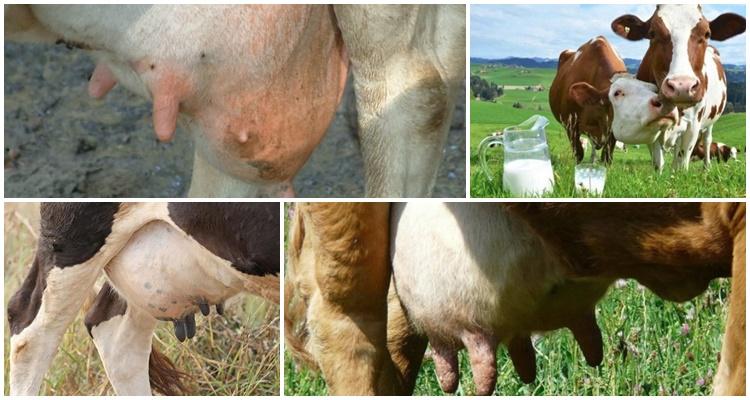
Owners of dairy cows need to know a lot about keeping animals, proper feeding, what diseases they can develop, and what the presence of blood in a cow’s milk may indicate. If this symptom is noticed, you should evaluate its degree and nature, the possible cause of its occurrence based on the signs that will be listed below, and take urgent therapeutic measures.
Causes and treatment of the problem
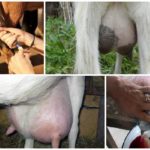
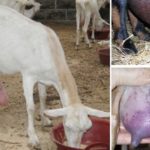
The reasons for the appearance of blood in a cow's milk can arise from mechanical, physical damage or the development of diseases.All conditions, except minor injuries, require consultation with a veterinarian and urgent treatment measures.
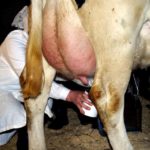
You can notice this sign immediately, by the coloring of the milky substance in a red-pink color or after aging in the refrigerator. Milk with blood separates into fractions, while normal milk does not separate.
Mastitis
The development of mastitis (inflammation of glandular tissue) is always associated with congestion in the udder and the presence of infections. The disease most often develops after calving, when it is difficult for the cow to milk, her immunity is reduced, and the calf does not suck out the colostrum completely. The skin of the nipples dries out, and cracks that appear are the gateway to infection.
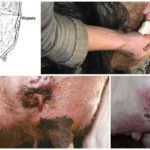
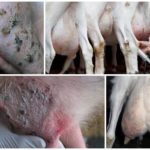
Manifestations of the disease can be obvious or hidden. In the absence of help or improper treatment, the disease worsens, and the stage of catarrhal phenomena is replaced by serous, then fibrous. Blood in milk during mastitis indicates an unfavorable course and the development of a hemorrhagic form. The animal is in a depressed state, the body temperature is increased to 41-42 degrees, the udder is painful, and lumps can be felt in it. The presence of blood in the form of clots and the analysis of milk for bacteria confirm the diagnosis.
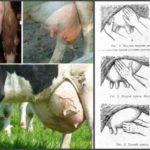
For hemorrhagic mastitis, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, and the cow is given herbal infusions (shepherd's purse, nettle, yarrow). Gentle milking is carried out every 3-4 hours, the teats are pre-washed with laundry soap, rinsed off with warm water, and the udder is lightly massaged. It is important to empty it completely when milking.After milking, ointments are used to lubricate the nipples. In severe cases of the disease, droppers with glucose, calcium chloride, and caffeine injections are necessary.
Vascular disorders
Fragility of blood vessels or hemolysis may be the cause of the symptom in question. Milk turns pink with varying degrees of intensity. Young cows experience fragility of the udder vessels immediately after calving. In this case, it is not recommended to massage the udder, so as not to provoke ruptures of other vessels. A blood test shows a low platelet count. Vascular hemolysis is possible with leptospirosis.
Vitamins are given to the cow for treatment C, K, injections of calcium chloride are performed. The veterinarian may prescribe the hemostatic drug Gemarktin. The calf is transferred to be fed milk from another cow.
Bruises
Animals grazing or moving in a herd or at a watering hole on a river can injure each other or get bruised by stones, logs, or low-growing tree branches. If blood is noticed after milking and it is known that there is no mastitis, then you should carefully examine the udder, perhaps there is swelling somewhere from a bruise.
It is recommended to apply cold to this area. In a day you will need a warming compress and an iodine mesh.
Udder damage
Immediately after calving, there are mechanical damage to the udder from milking equipment, and also during walking and grazing - scratches, cuts, abrasions. In this case, blood in the milk contents occurs only at the beginning of milking, if the affected area is affected. To treat such injuries, wound healing ointments are used. Disinfection of purulent wounds is carried out with hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexidine.
Prevention
For large and small farms, mastitis prevention is critical.It is as follows:
- The premises where animals are kept must be clean, well ventilated, and the bedding must be changed regularly.
- Cows' feed should be balanced, include a lot of coarse fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- Before milking, the udder must be washed or disinfected. After milking, wash with soda and wipe with ointment with softening properties.
- Milk cows correctly.
- If pus or white flakes appear in the milk, begin treatment immediately, without leading to the hemorrhagic stage.
Is it possible to drink milk with blood?
People, calves and other animals should not drink bloody cow's milk. The reason is that the product, when blood particles enter it, greatly changes its properties.
Valuable proteins, casein, calcium are replaced in it with other substances, for example, chlorides. The composition contains microbes that can be pathogenic to humans. When treating a cow, antibiotics and other substances are released along with the milk. Despite the fact that the cow continues to be milked, the milk must be disposed of after testing.
It is important not to stop milking, continue to care for the animal, provide it with complete vitamin food, along with roughage, and not stop walking. With proper treatment and good care, the condition when a cow has blood in her milk goes away quite quickly, and this valuable product can again be used by people and for feeding a calf.