The success of a farmer depends entirely on the health of his animals, and for a farm, a cow is the source of well-being for the whole family. Like people, animals, and dairy cows in particular, are susceptible to various diseases, including infectious ones. Against diseases caused by bacteria, the use of tetracycline for animals, which exists in several variations, is practiced.
- Features of tetracyclines
- Indications for use
- Varieties
- Oral
- "Biovit"
- "Terravetin"
- "Mepatar"
- "Doxycycline"
- External
- "Terramycin spray"
- Eye ointment
- Tetracycline ointment
- Parenteral
- "Nitox"
- "Morphocycline"
- "Doxycycline-200"
- Rules of application
- Advice and recommendations from experts
- Can I drink milk while using antibiotics?
Features of tetracyclines
Antibiotics of the tetracycline group are used to destroy most gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including Escherichia, Salmonella, staphylococci, streptococci, as well as rickettsia and some types of mycoplasmas. It should be borne in mind that antibiotics are ineffective against viruses and fungal infections, so they can be prescribed only after identifying the causes of the disease and making a diagnosis.
In some cases, feed containing low doses of antibiotics is used to feed cattle to prevent various diseases. This method allows you to relieve livestock from the risk of infection, but has a negative impact on the quality of meat and dairy products. In a number of countries, the method is banned.
The drugs come in several forms. The powder is used for injection; tablets, ointments and irrigation sprays are made from it. When using tetracycline, the color of tooth enamel may change. Livestock can be slaughtered only 6 days after finishing taking the drug. If the animal was slaughtered before this period, its carcass is used to feed fur-bearing animals or to produce meat and bone meal. Such meat should not be used as food for people or pets.
Indications for use
Tetracyclines are used to treat a number of infectious diseases caused by gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria that are sensitive to these substances. The agent destroys the bonds formed between the ribosome and transfer RNA.This causes suppression of protein synthesis and leads to the death of the pathogen.
The list of pathogens against which tetracyclines are effective includes the following:
- Escherichia.
- Salmonella.
- Staphylococci.
- Streptococci.
- Rickettsia.
- Some varieties of mycoplasmas.
- Pasteurella.
- Listeria.
- Anthrax microbes.
- Leptospira.
- Clostridia and a number of other pathogens.
Proteas, a significant proportion of fungi, acid-resistant bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and viruses are insensitive to tetracyclines or show low susceptibility.
Tetracycline-based drugs are prescribed for diseases provoked by the listed pathogens, as well as for the following diseases:
- Pneumonia.
- Mastitis.
- Metritis.
- Erysipelas.
- Gastroenteritis.
- Lesions of the urinary tract.
- Eczema, burns and wounds of various origins, especially infected ones.
- Diseases of the eyes, ears, mouth.
Tetracycline is not prescribed to pregnant cows due to negative effects on the fetus. Also, drugs can cause allergies, including anaphylactic shock in case of hypersensitivity to them.
Varieties
Depending on the method of use, there are the following types of drugs.
Oral
These antibiotics come in tablet form and are given to calves by mouth (orally). They dissolve in the digestive tract and are absorbed into the blood, so such drugs are often prescribed for diseases associated with damage to internal organs.
"Biovit"
The drug is a dry culture liquid on which chlortetracycline was grown. Available in several versions: “Biovit-40”, “Biovit-80”, “Biovit-120”, which contain, respectively, 40, 80 and 120 milligrams of tetracycline and 4, 8 and 12 micrograms of vitamin B12. This is a therapeutic and prophylactic drug that is given to calves and other animals and poultry when there is a threat of infection, especially when housing is crowded.
"Terravetin"
A domestic drug, 1 gram of which contains 500 micrograms of oxytetracycline hydrochloride. Supplied in 250 gram plastic bags placed in cardboard boxes. It is prescribed to calves 20-40 milligrams 2-3 times a day in the form of a solution in water.
"Mepatar"
This is an analogue of Terravetin-500, produced in Poland, containing 50 milligrams of oxytetracycline in 1 gram of the product. Calves are prescribed 40-60 milligrams of the drug, which are divided into 2 or 3 doses, dissolved in drinking water.
"Doxycycline"
This is a semi-synthetic derivative of oxytetracycline, a broad-spectrum antibiotic. Suppresses protein synthesis of pathogens. It is characterized by accelerated absorption, almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and excreted in urine and manure. It has the property of spreading throughout the tissues and fluids contained in the body. In cattle, Doxycycline (Vibramycin) is most often used to combat brucellosis.
External
These types of drugs are used exclusively for the treatment of external lesions. They exist in the form of ointments, emulsions or aerosols that form a thin active film or layer on the body.
"Terramycin spray"
The aerosol product is used in veterinary medicine to treat wounds, skin irritations, eczema, as well as hoof rot, skin diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to tetracycline antibiotics.
Eye ointment
This remedy is effective for bacterial conjunctivitis, blepharitis and other eye infections.The ointment is applied to the affected areas and placed behind the eyelid. Antibiotic content – 1%.
Tetracycline ointment
For the treatment of eczema, infected skin lesions, abrasions, wounds, suppurations, boils, and inflamed burns, 3% tetracycline ointment is used.
It is distributed in a thin layer over the affected area 1-2 times a day or used for dressings daily, until signs of infection completely disappear and the sore spot heals.
Parenteral
This type of drug is intended for administration by injection, which eliminates absorption through the digestive tract, accelerating the penetration of the drug into the blood and lymph.
