Ringworm is a disease that is most often caused by pathogenic fungi. A variety of animals and people can suffer from it. Although it most often affects stray cats and dogs, lichen can also occur in rabbits. To prevent it from spreading to the entire livestock, it is important to identify sick animals in time, immediately show them to a veterinarian and begin treatment.
Information about the disease
The causative agents of lichen are various microorganisms, most often fungi. The following types of skin diseases occur in domestic rabbits:
- pityriasis rosea, it is of a viral nature and most often goes away without treatment;
- pityriasis versicolor is caused by yeast-like fungi;
- herpes zoster occurs when infected with herpes viruses and does not require special treatment;
- tinea versicolor, or eczema, is a non-contagious disease associated with exposure to external or internal factors.
Rabbits also suffer from trichophytosis, microsporia, or ringworm. The disease is one of the most dangerous types of fungal skin infections. Not only other animals, but also humans quickly become infected with it. Ringworm is accompanied by hair loss and requires immediate treatment. Success in treating trichophytosis in domestic rabbits begins with diagnosis.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
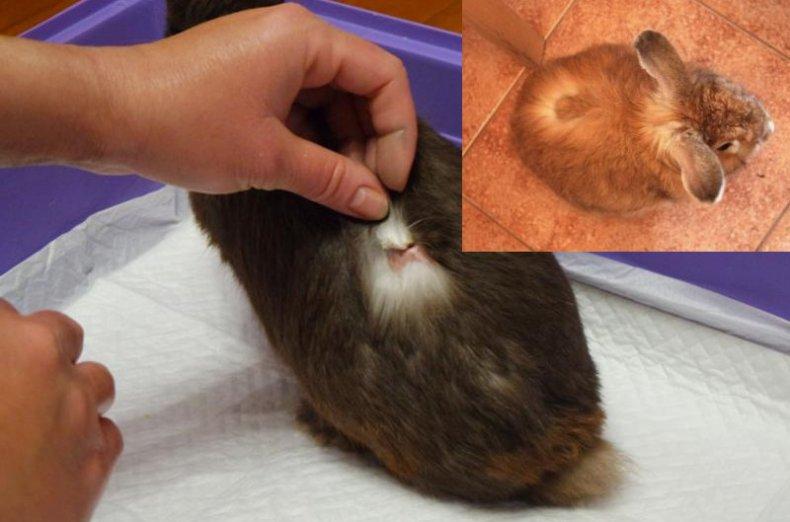
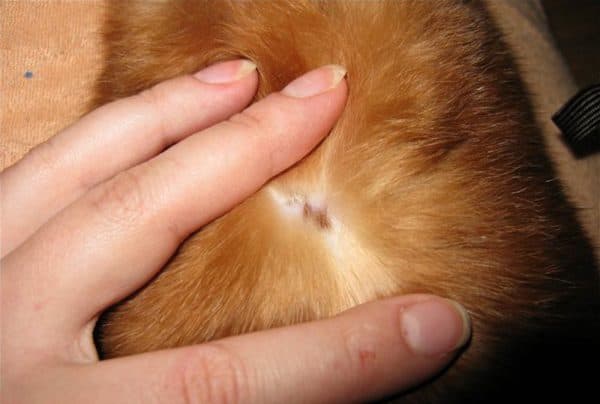
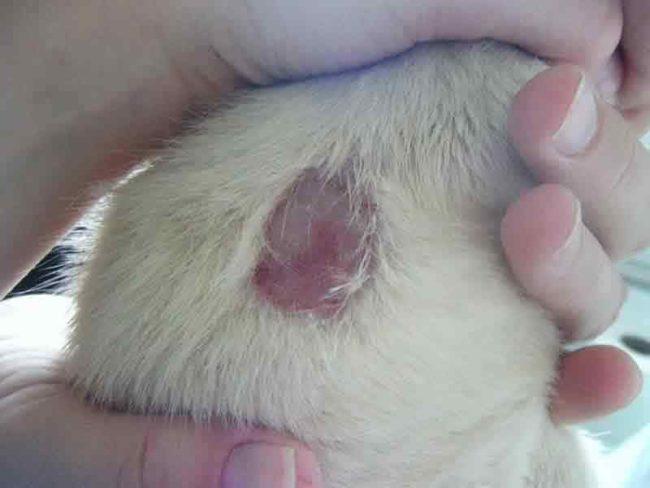
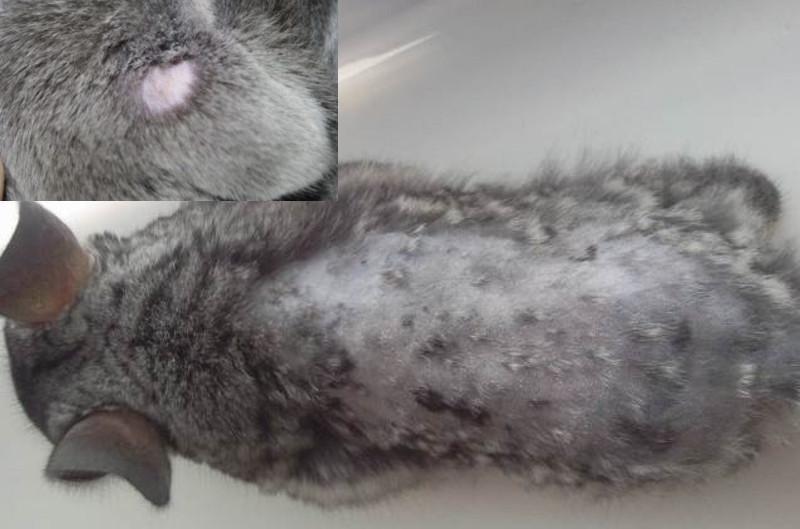
With lichen, the latent period lasts from two to four weeks. During this time, quite a lot of animals on the farm can become infected. Ringworm is especially dangerous for young animals no older than 6-7 months. To detect the disease in time, animals are regularly examined. The alarm should be sounded when the following signs appear:
