Herbicides against the spread of ragweed help increase yields. After all, even two weeds on one square meter reduce soil fertility and reduce the amount of harvest by 15 percent. To successfully grow almost all crops, it is necessary to combat field weeds. Ambrosia is destroyed by spraying with a herbicide solution. Field cultivation is carried out in calm weather at temperatures from 10 to 24 degrees Celsius.
Description of the weed
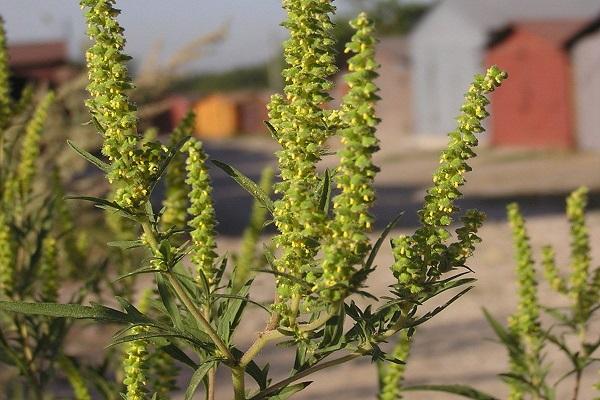
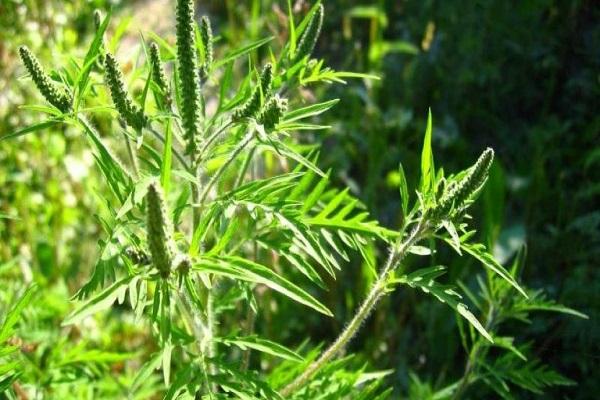
Ambrosia is an annual weed that quickly spreads across the field, robbing the main crops of water and nutrition. Propagated by seeds and growth of the root system. The height of the weed reaches from 19 to 199 centimeters.
The weed has a straight, branched stem upward, double pinnately dissected leaves, and spike-shaped inflorescences with numerous yellow flowers. The weed has a long taproot. One bush remains viable for up to 40 years and produces over 200 thousand seeds. Massive weed shoots appear in May. The weed blooms in July-August. Pollen can cause allergic conjunctivitis. There are three types of ragweed: perennial, tripartite, and wormwood.
What harm does ragweed cause?
This weed vegetation is dangerous for lands on which grasses grow that are used to feed livestock. Animals try not to eat this plant, as it contains a lot of essential oils. In addition, ragweed worsens the taste of milk. This weed, unpretentious to its environment, quickly spreads across the field and greatly dries out the soil. It inhibits the sown crops, taking away their water and nutrients.
The powerful root system of this weed prevents grain seeds from germinating. By selecting useful substances, ambrosia itself can grow up to 3 meters in height. To create one kilogram of green mass, this weed removes tens of liters of water, a lot of phosphorus, potassium and nitrogen from the soil. The plant, wherever it appears, begins to grow strongly, develops a powerful above-ground part and root system.
Pest control measures
It is recommended to combat ragweed in several ways. You can get rid of weeds by uprooting them. True, ragweed will have to be removed for several years in a row. Young shoots will appear on the field every season.
How to get rid of it using herbicides
Ragweed is sensitive to many types of herbicides if used early in the weed's growth (2 to 6 leaf stage). With later use of chemicals, the weed may become resistant to these drugs.
The most effective herbicides for controlling ragweed are: Roundup, Grenadier, Impex Duo, Helios, Bazagran, Promex.
