The use of feed yeast when breeding cattle is an important point for farmers who want to fully feed livestock, maintain their health and reduce the cost of maintenance. Yeast is not an independent type of food; it is added to the usual feed to accelerate weight gain, increase milk yield, and the productivity of cattle in terms of meat. When selecting, using and storing a supplement, it is important to follow the instructions given by the manufacturer.
How feed yeast is made
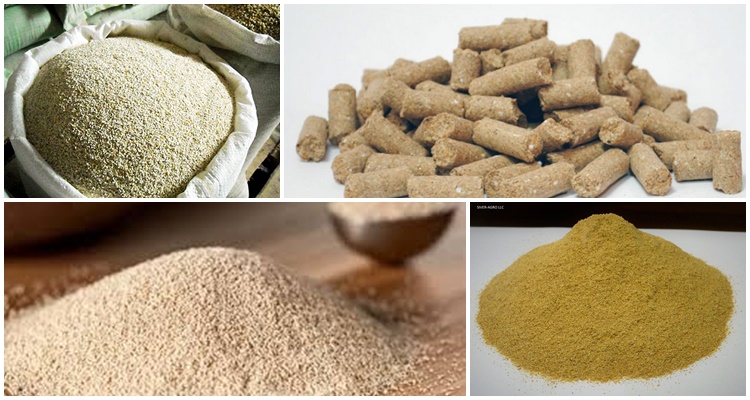
Feed yeast is a fungus that has only a positive effect on the organisms of animals and people, due to which they are used in various spheres of life. Feed products used when feeding cows are granules or a brown powder mixture with a pronounced yeast aroma. Biomaterial is produced in specialized workshops where optimal temperature and humidity levels are maintained.
Crops are grown in the most nutritious environment enriched with oxygen. During production, GOST 20083-74 is observed, the finished additive is dried, packaged, then packaged and sent to points of sale.
Composition of the product
The yeast product is made from the remains of organic derivatives:
- sunflower seed skins;
- straw, reeds;
- corn cobs;
- waste left over from wood production.
The highest quality additives are those made with the addition of alcohol stillage. Feed for cattle contains a small amount of protein compounds, so feed yeast is recommended for use in livestock nutrition to compensate for the deficiency of minerals and organic substances.
The chemical composition of the product includes:
- protein – 31-37%;
- protein – 37-52%;
- fiber – 1.3-2.8%;
- fats – 1.8%;
- dietary fiber – 1.8%;
- wood ash – 10%.
The product contains vitamins B, E, D, K, which support full digestive function, and substances necessary for the absorption and high absorption of vitamins, microelements, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Benefits and harms
It has been established that the norm for cattle is the consumption of 110 grams of protein per unit of feed, and when feeding livestock with conventional compound feed, only 85 grams of protein are present on the menu.This leads to poor absorption and digestion of food, decreased productivity, weight gain and the volume of milk produced.
Advantages of using feed yeast in barns:
- acceleration of weight gain in young animals;
- increasing the production indicators of cattle - milk yield, increasing the volume of slaughter weight;
- normalization of digestive processes;
- positive effect on the composition of gastric and intestinal microflora;
- improving sperm quality in breeding bulls;
- strengthening livestock immunity and preventing infectious diseases;
- increasing the nutritional value of food;
- reduction in feed consumption, which has a beneficial effect on the cost of raising cattle.
Protein and protein are vital for cows, but it is difficult to get enough of them on plant foods alone.
There are no disadvantages to the supplements. But if a farmer consistently exceeds the dosage recommended by the manufacturer or uses poor quality products, cows may develop obesity or digestive dysfunction.
Varieties of feed yeast
Products can be divided into three groups, based on the method of their production:
- Hydrolysis - waste from food and wood production is used in production. Under intense acid and temperature influence, fungi multiply in the raw materials. A ton of hydrolytic yeast contains from 240 to 450 kilograms of protein. The product has a yellowish or brownish tint and is produced in granular or powder form.
- Classic - considered the most beneficial for animals, since they contain a large mass of proteins (about 400 kilograms per ton) and a minimal amount of crude protein. They are produced using stillage. The product comes in the form of a flake powder and is also available in granular form.
- Protein-vitamin concentrates (PVC) - colonies of fungi are grown on waste left over from the processing of petroleum products, on organic alcohol and natural gases. BVK include the maximum amount of protein (up to 800 kilograms per ton) and vitamin B.
During production, many manufacturers subject the finished product to ultraviolet treatment. This increases the concentration of vitamin D in it, and the natural value of vitamin B disappears. Farmers need to take this fact into account when purchasing a product.
Application for cows
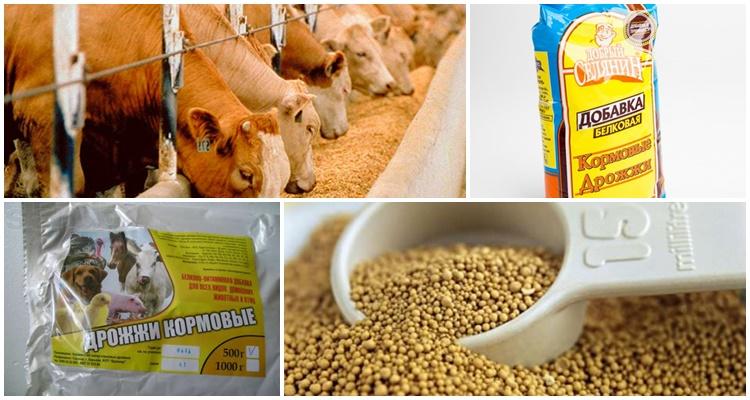
It is important for animals to receive the required daily dose of protein, which is why a yeast feed product should be included in the menu:
- cows with high milk yields (more than 20 liters) during lactation and milking. The protein contained in the supplement helps to normalize microflora in the rumen and stabilize its functions, prevent acidosis, and maintain stable lactation. Daily portion – 500-800 grams;
- for cows consuming sour silage, fresh and sour pulp - to preserve digestive function, protect it from the pathological effects of acid, improve the intrauterine formation of calves, and increase milk yield. One cow can be given from 500 grams to 1 kilogram of the supplement per day;
- for dairy cows fed chaff - to maintain optimal acidity levels, improve food digestion and absorption of nutrients.The daily dose of the supplement for a cow is 1 kilogram;
- for breeding bulls - the product begins to be given 2-3 weeks before mating the cows or collecting material for fertilization, 0.5-0.8 kilograms per day and is fed until the end of the mating period;
- for young animals - with inadequate nutrition or feeding with low-quality hay. Calves are given 0.2-0.3 kilograms of yeast per day; as the calves grow, the dosage increases.
According to the instructions, yeast should be added to the main grain and combined mixtures.
When stirring, if a little more yeast was added than required, nothing bad will happen, since their use does not cause harm to animals.
How to select and store
Good yeast should have a pleasant yellowish-brown tint, a pronounced yeasty aroma, and be dried. Elements of rot or mold are not allowed.
Yeast storage conditions:
- temperature – from -30 OFrom to +30 OWITH;
- darkened room, without access to moisture;
- away from chemical compounds and poisons, since yeast is able to absorb pathological evaporation.
If a farmer suspects that the yeast is expired, has rotted, or notices moldy inclusions in the packages, it is better not to purchase such a product. It will not benefit livestock, but can provoke the development of serious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
The shelf life of feed yeast is 6 months, after which it is not recommended to give it to cows. Feed yeast has long won the trust of farmers by increasing livestock productivity and milk yield, improving the quality of meat and milk, and maintaining animal health at the proper level. Using the product in livestock farming also helps to save finances and increase the profitability of the farm.