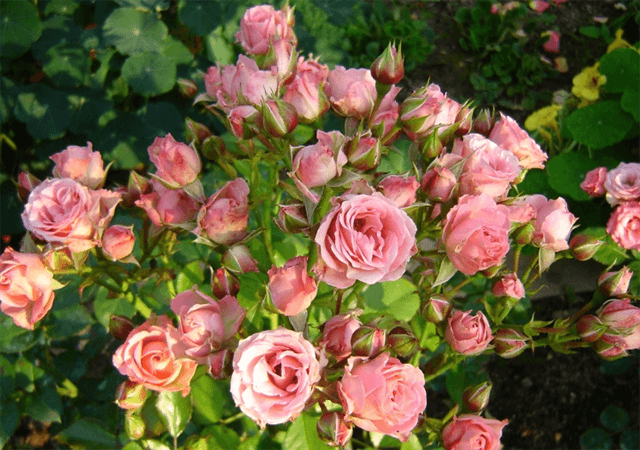
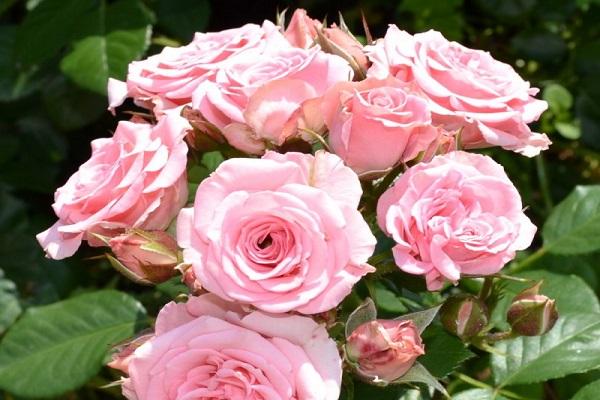
With proper care, a compact flowering bush becomes the main decoration of a garden plot. The main advantages of the culture are cold resistance, the ability to withstand frosts down to -20 °C, abundant flowering before the arrival of autumn frosts. Rose Lydia is grown both in greenhouse conditions and in open areas; it feels great in the cool climate of temperate latitudes.
- History of origin
- Description and characteristics of culture
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Overview of popular types
- Lovely Lydia
- Spray White Lydia
- Floribunda Classic Lydia
- Subtleties of cultivation
- When they plant
- Site selection
- Preparation of planting material
- Planting scheme
- Nuances of flower care
- Watering
- Top dressing
- Trimming
- Wintering
- Diseases and pests
- How to propagate the plant
- Use Cases
History of origin
The Lydia variety was developed by specialists from a Dutch company in 1995. This is a bush rose, according to its varietal characteristics it belongs to the floribunda category: a small plant with abundant flowering and the formation of large flower rosettes.
Description and characteristics of culture
The Lydia variety bush has a neat compact shape, grows up to 60 cm. It is characterized by low susceptibility to fungal infections and insect pests.
External features of the rose:
- absence of thorns;
- leaves are oval, smooth, rich green in color;
- buds of deep pink color, about 4 cm in diameter;
- inflorescences include from 5 to 15 buds.
The varietal feature of the rose is abundant flowering, but this can only be achieved with proper care of the plant.
Advantages and disadvantages
Flower growers call the advantages of the Lydia variety:
- frost resistance;
- immunity to fungal pathologies and pests;
- inconsistency in cultivation;
- flowering throughout the growing season.
The only drawback that displeases some gardeners is the black core of the flower, which becomes noticeable when the petals are fully opened.
Overview of popular types
The Lydia variety includes 3 subvarieties.
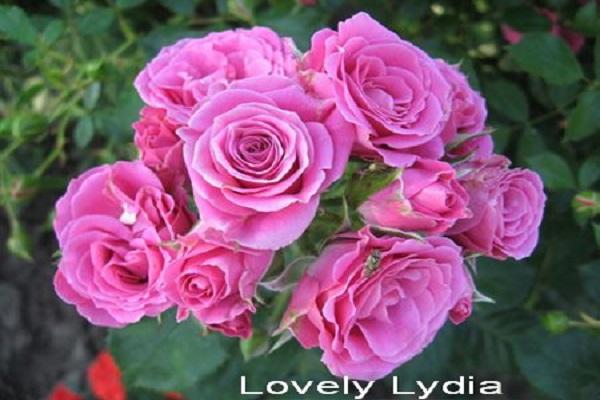
Lovely Lydia
The most common variety of rose. The bush does not grow higher than 60 cm. The diameter of the buds is 4 cm. The color of the petals of the Love Lydia rose can be light pink with a cream tint or deep pink, almost crimson. When there is excessive light, the petals fade, causing the color of the buds to become less intense.