- areas with broken hair of different lengths became noticeable;
- pink spots with a diameter of up to 20 mm appeared on the skin;
- the skin in the affected areas began to peel off;
- crumbling scales have a grayish color;
- rounded hairless areas with a diameter of 10 to 30 mm appear;
- The fur of sick animals gives off an unpleasant odor.
Foci of inflammation may appear on the eyelids, neck, ears, muzzle, and limbs of the rabbit. After a few days, the skin in the affected areas swells, and blisters with purulent contents appear. The animal suffers from severe itching and its behavior becomes aggressive.
Ringworm is caused by trichophyton and microsporum fungi. They can only be detected by laboratory methods:
- Irradiation of wool with a special ultraviolet lamp, if there are colonies of pathogenic fungi, they reflect not an even blue color, but an emerald green or yellow-green color.
- Examination of skin scrapings under a microscope.
- Sowing on nutrient media.
Important! In some cases, the microorganisms that cause ringworm do not glow under ultraviolet light. This diagnostic method is preliminary and requires confirmation.
How to properly treat ringworm in rabbits?
At the first stage of treatment, all sick individuals are placed in a separate enclosure. Treatment is carried out both with the help of external preparations and with the help of drugs that are administered by injection or given with food and water.
Vaccines
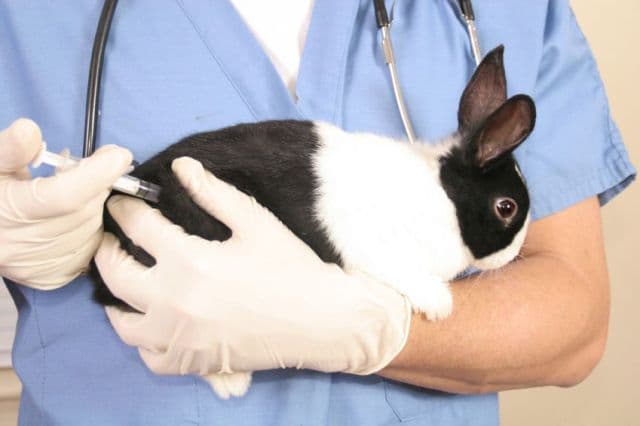
The use of vaccines is primarily of preventive value. Most provide immunity for 12 months after vaccination. A popular vaccine is Vakderm. This is a domestic drug for the prevention and treatment of lichen. One dose consists of two components, packaged in separate bottles or ampoules.
