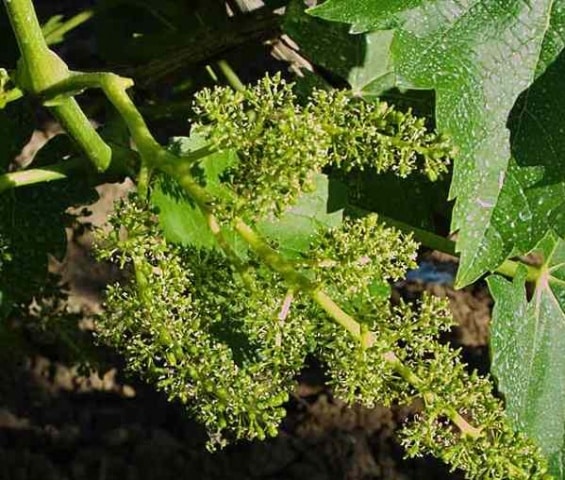
Among garden crops, one cannot fail to note those varieties that were bred not by scientific breeders, but by amateurs. Every summer resident knows about Sofia grapes. This table hybrid has many advantages. And in the southern regions it is widespread. But lovers of fruit crops in regions with temperate climates also cultivate the vine, creating favorable conditions for it.
History of selection
The Ukrainian gardener V. Zagorulko, well-known among winegrowers, has been breeding new varieties for many years. And I got a hybrid that combines the best qualities of the Arcadia and Kishmish Radiant grapes.From its parents, the Sofia variety received the sweet taste of berries, fleshy and juicy. In addition, the grapes have a strong vine and bear fruit abundantly.
Description
The Sofia grape has a distinctive feature:
- the strength of a bush with large leaves, slightly dissected;
- large conical brushes, reaching a weight of 1.5-2 kilograms;
- pinkish berries weighing 10-20 grams;
- juicy sweet fruit pulp, almost seedless.
The description of the variety also includes high vine productivity. In favorable conditions, you can remove up to 40-50 kilograms of berries from one bush. In addition, the vine is decorative and will become a true decoration of the garden. The leaves on brownish stems are slightly wavy, large, and have a bright green color, acquiring a yellowish tint in the fall.
Characteristics of grapes
The main advantage of the Sofia variety is the power of the vine and the appetizing nature of the fruit. Among the large leaves, giant clusters of grapes look great. There are a lot of berries on each, and they fit tightly together. The color of the grapes is interesting. The soft pink fruits seem to glow when illuminated by the sun.
Despite the predominance of female flowers on the vine, the Sofia variety sets fruit perfectly, taking in pollen from neighboring bushes.
The grapes bloom for a long time, and the duration of fruit ripening reaches 110-115 days. At the beginning of August, the first berries are already picked. You shouldn’t keep them on the bushes too long, otherwise they will begin to crack and fall off.
What makes the Sofia grape different:
- drought resistance;
- excellent survival rate of seedlings during planting;
- average immunity to fungal infection;
- poor tolerance to low temperatures.
Although the variety requires special growing conditions, it is grown both in Siberia and the Far East.
Rules for planting and care
Grape seedlings for planting are chosen one or two years old. The pits are prepared in advance up to 80 centimeters deep and 50-60 wide. Be sure to mix the soil with compost or humus, superphosphate and potassium salt. Before planting, the roots of the cuttings are shortened to 20 centimeters. You can dip the seedling in the Kornevin solution and then place it in a mash of clay and manure. After planting, it is necessary to water the seedlings abundantly. Watering should be done moderately. The Sofia grape variety does not like excessive waterlogging, but does not tolerate prolonged drought.
Berry bushes need to be formed by annual pruning. Every year, 10-12 buds are left on each vine. The lateral processes break off completely. It is imperative to thin out the branches, creating better permeability of the plantings for air and light. The berries in the bunches also need thinning, otherwise they begin to rot at such a high density. They are trimmed with scissors, unloading the brush by 30-40% at the pea stage.
Disease and pest control
To prevent infection of the variety with oidium or mildew, spray the bushes with a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture, first in the spring, when the leaves have blossomed. The next treatment is needed in 10-15 days. Among the drugs active against pathogenic fungi are “Skor” and “Topaz”. They are also used in the treatment of diseases.
Wasps are attracted to Sofia's sweet berries. They can ruin the entire harvest. Insects are repelled from the vine with sticky baits. The nests near the vineyard are sprayed with Dichlorvos and Karbofos.
Reproduction
There is such a common way of propagating Sofia grapes as by cuttings. They are grown in pots and then transferred to open ground after a strong root system has emerged.
Grafting is used as propagation to increase the variety's resistance to frost. The Arcadia variety is suitable as a rootstock.