The subvariety is characterized by lush and long-lasting flowering, if the bush grows on fertile soil and does not suffer from lack of care.
Spray White Lydia
A compact bush, the height of which does not exceed 50 cm, suitable for container growing.
The inflorescences include 10-15 flowers of pale cream, almost white color. The bud has almost no smell and is 4-6 cm in diameter.
Floribunda Classic Lydia
A compact but voluminous bush, reaching a height of 60 cm and a width of 50 cm. For lush flowering, it requires an abundance of light, regular watering and a fertile substrate.
The buds are small, not exceeding 3 cm in diameter. The inflorescence includes 10-12 flowers. Petals are pale pink. Elastic stems may have rare thorns.
Subtleties of cultivation
Even an inexperienced gardener can cope with planting a Lydia rose. Growing the crop is hassle-free; the main thing is to follow the watering and fertilizing regime.
When they plant
Roses are planted in the second half of spring, when the soil thaws after winter and is thoroughly warmed by the spring sun.
Site selection
For the Lydia rose, choose a lighted place, but not an open one. The bush should not be exposed to direct sunlight. The best option is an area with openwork penumbra. Also, the chosen location should be protected from drafts and strong winds.
Preparation of planting material
The selected rose seedling must be carefully examined. The plant should be free of damage, signs of rot and fungal infection.
Before the planting procedure, the shoots of the seedling are pruned. Buds, injured and dried branches are also cut off. There should be 4-5 buds left on the main shoots. Secondary branches must have at least 3 buds. You also need to remove weak and broken roots and shorten the side roots a little.
To make the cuts heal faster, they are lubricated with garden varnish.Next, the seedling is placed in a container with an aqueous solution of sodium humate for half a day.
Planting scheme
The planting hole is prepared in the fall. The area chosen for planting is cleared of weeds, and the roots remaining from other plants are removed.
If other species of the Rosaceae family, a hawthorn bush, a cherry or quince tree previously grew on the site, then it is advisable to remove 50 cm of the top soil layer and replace it with a new one. Otherwise, the rose will be weak due to lack of nutrition.
The soil on the site is dug up to the depth of a shovel blade. Lumps of soil are turned over, but not broken. This will help destroy soil pests and fungal infections during the winter cold. Break up lumps and level the soil in the spring.
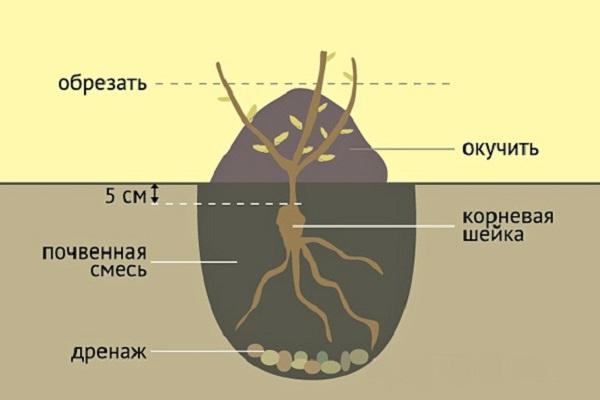
The Lydia rose is planted according to the following algorithm:
- dig a shallow planting hole (45x45 cm);
- the bottom is filled with drainage, a mixture of expanded clay, gravel, and sand is made;
- top dressing is placed on top, consisting of humus, peat, and rotted manure;
- the rose is placed in the hole so that the grafting area is immersed in the ground to a depth of 2 cm;
- the roots are straightened, the seedling is covered with earth;
- the surface of the soil is lightly compacted, the bush is watered abundantly (8 liters of water per plant).
Nuances of flower care
Rosa Lydia is not capricious in terms of care. It is enough to follow standard agrotechnical procedures: water and feed the plant, form a crown, put up a shelter for the winter.
Watering
Water the rose regularly: 2-3 times a week. If it is hot, then additionally spray the crown.
Top dressing
The roots of the rose become stronger by the age of 3; before that, it is not recommended to apply fertilizer to the bush.
Feeding is carried out:
- in spring – with a nitrogen preparation;
- in summer - potassium-phosphorus complex.
When the buds form, it doesn’t hurt to fertilize the rose with manure.