Contains inactivated (killed) pathogens of several types. For injection, use a sterile needle and syringe.
First, the liquid component is drawn into a syringe and transferred to a bottle with a dry mixture. Shake and after complete dissolution, draw the solution into a syringe and inject into the thigh area. For preventive purposes, it is administered twice with an interval of two weeks. The second time the injection is given in the other thigh. Immunity occurs 14 days after the second administration. It is recommended to vaccinate rabbits at the age of 50 days. They are administered the drug in the amount of 1/2 dose, and animals older than three months are injected with a full dose.
If vaccination is given during the incubation period, it accelerates the onset of symptoms. Such an animal is administered Vakderm twice more for therapeutic purposes. This is done every 15-20 days. The Microderm vaccine is also used in a similar way, but it must be taken into account that it is much more expensive than Vakderm.
Ointments
To treat lichen in rabbits, you can use a special ointment “Yam”. This is a domestic fungicidal preparation containing salicylic acid, tar, sulfur, turpentine and petroleum jelly. It is an effective means of combating pathogens of lichen and scabies. The affected areas are cleaned of crusts, the hair around them is trimmed and a thin layer of ointment is applied. The procedure is carried out twice a day. After 10 days, laboratory tests are carried out; if the pathogen is detected, then treatment is continued for several more days.
Lesions can also be treated:
- salicylic ointment;
- iodine vasogenome;
- "Unisan."
The imported drug for external use "Imaveron" has proven itself well, but it is quite expensive and is not always available in pharmacies. Ointments must be used strictly according to their instructions.
Antibiotics
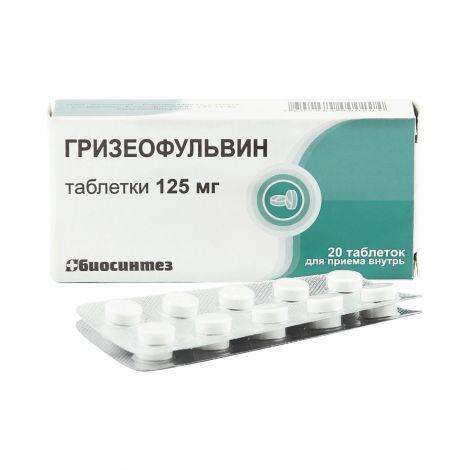
Veterinarians may prescribe antibiotics to treat ringworm in rabbits. The most popular drug is Griseofulvin. It is given to sick animals twice a day. The medicine is added directly to the rabbit food for 3 to 5 weeks. Antibiotics are not used to treat pregnant females and lactating rabbits.
Shampoos
The use of shampoos is an additional, and not the main, way to treat rabbits for ringworm. Pet shampoos containing antifungal drugs, such as Nizoral, are suitable for this.
Is there a danger to humans?
Ringworm is also dangerous for humans. If sanitary standards are not observed, the pathogen easily gets on people’s skin or hair. A person's head, face, neck and nail beds may be affected.
Children and people with weak immune systems are especially susceptible to infection. If domestic rabbits have been diagnosed with lichen, then when working with them, you must strictly observe safety precautions and do not allow children near the animals.
Preventive actions
The basis of preventive measures is compliance with sanitary standards when keeping and breeding rabbits. They are as follows:
- regular cleaning of cells once every two days, you need to add a chlorine-containing product to the water for cleaning, for example, “Belizna”, use 1 liter of product for 10 liters of water;
- do not expose animals to hypothermia;
- keep in dry rooms, without drafts, but with good ventilation;
- vaccinate rabbits in a timely manner;
- avoid excessive crowding of animals;
- Do not breed your pets with unvaccinated rabbits from other farms.
To improve immunity, animals need high-quality and balanced feed. New rabbits should not be immediately placed in common cages. They are kept in strict quarantine for 10-14 days. Sadly, in severe and intractable cases the animal will have to be euthanized.