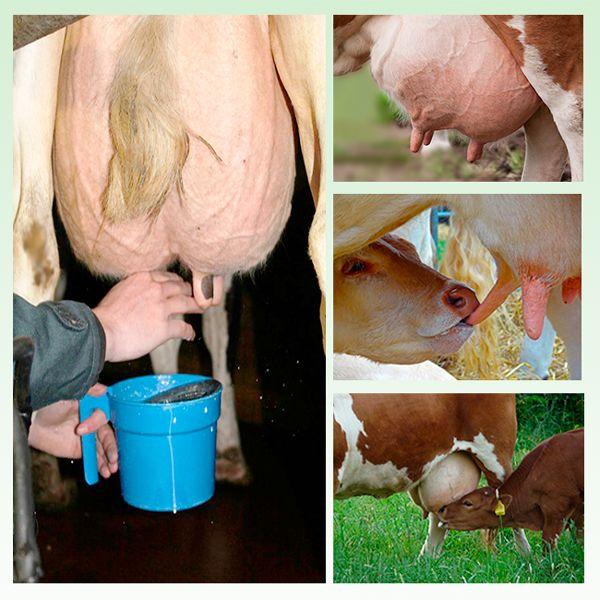
Cattle owners sometimes face the problem of reduced milk yield. Lactation affects the feeding of offspring, and obtaining livestock products is important for the development of the economy. Therefore, farmers are concerned about the question of why a cow squeezes milk and does not give it all away. If the reasons are not figured out in time, milk production may stop completely.
Poor living conditions
Lactation period in a cow begins immediately after calving and ends a month before the next birth. Productivity during this period is influenced by various circumstances.If the animal is healthy, the problem is often easy to fix. The conditions under which livestock are kept are of great importance. A caring owner always makes sure that normal conditions for animals are created in the barn:
- absence of drafts;
- regular ventilation;
- maintaining optimal humidity and air temperature;
- timely removal of feces;
- replacing old and dirty bedding.
The animal pen is kept clean at all times and disinfected every 2 months. Sometimes the amount of milk produced is affected by loud noise, an abundance of blood-sucking insects or flies. Compliance with husbandry rules has a beneficial effect on lactation and reduces the negative effects of stress caused by the birth of a calf.
Poor nutrition
To prevent milk yield from decreasing, it is important to provide a complete, balanced diet and follow a number of rules:
- The diet of cows includes hay and straw, as well as mixed feed, various root vegetables, and vitamin and mineral supplements.
- They control the quality of the feed to prevent stale or rotten products from getting into the food.
- Provide plenty of fluids. Lack of fluid leads to decreased milk production. Sometimes a little salt is added to the water.
- Follow the feeding schedule. Animals get used to receiving food at a certain time. Violation of the schedule leads to the fact that cows begin to keep milk.
Sometimes failures in milk yield are caused by switching to another type of feed. It takes cows about 3 weeks to get used to a new product. This is due to the production of microorganisms necessary for food processing.
Incorrect milking
Inept and rough actions during milking lead to stress in the animal and affect the amount of milk obtained. Movements should be natural and easy. It is recommended to divide the process into several stages:
- Before starting the procedure, the udder is washed with warm water.
- Massaging the udder and nipples for a minute promotes milk flow.
- If milk is expressed by hand, they are first cleaned and treated with Vaseline. The ointment promotes the healing of wounds that occur due to friction.
- After completing the process, it is advised to massage again.
- Squeeze out the remaining milk to prevent the risk of inflammation.
When performing the procedure, adhere to the schedule. Milk is collected 2 times a day, morning and evening. If one of the animals gets sick, it is milked last so as not to infect the rest of the livestock.
A week after reproduction, the calf is separated from the cow, but milk continues to be expressed. The animal perceives this as feeding.
Old age of the animal
The amount of milk yield directly depends on the age of the animal. Cows reach sexual maturity at the age of 7 months. It is better to carry out the first mating later, when the formation of the body from a physiological point of view is completely completed. Early pregnancy does not contribute to the production of large amounts of milk.
There are 3 groups of the lactation period:
| Stages of lactation | Animal age |
| Puberty | From birth to 1.5 years. Lactation begins after the animal's first pregnancy |
| Maturity | From 1.5 to 12-14 years |
| Old age | After 15 years, milk production stops |
Animals show maximum productivity between the 5th and 9th calving. After this, there is a gradual decrease in milk yield. A balanced diet and proper care prolong the lactation period.There are cases where a cow gave milk at the age of over 15 years.
Diseases
A sharp decrease in milk yield often indicates health problems. If a cow has a fever or a swollen udder, the cow is taken to the veterinarian. It is necessary to undergo tests to determine the cause of the malaise.
Diseases almost always cause a decrease in productivity and can have serious consequences.
Dysfunction of the milk ejection reflex
A drop in milk production often causes stress. Unfavorable factors contribute to the release of epinephrine into the blood. The hormone acts on the brain and blocks areas that are responsible for the production of milk.
Causes of impaired milk ejection reflex:
- Rough treatment.
- The milking machine causes pain to the cow.
- Different people express milk.
- Noise and sounds unfamiliar to the animal in the room.
- Calf weaning.
These reasons cause a decrease in productivity at any stage of lactation. To eliminate the problem, it is necessary to make the cow's living conditions more comfortable and eliminate the causes of stress.
Injury to the nipples or udder
A decrease in milk production is caused by injuries to the udder or nipples. Hematomas cause pain and cause the cow to hide the damaged organ.
Treatment and care of a sick animal:
- The cow is placed in a separate stall.
- Reduce fluid intake and exclude succulent foods from the diet.
- Ointment is applied to the affected area.
- Lotions are applied to the site of the injury to relieve swelling. For the first 2 days, apply cooling compresses, then warm ones.
- Treatment is supplemented with udder massage and milk is expressed.
Timely measures will calm the animal. After recovery, milk production will resume.
Mastitis
The productivity of cows is affected by mastitis, which often occurs after birth. Inept actions during milking also lead to damage to the udder and teats. To prevent the spread of infection, it is important to identify the signs of the disease in time.
To identify signs of mastitis, milk is periodically submitted for biological analysis.
Treatment is prescribed by a veterinarian. An integrated approach combines the use of medications, physiotherapeutic procedures, hygiene and dietary adjustments. The sick animal is isolated from the rest of the herd to eliminate the risk of infection of the entire herd.
Ketosis
Another dangerous disease that affects milk loss is ketosis. This is a metabolic disorder, which is expressed in a malfunction of carbohydrate, fat and protein balance. A sign of pathology is the presence of blood in milk.
Laboratory tests will help establish an accurate diagnosis. In addition to using medications, it is important to follow dietary recommendations. Timely prevention will preserve the health of the animal, and the farmer will avoid financial losses.
Productivity is influenced by many factors. Cows are sensitive and easily hurt animals. In addition to feeding and ensuring normal living conditions, the health of the livestock is also affected by the attitude of the owners. Attention and care are the best ways to increase milk yield.