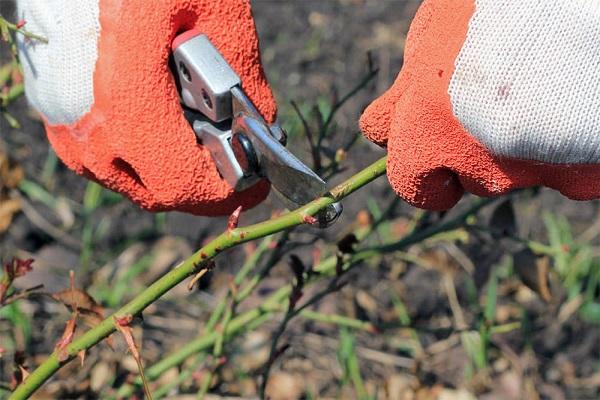
Trimming
Pruning a rose for:
- formation of shoots;
- ensuring more luxuriant and longer flowering.
The procedure is carried out three times a season:
- in the spring, cut off shoots up to 12-15 cm, leave 2-3 buds on the main shoots, 1-2 on secondary ones;
- in summer, they rid the plant of withered branches and faded buds;
- In the fall, cut off diseased and weak branches.
Wintering
Despite its winter hardiness, rose Lydia needs winter insulation. Insulation is installed if the night air temperature in winter falls below -8 °C. Spruce paws are used as covering material. A frame is placed on top, which should be 20 cm higher than the plant. It is covered with plastic film or agrofibre.
In early spring, the insulation is periodically opened for ventilation. And with the arrival of constant heat they are removed.
Diseases and pests
The Lydia variety is immune to infectious pathologies and insects, subject to proper care. A rose gets sick if it is adjacent to weeds and diseased vegetation, and also if the owner does not take care of it.
Rose can be affected by:
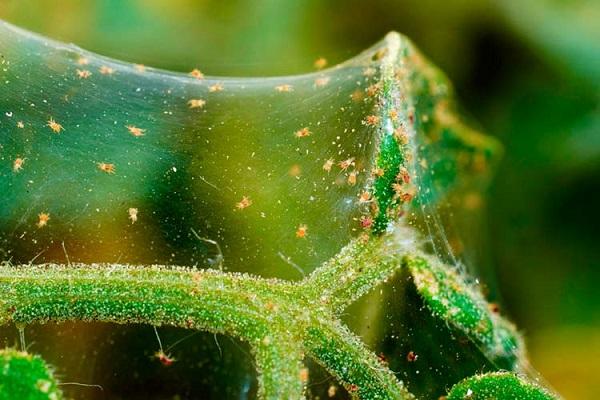
- Spider mite. To combat it, the insecticide Fitoverm is used. For prevention, the plant is regularly inspected for the presence of cobwebs, and spraying is carried out in hot weather.
- Aphid. If there is not much of it, then just wash the plant with soapy water. If the lesion is advanced, then you will have to use insecticides - Karbofos, Actellik.
- Powdery mildew is a fungal infection that develops under excess humidity and low temperature. To combat the disease, spray with 0.5% soda ash. Bordeaux solution is used for prevention.
How to propagate the plant
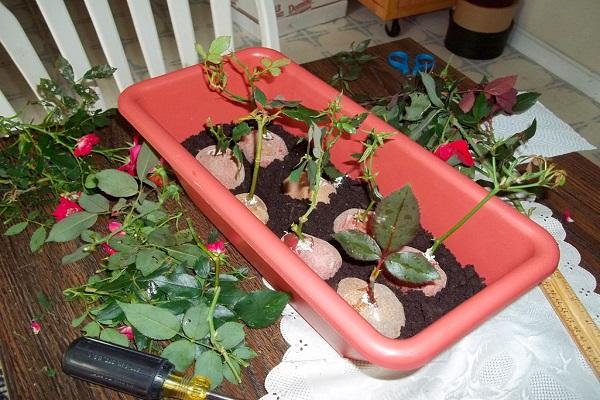
Rose Lydia is propagated by cuttings. The procedure is carried out in the summer months. Select the lower shoots with 3-4 leaves and cut them obliquely so that the cut has an angle of 45°. The cutting should have one leaf and 2 buds at the bottom.
A rose is cut according to the following algorithm:
- the cutting is placed in a root growth stimulator solution for 2 hours;
- then planted in a container filled with peat and sand mixed in a ratio of 3:1;
- the substrate is moistened, the container is covered with polyethylene to form a greenhouse effect;
- The film is periodically removed for ventilation.
The young plant is pruned the following year in the spring. Leave the main shoots with 2-4 buds and cut them to about 15 cm.
Use Cases
The Lydia variety is considered a greenhouse variety, but due to its winter hardiness, it is suitable for growing in open ground, and due to its compactness and unpretentiousness, it is often used in landscape design.
Rose Lydia is used for:
- formation of rosaries;
- drawing up border compositions;
- decoration of the terrace, porch, gazebo (as a potted plant).
Florists also love to use roses to create lush holiday bouquets.