Mechanical impact
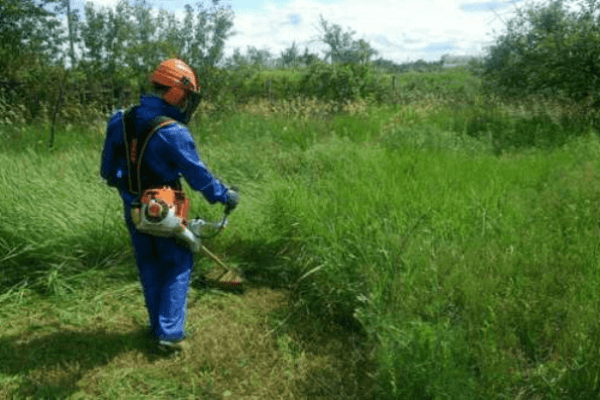
They try to get rid of ragweed by constantly mowing this weed. True, mowing too often is harmful. After all, it provokes branching of the root system and the appearance of new shoots. After each mowing, ragweed produces 2-3 times more sprouts than were removed.
You need to mow the weed 3-5 times per season, preventing it from forming buds and blooming.
In the field, ragweed is combated by loosening, weeding, hilling, and harrowing. After carrying out such agrotechnical measures, the growth of weeds is partially suppressed or completely destroyed.
How to fight a plant using biological methods
The biological method of weed control is considered the most cost-effective. You can get rid of the weed with the help of ambrosia cutworm or ambrosia leaf beetle. Thanks to these insects, it is possible to control the spread of weeds. True, humans cannot influence the number of insects themselves.
You can fight ragweed in another biological way - by replacing it with perennial grasses. Alfalfa, mustard, foxtail, wheatgrass, fescue, wheatgrass, and brome are capable of conquering the entire territory from this weed. If these grasses are constantly sown on pastures, then in 2-3 years they will displace ragweed.
How can weed be useful?
Ambrosia is rich in vitamins, microelements, and essential oils. All parts of this plant are used for medicinal purposes. Tinctures, ointments, and decoctions are made from plant materials. Medicinal products are used externally and internally.
This plant is used to treat helminthiasis, dysentery, and diarrhea. The herb has antipyretic and anti-inflammatory properties. The substances contained in this plant stop the growth of cancer cells. Crushed leaves are used for compresses for wounds, bruises, radiculitis, and osteochondrosis.
How to prevent ragweed
Chemical field protection is considered the most effective. Herbicides kill this weed quickly and for a long time. Before using any of the drugs, dilute with water in the dosage indicated in the instructions.
To combat ragweed, herbicides based on the following active ingredients are used:
- Dicamba. This substance is allowed to be used to protect grain. The active substance stops cell division and inhibits weed growth.
- Triasulfuron. This substance, in combination with dicamba, is used to protect grains. After spraying, the weed immediately stops growing, and after 10 days signs of wilting (necrosis, chlorosis) appear. Complete death occurs after 2-4 weeks.
- Prosulfuron. Protects grains from weeds. This herbicide can be used in the early stages of growth.
- Glyphosates. The herbicide disrupts the processes of protein synthesis, blocks photosynthesis and respiration of weeds, and leads to wilting. Glyphosates are used before sowing main crops.
- Dimethenamide-P. It is used for pre-emergence and post-emergence treatment. If there is a lack of moisture, this product can be embedded in a damp layer of soil.The drug inhibits the cell division of weeds.
- Pendimethalin. The product is used before sowing or emergence of the main crops. In dry weather conditions, the herbicide is incorporated into the soil.
- Imazamox. Suppresses protein biosynthesis, leading to the death of leaves and growth points. The herbicide begins to act immediately after spraying.
- Bentazone. Inhibits photosynthesis processes. Weeds stop growing and quickly die.
- Thifensulfuron-methyl. Stops cell division, inhibits the ALS enzyme. A few hours after spraying, the weed stops growing and begins to wither.
- Imazethapyr and chlorimuron ethyl. It is used in the early stages of weed growth, regardless of the development phase of the main crop.