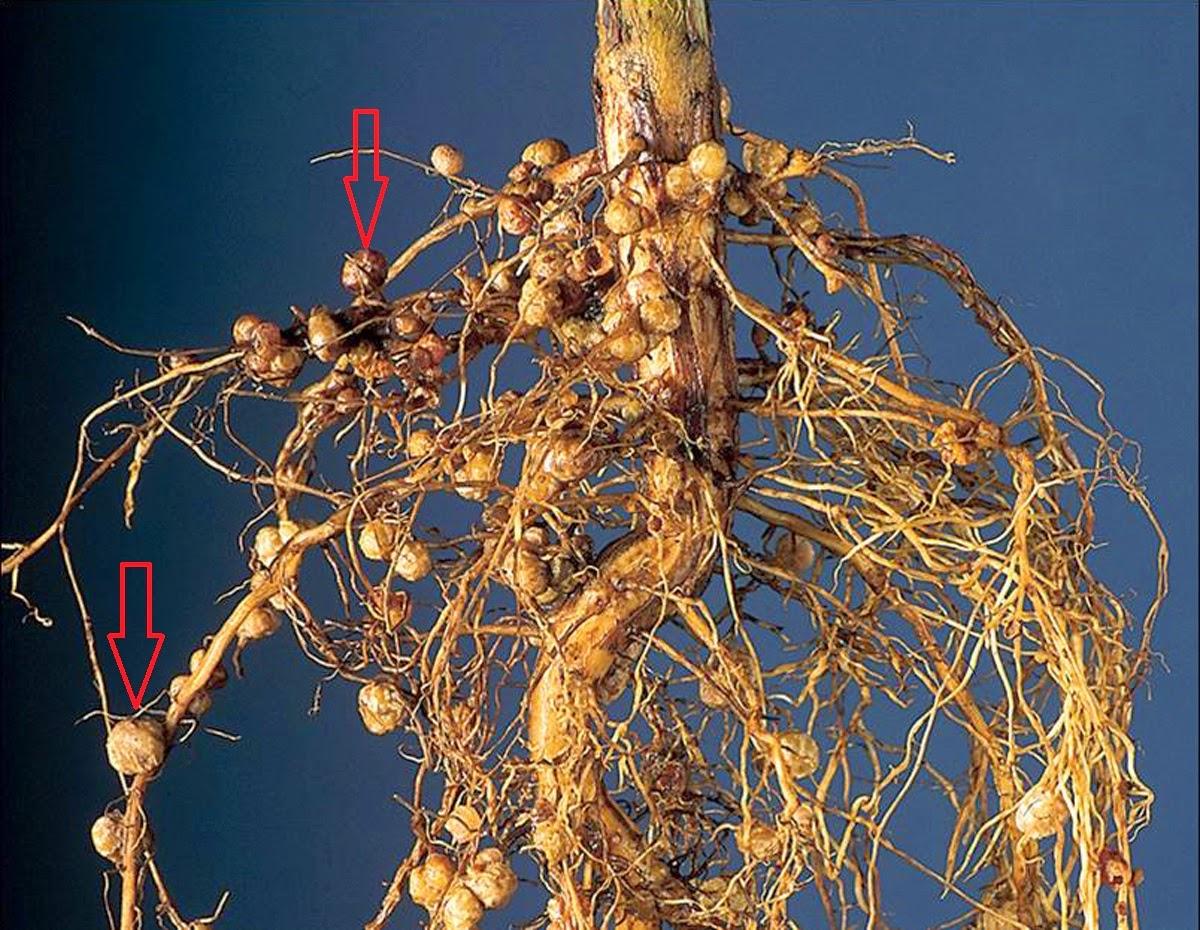
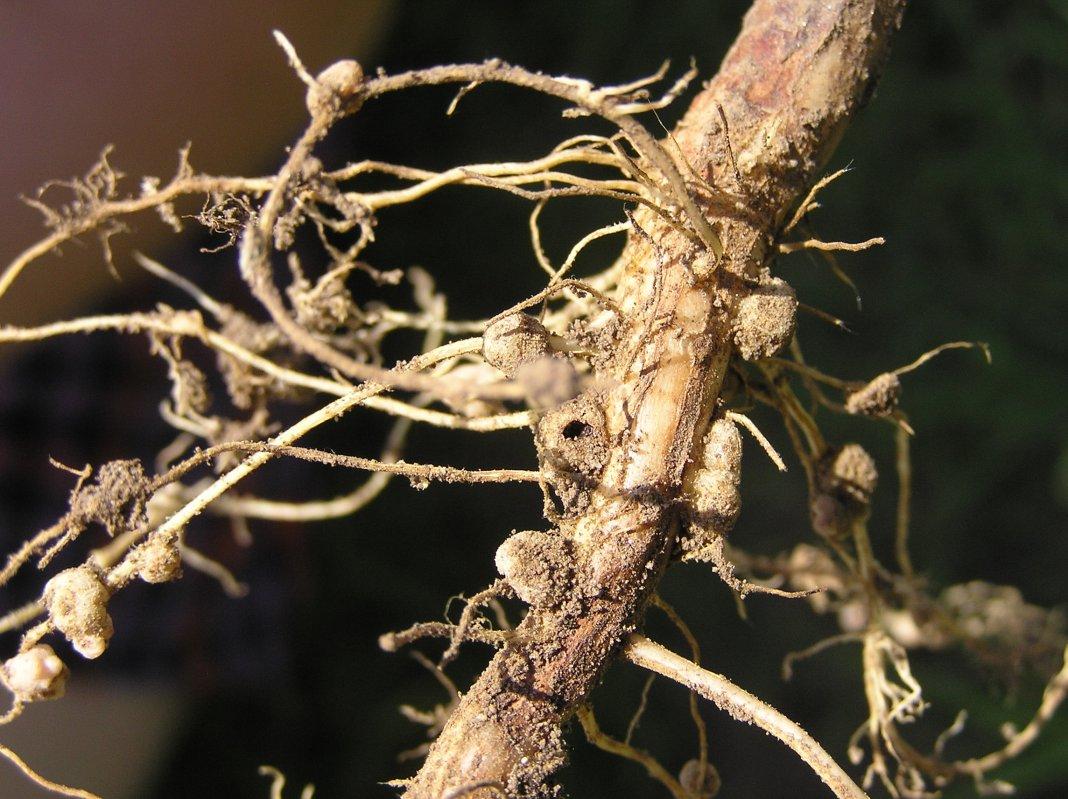
Many varieties of bacterial microorganisms are characterized by a tendency to symbiosis, which is a mutually beneficial cohabitation. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria settle on the roots of legumes and form nodules. These microorganisms transform atmospheric nitrogen, which is important for the full development of crops.
