When growing various plant crops, it is necessary to change their planting sites annually, as this will allow you to obtain maximum yield and maintain an optimal acid-base balance of the soil. Almost all gardeners grow tomatoes, so they often wonder: what can be planted after tomatoes?
There are a number of plant crops that respond favorably to planting in the former tomato growing area. However, before transplanting them, it is necessary to prepare the soil, saturate it with fertilizers using organic and mineral fertilizers.
Growing in greenhouses
Most often, summer residents grow tomatoes in greenhouses.If you have several greenhouses in your garden, the best option is to alternate planting tomatoes and cucumbers. After the end of each season, the soil in the greenhouse should be thoroughly disinfected to prevent the spread of fungus.
This approach to cultivation will reduce the likelihood of diseases occurring in planted crops, since they belong to different families.
Before planting cucumbers where tomatoes grow, the soil in the greenhouse should be thoroughly disinfected and fertilized. After a year, tomatoes can be planted again in place of the cucumbers.
Is it possible to plant tomatoes in the same place for years if only one greenhouse is built in the garden?
If a summer resident does not have the opportunity to change the location of planting tomatoes, then to grow them in a greenhouse for several years, in the winter - after harvesting, it is necessary to plant mustard. At the same time, mustard should be grown to fertilize the soil. In addition to its fertilizing function, mustard perfectly disinfects the soil, equalizes its acid-base balance and normalizes its composition.
In the fall, it is necessary to collect and burn the remains of tomato bushes. In the spring, the mustard is removed, and after that the tomatoes can be planted in their original place.
Tomato bushes should not be planted several times in a row in a greenhouse. Between plantings, crops must be planted that will help the soil normalize the acid-base balance and make it more fertile. This is due to the fact that tomatoes deplete the soil, and in greenhouse structures this process is activated, since the soil in them is isolated from the influence of the external environment.
Also, such cultivation provokes the accumulation of harmful bacteria and spores, which increases the risk of re-infection of tomato bushes with phytospores or other characteristic pathologies even after cultivating the land.
Growing in open beds
What can you plant after tomatoes other than cucumbers? Instead of tomatoes, you can plant zucchini or squash. These plants will not only delight the summer resident with a rich harvest, but also with the density and quality of the grown vegetables. Next year, instead of tomatoes, you can grow onions and garlic.
This arrangement will not affect the yield of these vegetables in any way. Moreover, onions and garlic perfectly disinfect the soil in which they grow. This treatment makes it possible to eliminate diseases that have previously spread on tomato bushes and prepare the ground for replanting tomatoes. It is worth considering that onions should be grown not for feathers, but for turnips.
You can also get an excellent harvest by planting legumes in place of tomatoes:
- beans;
- peas;
- soy;
- beans.
These plants are undemanding to soil and do not require large amounts of nutrients. On the contrary, planting them will only benefit the soil. This is due to the fact that legumes saturate the soil with nitrogen and enrich it with organic compounds.
After what transplants can you get a good harvest of vegetables? If you follow the recommendations describing the need to change plant crops with different depths of the root system, carrots, beets or radishes will be a good replacement for tomatoes. These root crops grow at a fairly great depth, compared to a tomato bush.
This arrangement of the vegetable helps restore the soil at an average depth level.This process is determined by the fact that root vegetables absorb nutrients from deeper layers of the earth than tomatoes.
In order for the new plant to be healthy and productive, it is better to plant crops belonging to a different family in place of tomatoes. For example, such plants include various herbs: dill, parsley, lettuce, celery. Such greens will not only actively grow and develop, but will also delight the summer resident with an excellent aroma, rich taste and composition, enriched with vitamins and nutrients. Also, different types of cabbage will do well in a tomato plant.
What to plant next year after tomatoes? The best option for planting in the place where tomatoes grew is green manure. These plants act as plant fertilizers, the main function of which is to restore soil balance, as well as enrich its composition with various useful substances and microelements. It is worth considering that after planting the grown green manure in the soil, tomato bushes can be replanted in their place. The best option green manure for tomatoes considered mustard.
Not recommended crops
The following crops should not be grown in the place where the tomatoes were planted:
- other or similar varieties of tomatoes;
- potato;
- tobacco;
- physalis;
- strawberries;
- strawberries;
- eggplant.
This recommendation is due to the fact that tomatoes with the listed crops are affected by similar diseases and pests. Therefore, even after disinfection of the soil, signs of pathologies that previously affected planted tomatoes may appear on newly grown plants.
In order to avoid this, the listed crops should be planted away from the growing areas and the former growing area of tomatoes.
There is another argument against planting these crops on the former site of tomatoes. The fact is that tomatoes make the soil more acidic, and in such an environment the listed plants cannot fully grow, develop, and most importantly, bear fruit. Because of this, crops planted in the wrong place either die or produce a poor harvest.
What can be planted after tomatoes from melons? The answer to this question is clear: nothing. This is due to the fact that watermelons, melons or pumpkins planted in a former tomato area will bear fruit poorly, and the summer resident will receive a very modest harvest.
Many summer residents plant bell peppers next to tomatoes. It is not recommended to carry out such planting in a bed where tomatoes were previously grown for only one reason: the yield of bell peppers may be reduced significantly. If such a prospect does not frighten the gardener, he can plant this plant crop in place of tomatoes without fear of the bush being damaged by diseases or pests.
general information
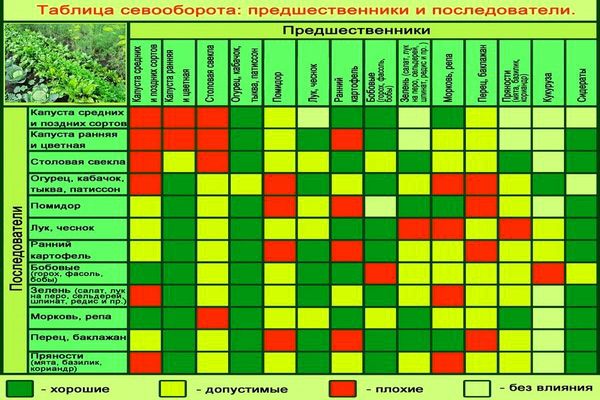
To understand which plant crop is best suited for planting tomatoes next year, the following table can be used.
It is also necessary to pay attention to the degree of feasibility of planting a particular crop.
| Plants that produce abundant harvests where tomatoes grow | Plants that are not affected by diseases and produce an average yield in the former place where tomatoes grew | Plants that respond unfavorably to being planted in place of tomatoes |
| Turnip | Medium and late varieties of cabbage | Potato |
| cucumbers | Beet | Tomatoes of a different or similar variety |
| Greenery | Onion | Strawberry |
| Various green manures | bell pepper | Strawberries |
| Cauliflower | Garlic | Physalis |
| Peas | Carrot | Tobacco |
| Soybeans | Eggplant | |
| Peanut | Pumpkin | |
| Beans | Watermelon | |
| Zucchini | Melon | |
| Patissons | ||
| Celery | ||
| Salad | ||
| Dill | ||
| Parsley |
All recommendations presented are of a general nature. It is up to the summer resident himself to choose what vegetables, berries or herbs to plant next year after the tomatoes. This is due to the fact that the soil in each region has its own individual characteristics, and certain areas are characterized by a more active spread of a particular disease.
Replacing the places where crops grow gives good results in the process of restoring the soil and providing preventive measures against diseases and pests.
Also, after such transplants, there is an improved absorption of nutrients from the soil by plants and rational use of fertilizers.