Among cattle diseases, infectious diseases occupy not the last place. Diseases spread among livestock, weaken animals, and cause various disorders in the body. Sick animals become less productive, which causes economic damage to the farm. Let's consider the causes and symptoms of nodular dermatitis, methods of diagnosis and treatment, and preventive measures.
Historical excursion
Lumpy dermatitis is native to Central Africa; in addition to African countries, until recently it was also registered in Madagascar, India, and the Middle East. Since the 2000s, the disease has appeared in Asian countries, since 2014 - in Turkey, Lebanon, Egypt, Iran, since 2015 - in Russia, Armenia, Cyprus, Greece, since 2016 - in Serbia, Macedonia, Albania, Kazakhstan.
Causes of infection
Lumpy dermatitis is an infectious disease of cattle of viral origin. The pathogen, Neethling virus, is similar to smallpox viruses. The sources of the pathogen are considered to be sick individuals and carriers of the virus. The pathogen is found in pieces of affected skin, saliva, blood, semen, milk, and discharge from the eyes and nose. In addition to these routes of infection, the virus can be transmitted through the bites of blood-sucking insects. The virus can be present in feed, transmitted through water, or through transport. Adult animals become infected during contact, calves - through milk.
Lumpy dermatitis has a seasonal manifestation (during the humid hot period); cases of the disease are observed in areas with wet, marshy areas. The infection spreads quickly, the incidence rate is 5-45% of the total number of animals in the herd. The mortality rate from dermatitis varies between 1-5%, and up to 90% of individuals can recover naturally.
The disease causes significant damage to livestock farms, as the meat and milk productivity of cows decreases, the reproduction process is disrupted, and skins are discarded. A complication of dermatitis can be the sterility of bulls, temporary or permanent, as well as the death of animals from other infections that developed against the background of lumpy skin disease, abortions in cows.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
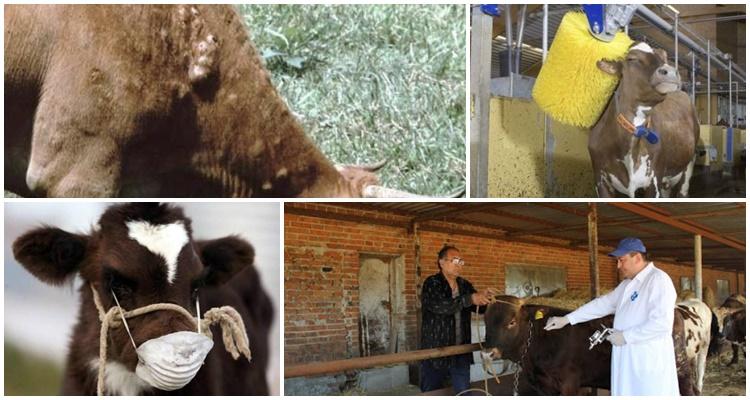
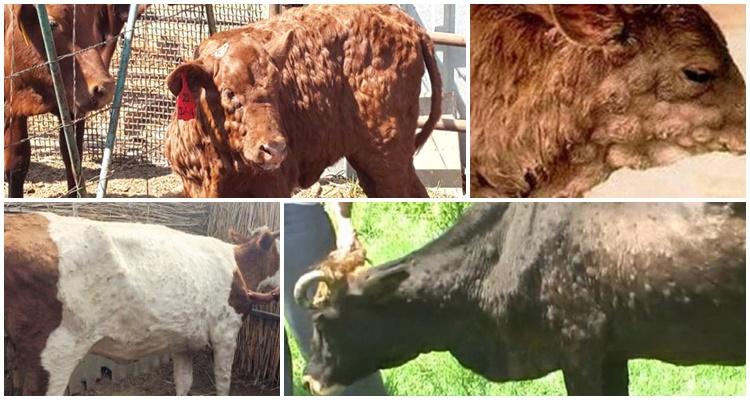
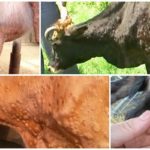
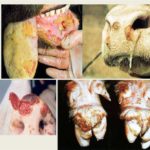
The incubation period for nodular dermatitis is 3-30 days.There are no symptoms at this time. Then fever, swelling of the subcutaneous tissues appear, nodes form on the skin, lesions affect the mucous membranes of the digestive tract and respiratory tract, and the eyes.