Eating methods
Prokaryotes are organisms that can feed themselves by any means. For example, purple and green bacteria are characterized by an autotrophic type of nutrition - thanks to the use of solar energy. Due to the presence of plastids, they differ in different shades, but always include chlorophyll.
It is important to consider that the process of photosynthesis in bacteria and plants is significantly different. In the first case, water is not an obligatory reagent. Hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide can act as an electron supplier. Therefore, oxygen is not released during this process.
A significant category of bacterial microorganisms are characterized by a heterotrophic type of nutrition. This means that they use ready-made organic elements. To saturate the bacteria with the necessary substances, they use the remains of dead organisms. At the same time, putrefactive microorganisms can lead to the decomposition of any organic matter. They are also called saprotrophs.
Some plant bacteria are capable of entering into symbiosis with other organisms. Thus, together with fungi, they are part of lichens. At the same time, nitrogen-fixing nodule bacteria are capable of mutually beneficial coexistence with the root system of legumes.
Who are chemotrophs
An important category, which is distinguished by the type of absorption of nutrients, is considered to be chemotrophs. They are microorganisms that are considered a type of autotroph. In this case, instead of solar energy, these bacteria use the energy of the chemical interaction of various elements. Chemotrophs, in particular, include nitrogen-fixing bacteria. They cause the oxidation of a number of inorganic compounds and at the same time provide themselves with the required amount of energy.
Habitat of nitrogen-fixing bacteria
In general, bacteria are ubiquitous. At the same time, nitrogen-fixing varieties live in the soil, or, more precisely, on the roots of legumes.
Body structure
The functions of nodule bacteria are related to their structure. Such microorganisms can be seen with the naked eye. They settle on the root system of legumes and cereals and penetrate plants. In this case, thickenings are formed in which metabolic processes are observed.
Plants need nitrogen for normal functioning. Nature contains a sufficient amount of this element. For example, in the air its amount reaches 78%. However, crops cannot absorb this substance in this form. Nitrogen-fixing microorganisms are able to absorb nitrogen from the atmosphere. After which they transform this substance into a form that is available to crops.
Performance
To better understand the function of nitrogen-fixing microorganisms, it is worth considering the example of a chemotrophic bacterium called Azospirillum. This organism lives on the root system of cereal plants - wheat or barley. It rightfully occupies a leading position among nitrogen producers. This organism releases up to 60 kilograms of this substance per 1 hectare of crop area.
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in legumes include rhizobitum, sinorizobium, and others. They are also highly efficient. Such plants are capable of producing up to 390 kilograms of nitrogen per 1 hectare of land. On perennial legumes, bacteria are formed that are characterized by maximum productivity. This parameter reaches 560 kilograms per 1 hectare of sown area.
Features of life
Depending on the characteristics of their life processes, all nitrogen-fixing microorganisms can be grouped into two categories. The first group is considered nitrifying. In this case, metabolic processes consist of a chain of chemical transformations. In this case, ammonium is converted into nitrites, which are salts of nitric acid. In turn, nitrites are transformed into nitrates. They are also salts of this compound. In this form, nitrogen is better absorbed by crop roots.
The second group is called denitrifiers. They carry out the reverse process. In this case, nitrates that are present in the soil are transformed into nitrogen gas. As a result, the circulation of this substance in nature is observed.
Among the life processes it is also worth highlighting reproduction. It is carried out by dividing cells in two. Much less often this occurs by budding. Bacterial microorganisms can also reproduce sexually. This method is called conjugation, during which genetic information is exchanged.
Since the roots of the culture secrete a large number of valuable elements, a lot of bacteria settle on them. They transform plant residues into substances that can be absorbed by plants.As a result, the layer of soil around it is endowed with special characteristics. It is called the rhizosphere.
How do bacteria get into the root?
There are several options for introducing bacterial cells into root tissue. This happens as a result of damage to the covering tissues or in areas where young root cells accumulate. Chemotrophs can also penetrate into crops in the root hair zone. After which they become infected.
As a result of active division of bacterial cells, nodules are formed. After this, infection threads appear that continue to penetrate plant tissue. Over time, a special substance called leghemoglobin is formed here. At the stage of optimal activity, the nodules become pink. This is due to the presence of pigment.
Importance in the economy
People have long been able to establish that if you dig up legumes with soil, plant productivity will improve. However, the point is not the plowing process. Such soil is better saturated with nitrogen, which is important for the development of crops. That is why nitrogen-fixing bacteria called a nitrate factory.
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are important microorganisms that are actively used in agriculture. This is due to their ability to obtain nitrogen from the air and transform it into a form accessible to plants.