Body temperature is a criterion by which one can judge the health of an animal. Normal indicates that no pathological changes occur in the body; an increase or decrease indicates the onset of a disease or pathological condition. Let's look at the normal body temperature of a cow, an adult and a calf, why it changes, how to measure it and how to bring it back to normal.
Normal body temperature of cows
They are different in adult animals and calves. In young animals they change with age, in cows and bulls they stabilize.
In adult animals
The normal temperature for cattle is considered to be 37.5-39 °C. Minor deviations upward or downward are acceptable, which are explained by the individual characteristics of the body. You can measure a cow's temperature using a veterinary thermometer.
| Animal age | Temperature |
| From 1 year and older | 37.5-39 ˚С |
In calves
Body temperature readings in young calves differ from those typical for adult animals. They also vary depending on the age of the calf. After calving, the temperature may drop while the calf dries out.
| Calf age | Temperature |
| 2-6 weeks | 38.5-41 °C |
| Up to 2 months | up to 40.2 °C |
| Up to 1 year | up to 40 °C |
Deviations of 1 °C or more may indicate the development of a pathological process.
Possible reasons for the increase
The temperature may rise due to illness, infectious and other diseases, and poisoning. In cows that have given birth, its rise may be observed due to complications after calving. An increase may be a consequence of poor animal care.
Poisoning
Cows have a poor taste for food, so they can eat plants and foods that are poisonous to them. An increase in normal temperature is one of the signs of poisoning, along with diarrhea, depression, changes in behavior, and decreased physical activity. Once poisoning is discovered, you should immediately contact a veterinarian. The poison can kill an animal within a few hours.
Poor nutrition
The increase may be caused by poor quality feed fed to cows. Bacteria and fungi enter the cattle's body, the toxins of which provoke a rise in temperature. Digestive upset is also observed, but animal death usually does not occur.
A reaction in the form of increased heat generation in cows may be due to the introduction of unfamiliar feed or additives into the diet, due to stress during transportation, or disruption of the walking regime.
Diseases
Infections that enter the body, bacteria and viruses, become the causative agents of dangerous diseases. The temperature rises as a result of the body's immune response to inflammatory processes. Diseases in which this occurs: leukemia, leptospirosis, pneumonia, brucellosis, foot and mouth disease, plague.
Complications after calving
Postpartum illnesses can also cause such a reaction in the body. Often this is a symptom of endometritis, paresis or mastitis. These are serious diseases that can lead to complications and even death of the animal.
Hyperthermia is explained by injuries to the birth canal and inflammation that occurs after childbirth, and retention of the placenta.
Mastitis develops in dairy cows, the inflammation is concentrated in the udder, but the temperature can rise throughout the body. The reason is streptococci and staphylococci that enter the open milk ducts.
Reasons for the drop in temperature
The causes of hypothermia, or decreased body temperature, in cows can vary. This may be hypothermia (a decrease is recorded once), weakening as a result of severe pathologies. A decrease may be caused by dehydration, enteritis, or severe blood loss.
To establish why a cow’s temperature dropped, you need to find out whether it was exposed to hypothermia, whether it had diseases or conditions characterized by a decrease in the level of thermoregulation.The degree of hypothermia can be determined by the symptoms:
- mild – drowsiness, tremor, weakness;
- moderate – bradycardia, hypotension, decreased respiratory rate and depth, stupor, muscle rigidity;
- strong – dilated pupils, coma, depressed breathing, slow heart rate.
Hypothermia associated with central nervous system depression must be differentiated from hypoglycemia, tumor diseases, water-mineral imbalance, and brain pathologies.
How to shoot down
Once the causes of hyperthermia have been established, treatment can begin. Cows are prescribed antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antipyretic drugs, vitamins, and given plenty of water.
However, when trying to eliminate hyperthermia, you need to remember that you should eliminate the cause, not the consequences.
In addition, by lowering the temperature, you can make it worse, because increasing the temperature is a protective function of the body, with the help of which it tries to fight viruses and bacteria. Therefore, it is possible to bring down the temperature only after a diagnosis has been made by a veterinarian and treatment has been prescribed. The duration and intensity of therapy is determined by the doctor based on the current condition of the animal.
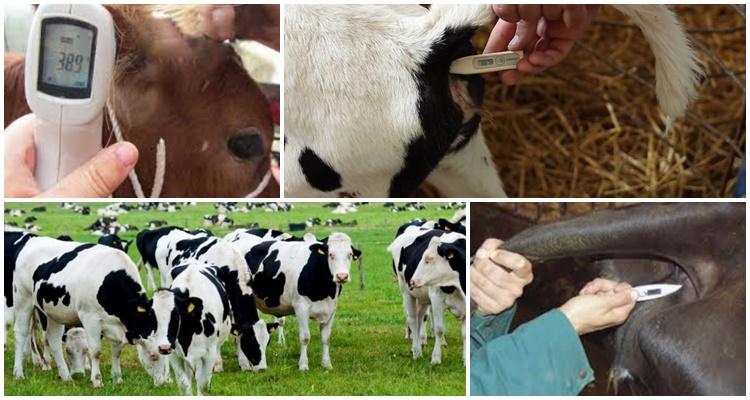
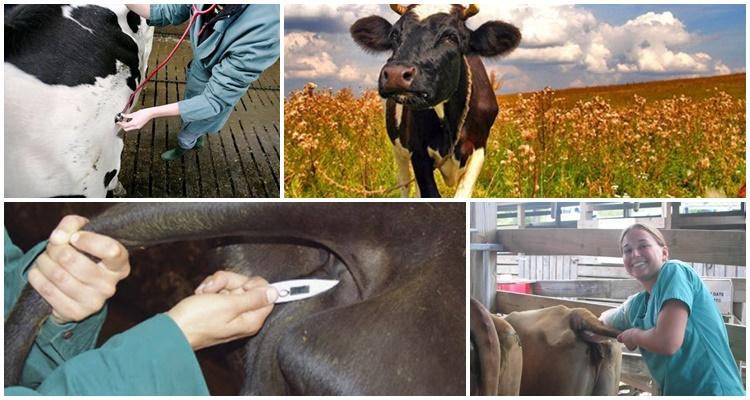
How to measure temperature
Various instruments are used for measurement. They are used both in veterinary clinics and at home. One common method is to insert a thermometer into the rectum. Thermometers can be mercury or electronic. Despite the higher cost, the electronic type makes measurements more accurate and is also safe for humans and animals.
The measurement process can be divided into stages:
- disinfection of instruments - wiping with a cotton swab soaked in alcohol;
- lubrication with Vaseline or other means to facilitate insertion into the rectum;
- insertion of the device 2-3 cm into the intestinal cavity.
To take measurements, the thermometer is kept in the cow’s body for 6-8 minutes. – mercury and 1 min. – electronic. After completing the procedure, the instrument is cleaned in soapy water and disinfected again with alcohol. The anal area of the cow is treated with an antiseptic. When measuring, you need to remember that some animals are nervous during the procedure and can be aggressive. Therefore, you need to work with cows following safety precautions.
During treatment, measurements can be taken up to 3-4 times a day until the animal recovers. After its completion, you can measure 1-2 times a day for 2-3 weeks. This is necessary to prevent the possibility of relapse of the pathology.
If the body temperature of cattle is normal, the animal is healthy. If there are deviations upward or downward, this is a signal that pathological changes are occurring in the livestock’s body and it needs treatment. This is why measuring and monitoring this body function is so important. Sometimes the life of a cow or calf depends on the timeliness of treatment.