The acute form of the disease in cows is characterized by an increase in temperature, loss of appetite, discharge from the eyes, and lacrimation.
The next day, nodules of a dense structure, reaching a size of 0.5-7 cm, form on the head, neck, chest, udder, groin and abdomen. Then, a depression forms in the center of the nodules due to separation of the epidermis, and the tissue begins to necrotize. Over time, the affected tissues fall off.
With severe development of the disease, cows experience prolonged fever, loss of appetite, the animals lose weight, round erosive lesions and necrotic areas of a grayish-yellow color appear on the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract and digestive organs. Calves may have an atypical form of the disease, with no characteristic signs of damage. Cows that have had lumpy skin disease are immune to the disease for life.
Carrying out diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, epizootological data, a clinical examination of sick individuals, laboratory tests, and identified pathological changes in tissue are required. For analysis, samples are taken from skin areas affected by dermatitis, bronchi, lymph nodes, smears from the oropharynx, conjunctiva, sperm, milk, and blood. The PCR method is used for the study.
How to Treat Lumpy Dermatitis in Cattle
No specific treatment for nodular dermatitis in cattle has been developed; symptomatic therapy is used. Cows are provided with proper housing conditions, care, and are fed nutritious food. With proper care, cows recover on their own in 90% of cases.
Folk remedies
From traditional medicine, nettle tincture is used to treat skin lesions. It’s easy to make: put fresh chopped nettles in a jar, add vodka and leave to steep for 3 weeks. Use the resulting product to disinfect nodules and make compresses.
In addition to nettle tincture, you can prepare a calendula tincture: pour the flowers with alcohol and leave to infuse for a month. Apply in exactly the same way as the previous one, to work you need to take a solution of 1 tsp. tinctures for 1 tbsp. water.
Medication
The affected areas are treated with disinfectants. To prevent infection by other pathogens, cows are given antibiotics and also prescribed drugs that support the immune system.
Proper nutrition
Cows with dermatitis must be fed in such a way that the animals do not lack nutrients. Good nutrition plays an important role in maintaining immunity and helps cows recover faster. In summer, animals are fed fresh grass; if they graze freely, sick people should not come into contact with healthy ones. When kept in stalls, sick individuals should be kept separate from uninfected ones. In addition to grass or hay, cows should receive nutrition in the form of concentrates, vegetables, root crops, and silage. These products contain vitamins and minerals necessary for recovery.
Quarantine
If cases of nodular dermatitis are detected on a farm, it is quarantined. Rules: it is prohibited to mix sick individuals with healthy ones in the general herd; strangers and vehicles must not be allowed into the farm territory. Sale of products is prohibited.Remains of feed and removed bedding must be disposed of and all premises must be disinfected. Milk should be pasteurized or boiled.
How dangerous is the disease for an animal?
In sick individuals, weight decreases as they lose weight; in lactating cows, milk production decreases, which affects milk yield. Mastitis may develop. Aggression and nervous disorders are noted, although rarely. Pregnant females may have abortions.
Prevention of the problem
Prevention work must be carried out with full responsibility, since the infection can spread quickly. In order not to waste time on treatment or waste money, you need to try to prevent the disease through sanitary measures and vaccination.
First of all, when purchasing cows, you need to choose them from farms where dermatitis has not been registered. Quarantine them and only then send them to the herd. Treat cows against insect attacks using repellents. Examine the skin of animals so as not to miss the first signs of the disease.
Vaccination helps prevent infection. Vaccinations begin with 3-month-old calves and are repeated a year later. In disadvantaged regions, adult animals are also subject to vaccination if they have not been vaccinated before.
Danger to humans
The lumpy skin disease virus is not dangerous for humans; only cows and small cattle become ill with it. You can work with sick animals without fear of becoming infected. But fresh milk should not be consumed. After boiling it becomes suitable for consumption.On large farms it is often fed to calves.
Lumpy dermatitis is a new disease that has already appeared in Russia and neighboring countries.
It is not fatal for cows, but it leads to economic damage in the form of loss of livestock weight, decreased milk yield, abortion, and decreased quality of milk and hides. Although there is no cure for this disease, with proper care and supportive therapy, animals will recover.