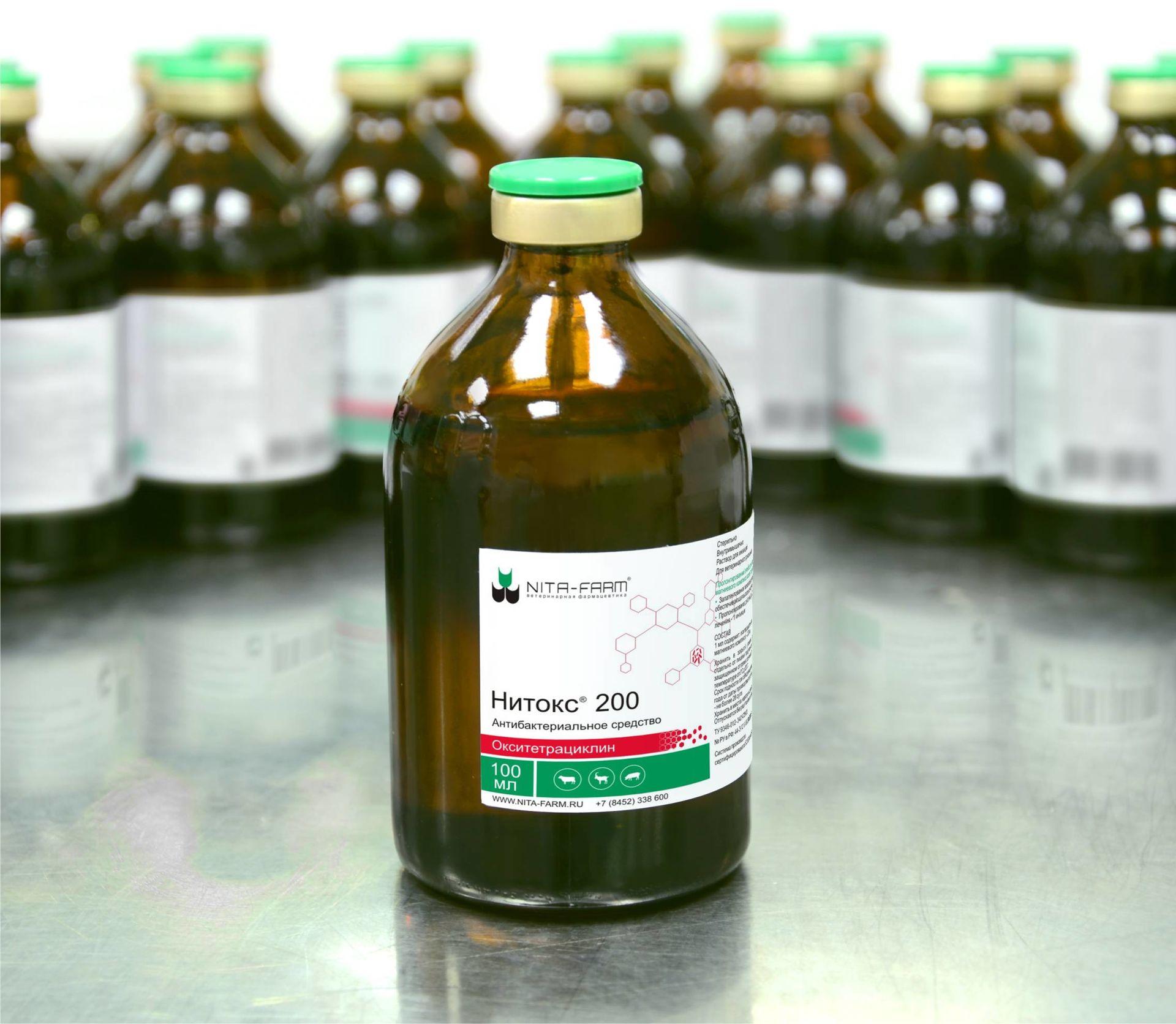
"Nitox"
This is the most commonly used veterinary injectable drug, released in water, a brown, clear liquid with a slight degree of viscosity. Nitox-200 is supplied to pharmacies in the form of glass bottles of 20, 50 or 100 milliliters.
"Morphocycline"
It is a synthetic, water-soluble tetracycline preparation used for intravenous injection. Contains from 600 IU (units of action) of antibiotic in 1 gram of the drug, diluted with a 5% glucose solution, available in bottles of 0.1 and 0.15 grams, administered 1-2 times a day at the rate of 0.001-0.002 grams per 1 kilogram of body weight.
"Doxycycline-200"
The active ingredient is doxycycline hyclate in a ratio of 200 milligrams per milliliter. Prescribed to small and large cattle, pigs for pneumonia, salmonellosis, hoof rot, pasteurellosis, keratoconjunctivitis and a number of other infections sensitive to tetracyclines.
Rules of application
When using any antibiotics, including tetracycline, be sure to follow the instructions for use.Contraindication for use is an allergic reaction and hypersensitivity to this group of drugs. The duration of treatment, dosage and form of the antibiotic, and method of administration are selected by the veterinarian based on the age and health of the animal.
Advice and recommendations from experts
Antibiotics are serious drugs that can either harm the body or be beneficial. They can cure dangerous bacterial infections that can harm the cow and cause mass destruction of the herd. At the same time, antibiotics, including tetracycline, can only be used as prescribed by a veterinarian and only if it is impossible to do without them.
It is risky and irresponsible to prescribe such complex medications randomly or without a reason.
Can I drink milk while using antibiotics?
Antibiotics pass into milk, so they are not used for human food or for feeding calves during treatment and for some time after completion. The milk is milked separately and disposed of because it is no good. After completion of treatment, cows can be milked and milk can be used for its intended purpose only if antibiotics are not detected in the samples.